Oregon Health and Science University OHSU Located in Portland Oregon with several campuses located throughout the state the Department of Radiation Medicine at OHSU offers a 117-credit BS in radiation therapy. They are also strongly linked to skin cancer.
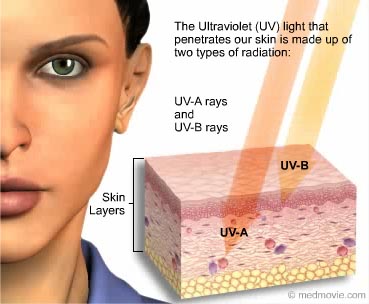
The adverse health effects that may occur are erythema sunburn photokeratitis a feeling of sand in the eyes skin cancer increased skin pigmentation.
Uv radiation in medicine. Ultraviolet UV is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz to 400 nm 750 THz shorter than that of visible light but longer than X-raysUV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10 of the total electromagnetic radiation output from the SunIt is also produced by electric arcs and specialized lights. UV radiation UV is classified as a complete carcinogen because it is both a mutagen and a non-specific damaging agent and has properties of both a tumor initiator and a tumor promoter. In environmental abundance UV is the most important modifiable risk factor for skin cancer and many other environmentally-influenced skin disorders.
However UV also benefits human health by mediating. Ionising radiation is used in medicine in 3 ways. Diagnostic radiology which uses x-ray machines to obtain images of the inside of the patients body.
Nuclear medicine which uses radioactive. Ultraviolet UV radiation is a form of non-ionizing radiation that is emitted by the sun and artificial sources such as tanning beds. The beneficial effects of UV radiation include the production of a vital nutrient vitamin D.
However overexposure may present risks. Sunburn premature aging and skin cancer are all risks to overexposure. Keeping you and others protected from UV radiation.
Ultraviolet radiation that portion of the electromagnetic spectrum extending from the violet or short-wavelength end of the visible light range to the X-ray region. Ultraviolet UV radiation is undetectable by the human eye although when it falls on certain materials it may cause them to fluoresceie emit electromagnetic radiation of lower energy such as visible light. Naturally occurring UV radiation is the environmental mutagen responsible for the largest percentage of environmentally induced skin pathologies including erythema and inflammation degenerative aging changes and cancer Humans are exposed to UV radiation primarily as a consequence of unprotected exposure to sunlight UV radiation has many deleterious effects on cells.
UV radiation levels can be high. Scattering can have the same effect as the reflectance by different surfaces and thus increase total UV radiation levels. ALTITUDE At higher altitudes a thinner atmosphere absorbs less UV radiation.
With every 1000 metres increase in altitude UV radiation levels increase by 10 to 12. Ultraviolet radiation UV is one of the non-ionizing radiations in the electromagnetic spectrum and lies within the range of wavelengths 100 nm to 400 nm see figure 1. The short wavelength limit of the UV region is often taken as the boundary between the ionizing radiation spectrum wavelengths 100 nm and the non-ionizing radiation spectrum.
UV can be classified into UVA 315 - 400 nm. Polar seas are under threat of enhanced UV-radiation as well as increasing shipping activities. Considering the ecological importance of marine viruses it is timely to study the impact of UV-AB on Arctic phytoplankton hostvirus interactions and also test the efficacy of ballast water BW UV-C treatment on virus infectivity.
This study examined the effects of. I ecologically relevant. Prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation on human skin can lead to mutations in DNA photoaging suppression of the immune system and other damage up to skin cancer melanoma basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma.
We reviewed the state of knowledge of the damaging action of UVB and UVA on DNA and also the mechanisms of DNA repair with the participation of the DNA-photolyase. UV radiation has enough energy to break chemical bonds. Due to their higher energies UV photons can cause.
An assistant professor of dermatology at Tufts University School of Medicine told. Irradiation is used in diagnostic imaging. The process which consists of striking plant seeds or germplasm with radiation in the form of X-rays UV waves heavy-ion beams or gamma rays essentially mixes the genes already existing in the genome.
