
The largest database 1 of organic compounds lists about 10 million substances which include compounds originating from living organisms and those synthesized by chemists. In aqueous solutions they are usually found in the ring form.
Because soaps form insoluble calcium and.
Unsaturated side chains tend to be linear. Unlike paraffin or other alkanes which tend to puddle on the waters surface these fatty acids spread evenly over an extended water surface eventually forming a monomolecular layer in which the polar carboxyl groups are hydrogen bonded at the water interface and the hydrocarbon chains are aligned together away from the water. This behavior is illustrated in the diagram on the right. In chemistry an alkene is a hydrocarbon containing a carboncarbon double bond.
Alkene is often used as synonym of olefin that is any hydrocarbon containing one or more double bonds. Two general types of monoalkenes are distinguished. Also called α-olefins terminal alkenes are more useful.
However the IUPAC recommends using the name alkene only for acyclic. The first industrially practical polyethylene synthesis diazomethane is a notoriously unstable substance that is generally avoided in industrial application was again accidentally discovered in 1933 by Eric Fawcett and Reginald Gibson at the Imperial Chemical Industries ICI works in Northwich England. Upon applying extremely high pressure several hundred atmospheres to a mixture of.
End-to-end joining of mers single long flexible chains van-der-Waals and hydrogen bonds hold chains together polyethylene etc b Branched Polymer. Side branch chains connected to main chain reduced chain packing capability and therefore density. Saturated vs Unsaturated Fats and Health.
It has long been recognized that saturated fats tend to increase the blood level of the bad LDL cholesterol. Monounsaturated one double bond and polyunsaturated fats two or more double bonds found primarily in vegetable oils tend to lower bad LDL cholesterolAn elevated LDL-C increases the risk of developing coronary heart disease. The different amino acid side chains can be grouped into different classes based on their chemical properties Figure 115.
For example some amino acid side chains only contain carbon and hydrogen and are thus very nonpolar and hydrophobic. Others contain electronegative functional groups with oxygen or nitrogen and can form hydrogen bonds forming more polar interactions. The side chains of these amino acids are hydrophobic and therefore tend to be located in the interior of proteins where they are not in contact with water.
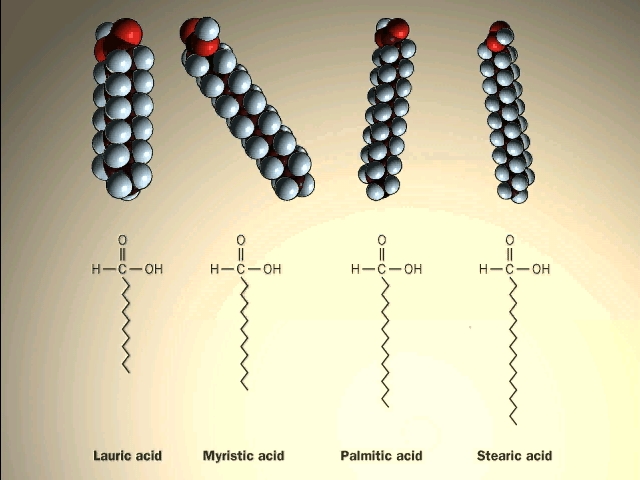
Proline similarly has a hydrocarbon side chain but it is unique in that its side chain is bonded to the nitrogen of the amino group as well as to the α carbon forming a cyclic structure. The side chains of two amino acids cysteine and. Fatty acids can be saturated meaning they have as many hydrogens bonded to their carbons as possible or unsaturated with one or more double bonds connecting their carbons hence fewer hydrogens.
A fat is solid at room temperature while an oil is a liquid under the same conditions. The fatty acids in oils are mostly unsaturated while those in fats are mostly saturated. Plasdone S-630 copovidone is a 6040 random linear copolymer produced by the free radical polymerization of N-vinyl-2-pyrollidone and vinyl acetate.
The pyrrolidone ring is responsible for excellent water solubility adhesion film forming and solubilization properties while the vinyl acetate monomer reduces glass transition temperature Tg and hygroscopicity compared to homopolymers of. Enzymatic catalysis depends upon the activity of amino acid side chains assembled in the active centre. Enzymes bind the substrate into a region of the active site in an intermediate conformation.
