Logoilwater 21 Ionicity in Water. Higher vapor pressure and volatility translate into a lower boiling point.

Choose the desired type of data.
Vapor pressure of benzene. Vapor pressure of liquid and solid benzene. Equilibrium vapor pressure can be defined as the pressure reached when a condensed phase is in equilibrium with its own vapor. In the case of an equilibrium solid such as a crystal this can be defined as the pressure when the rate of sublimation of a solid matches the rate of deposition of its vapor phase.
For most solids this pressure is very low. This is caused by a principle called vapor pressure. In chemistry vapor pressure is the pressure that is exerted on the walls of a sealed container when a substance in it evaporates converts to a gas.
To find the vapor pressure at a given temperature use the Clausius-Clapeyron equation. LnP1P2 ΔH vap R1T2 - 1T1. Vapor pressure of pure benzene at 60 C is 391 torr.
Raoults Law can be used to express the vapor pressure relationships of solutions containing both volatile and nonvolatile solvents. Raoults Law is expressed by the vapor pressure equation. P solution Χ solvent P 0 solvent where P solution is the vapor pressure of the solution Χ solvent is mole fraction of the solvent P 0.
The vapor pressure of a liquid is defined as the pressure exerted by the molecules that escapes from the liquid to form a separate vapor phase above the liquid surface. The pressure exerted by the vapor phase is called the. Vapor or saturation pressure.
Vapor or saturation pressure depends on temperature. If a fluid consist of more than one component a solution components with. At 250 C the vapor pressure of benzene C 6 H 6 is 01252 atm.
When 1000 g of an unknown non-volatile substance is dissolved in 1000 g of benzene the vapor pressure of the solution at 250 C is 01199 atm. Calculate the mole fraction of solute in the solution assuming no dissociation by the solute. 1 Because solute is non-volatile the vapor of the solution.
The vapor pressure is the pressure exerted by a pure component at equilibrium. For example the compounds benzene and chloroform have nearly identical values of K H and K ow yet benzene is far less persistent in the environment. Keeping these caveats in mind however relative affinity for a substance to reside in air and water can be used to estimate the potential for the.
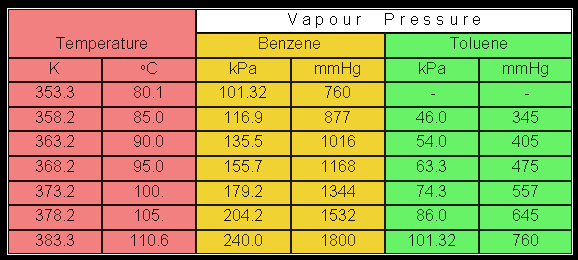
Calculate the vapor pressure of a solution of 740 g of benzene C 6 H 6 in 488 g of toluene C 7 H 8 at 250 C. The vapor pressure of benzene is 951 torr and of toluene is 284 torr at this temperature. 1 Determine moles of benzene and toluene.
The concentration of a vapor in contact with its liquid especially at equilibrium is often expressed in terms of vapor pressure which will be a partial pressure a part of the total gas pressure if any other gases are present with the vapor. The equilibrium vapor pressure of a liquid is in general strongly dependent on temperature. At vaporliquid equilibrium a liquid with individual.
Density of benzene along the boiling and condensation curve SI and Imperial units. The density of liquid benzene is nearly the same for all pressures up to 100 bara and the density of the liquid at equilibrium pressure can be used for most practical purposes. Density of benzene vapor singel phase at varying temperature and given pressures SI and Imperial units.
Vapor Pressure Depression. Physical properties can be divided into two categories. Extensive properties such as mass and volume depend on the size of the sampleIntensive properties such as density and concentration are characteristic properties of the substance.
They do not depend on the size of the sample being studied. This section introduces a third category that is a subset of the. BENZENE reacts vigorously with allyl chloride or other alkyl halides even at -70 C in the presence of ethyl aluminum dichloride or ethyl aluminum sesquichloride.
Explosions have been reported NFPA 491M 1991. Ignites in contact with powdered chromic anhydride Mellor 11235 1946-47. Incompatible with oxidizing agents such as nitric acid.