The UN has been an active participant through the International Atomic Energy Agency. Irradiation is also employed to prevent the. All types of UV radiation have the potential to damage your skin but each type affects your skin differently.
UVA rays which account for 95 percent of radiation that reaches the earths surface cause wrinkles sun spots and other types of premature aging. They are also strongly linked to skin cancer. UVB rays which affect skins top layer cause skin cancer and most sunburns.
UV-A radiation 315 to 400 nm and UV-B radiation 280 and 315 nm have a similar effect on the body. They can trigger acute medium- and long-term damage. Enjoyed in moderation UV-A and UV-B rays tan the skin but high doses can cause redness rashes allergies or sunburn for instance on the eyelids.
UV-B radiation can cause. Another form of radiation that comes from our sun is ultraviolet UV radiation. UV radiation is not considered cosmic radiation.
Unlike cosmic radiation UV radiation is lower in energy and is considered non-ionizing radiation. For more information on UV radiation click here. Radiation dose due to cosmic radiation will vary with altitude.
Higher altitudes mean greater exposure to cosmic. Vitamin C also known as ascorbic acid AA is involved in all phases of wound healing. In the inflammatory phase it is required for neutrophil apoptosis and clearance.
During the proliferative phase AA contributes towards synthesis maturation secretion and degradation of collagen. When UV radiation suppresses immune responses the bodys ability to fight certain diseases including skin cancer is reduced. It is suspected that overexposure to UV radiation also interferes with the effectiveness of immunizations given through the skin.
Studies have shown that sunscreens can prevent UV-induced wrinkling. Animal studies demonstrated that sunscreens with. A quick primer on UV light.
UV light comes primarily from the sun but there are also man-made sources of UV light including tanning beds and the currently buzzed-about UV disinfection lamps. Ultraviolet radiation is divided into three regions. 315-400 nanometers nm UV-B.
280-315 nm and UV-C. UV can be associated with adverse health effects depending on duration of exposure and the wavelength. The adverse health effects that may occur are erythema sunburn photokeratitis a feeling of sand in the eyes skin cancer increased skin pigmentation.
Standard window glass according to the International Ultraviolet Association will allow UV-A to pass through while almost 100 of the UV-B and UV-C light is blocked. Therefore some UV light will enter your home and potentially affect your skin. Some of these effects could include increased freckles and increased sensitivity to sunlight that could result in rashes such as photodermatitis.
Youll protect yourself from future UV radiation and give your skins enzymes time to. MD associate clinical professor of dermatology at Yale School of Medicine New Haven CT. National Library of Medicines Medical Subject Headings.
Online file MeSH 2017. Available from as of July 6. In this study we examined the metabolism of BP-3 by rat and human liver microsomes and the estrogenic and anti-androgenic activities of the metabolites.
When BP-3 was incubated with rat liver microsomes in the presence of NADPH 245. The Radiation Protection and Nuclear Science Division RPNSD was established on 1 August 2013 formerly known as the Centre for Radiation Protection and Nuclear Science CRPNS. Its origins can be traced back to 1972 when the Radiation Protection Inspectorate RPI was formed as a unit under the Department of Scientific Services.
And thats not to mention the damage caused by the suns longer-wave UVA radiation 320-400 nm the key UV rays behind premature skin aging as well as a cause of skin cancer. A 2015 study published in Science found that UVA damage can start in less than a minute in the sun. The damage to the skins pigment cells melanocytes actually keeps developing hours after the sun exposure ends.
Oregon Health and Science University OHSU Located in Portland Oregon with several campuses located throughout the state the Department of Radiation Medicine at OHSU offers a 117-credit BS in radiation therapy. This program was established in 1971 and boasts an 87 percent degree completion rate a 100 percent ARRT exam pass rate and a 100 percent job placement rate. Admission to this.