A flask contains methane chlorine and carbon monoxide gases. Free bromine is a reddish brown liquid with an appreciable vapour pressure at room temperature.
Chemicals - Phenol.
Vapour pressure chlorine. Vapour pressure is a measure of the ability of a compound to bond with itself. Compound molecules that bond well with each other will have a low vapour pressure less tendency to escape to the vapour phase while poorly bonding compounds will have a high vapour pressure. From a thermodynamic standpoint this can be viewed from the well-known ClausiusClapeyron expression.
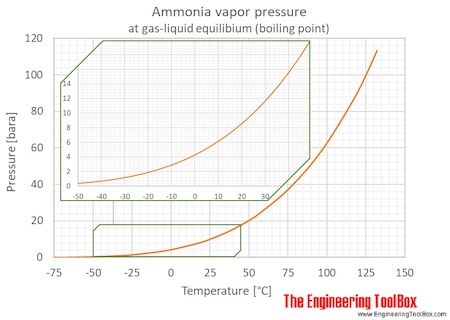
The vapour pressure of ammonia is the pressure at which ammonia gas is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state. At higher pressures ammonia would condense. At this equilibrium condition the vapor pressure is the saturation pressure.
See also properties of Ammonia at varying temperature and pressure. Density and specific weight Dynamic and kinematic. Vapour-compression refrigeration or vapor-compression refrigeration system VCRS in which the refrigerant undergoes phase changes is one of the many refrigeration cycles and is the most widely used method for air-conditioning of buildings and automobiles.
It is also used in domestic and commercial refrigerators large-scale warehouses for chilled or frozen storage of foods and meats. Chemical vapor deposition CVD is a vacuum deposition method used to produce high quality and high-performance solid materials. The process is often used in the semiconductor industry to produce thin films.
In typical CVD the wafer substrate is exposed to one or more volatile precursors which react andor decompose on the substrate surface to produce the desired deposit. Slightly soluble in water. Chemical Properties of Chlorine gas Cl 2.
Chlorine reacts with organic compounds and ammonia to form chloro-organics or chloramines. Chloramines are part of the group of chlorine compounds that have disinfectant properties and show up as part of the chlorine residue test. It acts as a reducing agent present in.
Vapour pressure 480 Pa at 0 C Water solubility 146 glitre at 0 C Organoleptic properties The taste and odour thresholds for chlorine in distilled water are 5 and 2 mglitre respectively. In air chlorine has a pungent and disagreeable odour 2. Major uses Large amounts of chlorine are produced for use as disinfectants and bleach for both domestic and industrial purposes and it is also.
Vapour pressure at 25 C Negligible Negligible Water solubility gL 301 25 C 101 20 C 390 17 C a Conversion factor in air. 1 part per million ppm 28 mgm3. National Academy of Sciences 1987.
Budavari ONeill. Meister 1989 13 Organoleptic properties The taste and odour threshold for chlorine dioxide in water has been reported to be. A measure of the propensity of a substance to evaporate.
It is defined as the equilibrium pressure exerted by the gas produced above a substance in a closed system. Pressure and temperature data advanced. Specific heat capacity J kg 1 K 1 824 Youngs modulus GPa Unknown Shear modulus GPa Unknown Bulk modulus GPa Unknown Vapour pressure Temperature.
He liberated the element by passing chlorine through an aqueous solution of the residues. Free bromine is a reddish brown liquid with an appreciable vapour pressure at room temperature. Bromine vapour is amber in colour.
Bromine has a pungent odour and is irritating to the skin eyes and respiratory system. Exposure to concentrated bromine vapour even for a short time may be fatal. Chemically Freon was created by the substitution of two chlorine and two fluorine atoms for the four hydrogen atoms in methane CH 4.
The result dichlorofluoromethane CCl 2 F 2 is odourless and is toxic only in extremely large doses. The basic components of a modern vapour-compression refrigeration system are a compressor. An expansion device which can be a valve a.
The critical pressure of a substance is the pressure corresponding to the critical point or the critical state of the substance. The critical point of a substance can be defined as the point on the temperature and pressure scale in which a liquid substance can coexist with its vapour. At temperatures above the critical temperature of a substance it cannot be liquified with the application.