Often the active site is a cleft or a pocket produced by the amino acids which take part in catalysis and substrate binding. Amino acids forming an. 41 Biological Molecules The large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules are called biological macromoleculesThere are four major classes of biological macromolecules carbohydrates lipids proteins and nucleic acids and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions.
Monosaccharides may exist as a linear chain or as ring-shaped molecules. In aqueous solutions they are usually found in the ring form. The chemical formula for glucose is C 6 H 12 O 6.
In most living species glucose is an important source of energy. During cellular respiration energy is released from glucose and that energy is used to help make adenosine triphosphate ATP. Unsaturated hydrocarbonshydrocarbons with double or triple bondson the other hand are quite.
Forces when compared with saturated fats. As a result they have lower melting points and boiling points and tend to be liquids at room temperature. It has been shown that the reduction or replacement of saturated fats with mono- and polyunsaturated fats in the diet helps to reduce levels of.
Fatty acids differ from each other in the number of C atoms from 12-C to 24-C and in the number of double bonds in the chain from none to one two or three. Seed oils in different species vary widely in the proportion of different fatty acids although 18-C unsaturated fatty acids generally predominate. The largest database 1 of organic compounds lists about 10 million substances which include compounds originating from living organisms and those synthesized by chemists.
The number of potential organic compounds has been estimated 2 at 10 60 an astronomically high number. The existence of so many organic molecules is a consequence of the ability of carbon atoms to form up to. Monosaccharides may exist as a linear chain or as ring-shaped molecules.
In aqueous solutions they are usually found in the ring form. The chemical formula for glucose is C 6 H 12 O 6. In most living species glucose is an important source of energy.
During cellular respiration energy is released from glucose and that energy is used to help make adenosine triphosphate ATP. Bonds that are short andor nonpolar tend to be relatively _____ whereas bonds that are long andor polar tend to be more _____. What name is given to an atom or group of atoms within a molecule that is largely responsible for the properties and reactivity of the molecule.
Organic compounds containing only C and H atoms. Amine reactive PEG reagents most often PEGNHS tend to be used in considerable stoichiometric excess to protein. Since there are often several available nucleophilic groups on the protein eg terminal amine.
Side groups of lysine serine non-selective PEG conjugation results in PEGprotein positional isomers and multiple PEGylated products which can make purification challenging. The glycerides used to make surfactants contain saturated and unsaturated carboxylic acids which have an even number of carbon atoms generally within the range 12-20 for example octadecanoic acid stearic acid CH 3 CH 2 16 CO 2 H. Synthetic surfactants have one very important advantage over soaps.
Because soaps form insoluble calcium and. When the aromatic rings are conjugated with adjacent unsaturated groups in the main chain. When side groups become much longer they may tend to form little crystallites among themselves generally referred to as side-chain crystallization which restrict molecular mobility and usually give stiffer more waxy type of properties.
Introduction of cross-linking into a regular linear polymer. In contrast unsaturated fatty acids combined with triglycerides tend to yield liquid oils. The kinked structure of unsaturated fats yields a looser more fluid substance at room temperature.
Phospholipids are made of a triglyceride with a phosphate group substituted in for a fatty acid. They can be described as having a charged head and hydrocarbon tail. Their heads are hydrophilic or water.
Blennow et al. Also demonstrated that phosphate groups may play important role in the size distribution of the amylopectin side chains of phosphorylated starches. Some researchers have reported that about 6070 of total phosphorus of starch monophosphate is located at C-6 while the rest is located at C-3 of anhydroglucose units.
Most phosphate groups 88 are on chain β of amylopectin. Three Na bind to the cytoplasmic side of the carrier. The carrier is phosphorylated by ATP.
3The carrier changes shape and releases 3 Na into the extracellular fluid. 4Two K bind to the extracellular side of the carrier 5. The carrier is dephosphorylated 6.
Some conformations include an alpha-helix and a beta-pleated sheet and result from weak hydrogen bonds between side chains of different amino acids. Tertiary structure is the twisting and curling of the protein in three-dimensional space and can involve disulfide bonds sulfur to sulfur and hydrogen bonds among others. Finally quaternary structure refers to more than one polypeptide chain.
Compacted side cast fills which must support part of the road become more difficult to construct with increasing side slopes. Sliver fills as described in Section 321 result from trying to construct fills on steep side slopes. For side slopes in excess of 25 to 27 50 to 55 the full road width should be moved into the hillside.
Excavated material can be side cast or wasted but.