Mixtures with bromine trifluoride bromine. At 20 o C the vapor pressures of pure benzene C 6 H 6 molar mass780 gmole and toluene C 6 H 5 CH 3 molar mass920 gmole are 22 mm Hg and 74 mm Hg respectively. What is the total vapor pressure above a solution containing 200 g of benzene and 200 g of toluene at 20 o C.
Mm Hg How many grams of the electrolyte Na 2 SO 4 molar mass142 gmole are required to make 325 mL of. 10 kPa 20C Vapor Density. 28 Air 1 Volatility.
468 ppm WaterOil Dist. The product is more soluble in oil. Logoilwater 21 Ionicity in Water.
See solubility in water diethyl ether acetone. Miscible in alcohol chloroform carbon disulfide oils carbon tetrachloride. Reid vapor pressure Winter oxygenates.
Gasoline sulfur. Fuel Waivers. Fuels Registration Reporting and Compliance Help.
Diesel Fuel Standards Fuels Regulatory Streamlining. Benzene is a clear colorless highly flammable and volatile liquid aromatic hydrocarbon with a gasoline-like odor. Benzene is found in crude oils and as a by-product of oil-refining processes.
In industry benzene is used as a solvent as a chemical intermediate and is used in the synthesis of numerous chemicals. Exposure to this substance. Benzene is primarily used as a feedstock or raw material to make other industrial chemicals such as ethylbenzene cumene and cyclohexane.
Benzene is also used as a solvent in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. Most benzene exposure comes from the air from a number of sources including forest fires auto exhaust and gasoline from fueling stations. Benzene in cigarette smoke is a.
Synonyms Trade Names Benzol Phenyl hydride CAS No. Class IB Flammable Liquid. Below 73F and BP at or above 100F.
Incompatibilities Reactivities Strong oxidizers many fluorides. Except for Those With Significant Vapor Pressure. Airborne Concentration as As or Condition of Use.
Required Respirator or 100 µgm 3 micrograms per cubic meter 1 Half-mask air-purifying respirator equipped with high-efficiency filter. Or 2 Any half-mask supplied air respirator. Or 500 µgm 3 1 Full facepiece air-purifying respirator equipped with high-efficiency filter.
Xylene and benzene are two volatile organic compounds with distinctive scents. Relationship Between Volatility Temperature and Pressure. The higher the vapor pressure of a compound the more volatile it is.
Higher vapor pressure and volatility translate into a lower boiling point. Increasing temperature increases vapor pressure which is the pressure at which the gas phase is in. Chlorpyrifos is an organic thiophosphate that is OO-diethyl hydrogen phosphorothioate in which the hydrogen of the hydroxy group has been replaced by a 356-trichloropyridin-2-yl group.
It has a role as an EC 3117 acetylcholinesterase inhibitor an agrochemical an EC 3118 cholinesterase inhibitor an environmental contaminant a xenobiotic an acaricide and an insecticide. Pressure of known boiling point. Below enter the boiling point under this pressure C C Above enter a pressure to calculate the boiling point.
Above enter a boiling point to calculate the pressure. Heat of evaporation equals about kJmol Any pressure unit can be used. The result will be displayed in the same units.
The results are only roughly evaluated and can sometimes differ a. Acetylene ethyne - C2H2. Pressure MPa bar atm.
Density moll molm 3 gml kgm 3 lb-moleft 3 lbmft 3. Energy kJmol kJkg kcalmol Btulb-mole kcalg Btulbm. Velocity ms fts mph.
Viscosity µPas Pas cP lbmfts. Surface tension Nm dyncm lbft lbin Surface tension values are only available along the saturation curve. Choose the desired type of data.
Data type Isothermal properties Isobaric. This means that for the sake of determining freezing point depression or boiling point elevation the vapor pressure does not effect the change in temperature. Also remember that a pure solvent is a solution that has had nothing extra added to it or dissolved in it.
We will be comparing the properties of that pure solvent with its new properties when added to a solution. Adding solutes to an.