Titanium dioxide coating and UV light. Some manufacturers supply aeration equipment that enhances the decomposition process by passing the airvapour mixture through a carbon filter. High reactivity penetrability and spontaneous decomposition into a non-toxic product make ozone a viable disinfectant for use in food production.
They exist inside the cylinder in a liquid-vapour balance or equilibrium. Initially the cylinder is almost full of liquid and gas fills the space above the liquid. As gas is removed from the cylinder enough liquid evaporates to replace it keeping the pressure in the cylinder constant.
Anhydrous ammonia chlorine propane nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide are examples of liquefied gases. A flask contains methane chlorine and carbon monoxide gases. The partial pressures of each are 0215 atm 50 torr and 0826 respectively.
What is the total pressure in the flask. A sample of chlorine gas is collected by water displacement at 23C. If the atmospheric pressure is 751 torr what is the partial pressure of the chlorine.
How do I determine entropy change between two states if. Ammonia - Vapour Pressure at Gas-Liquid Equilibrium - Figures and table with ammonia saturation pressure at boiling points SI and Imperial units. Ammonia Gas - Density vs.
Temperature and Pressure - Online calculator with figures and tables showing density and specific weight of ammonia for temperatures ranging -50 to 425 C -50 to 800 F at atmospheric and higher pressure - Imperial and. Vapour pressure. ASNZS 17162003 A1 Formalde-.
Air helium and chlorine are gases at room temperature. Water vapour is water as a gas. In a gas are.
The particles in a gas move quickly in all directions but. Then the coating material is heated or the pressure around it is reduced until the material vaporizes either inside the vacuum chamber or in an adjacent area from which the vapor can be introduced. There the suspended material begins to settle onto the substrate material and form a uniform coating.
Adjusting the temperature and duration of the process makes it possible to control. Chlorine and oxygen are strong oxidizers so their compounds are used for eg. In fact it is the most cost-effective home disinfectant sodium hypochlorite solution is used to clean toilets drains surfaces swimming pool.
Phenolics It is oldest known disinfectant for eg. Chemicals - Phenol. Conversion of density units Definition.
Density mass divided by volume. Symbol ρ m V ρ rho density m mass V volume. The SI unit of density is kgm 3.
Water of 4 C is the reference ρ 1000 kgm 3 1 kgdm 3 1 kgl or 1 gcm 3 1 gml. Fill in the appropriate line the known density value. We usually presume the air pressure to be 1 atmosphere.
The boiling point of water is 100 o C or 373 K. At the boiling point the vapour pressure of an element or compound is 1 atmosphere. Vanderwaals radius Even when two atoms that are near one another will not bind they will still attract one another.
This phenomenon is known as the Vanderwaals interaction. A mixture of hydrogen and ethene is passed under pressure into the slurry and ethene is polymerized to HDPE. The reaction takes place in a large loop reactor with the mixture constantly stirred Figure 4.
On opening a valve the product is released and the solvent is evaporated to leave the polymer still containing the catalyst. Water vapour on flowing with nitrogen through the polymer. Jurisdiction Definition USA.
Indoor VOCsOrganic chemical compounds whose composition makes it possible for them to evaporate under normal indoor atmospheric conditions of temperature and pressure. Any compound of carbon excluding carbon monoxide carbon dioxide carbonic acid metallic carbides or carbonates and ammonium carbonate which participates. Investigate a displacement series of non-metals using oxygen and chlorine in this class practical or demonstration.
Includes kit list and safety instructions. Dissolved substances in tap water and seawater. In association with Nuffield Foundation.
Compare the solids and gases dissolved in tap water and seawater in this class practical and demonstration. Includes kit list and safety. A measure of the propensity of a substance to evaporate.
It is defined as the equilibrium pressure exerted by the gas produced above a substance in a closed system. Pressure and temperature data advanced. Specific heat capacity J kg 1 K 1 Unknown Youngs modulus GPa Unknown Shear modulus GPa Unknown Bulk modulus GPa Unknown Vapour pressure Temperature.