
The IUPAC system requires first that we have names for simple unbranched chains as noted above. Disaccharides are sugar molecules.
It is the major carbohydrate storage form in animals and fungi.
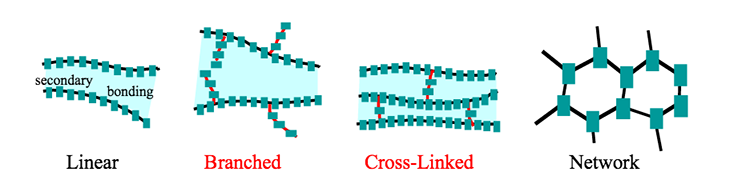
Unbranched linear chains. Unbranched saturated hydrocarbon chains are named systematically with a Greek numerical prefix denoting the number of carbons and the suffix -ane. 5 In 1866 August Wilhelm von Hofmann suggested systematizing nomenclature by using the whole sequence of vowels a e i o and u to create suffixes -ane -ene -ine or -yne -one -une for the hydrocarbons C n H 2 n 2 C n H 2 n C n H 2. A brush polymer molecule consists of a main chain with linear unbranched side chains and where one or more of the branch points has four-way functionality or larger.
A polymer network is a network in which all polymer chains are interconnected to form a single macroscopic entity by many crosslinks. See for example thermosets or interpenetrating polymer networks. A dendrimer is a repetitively.
The long polysaccharide chains may be branched or unbranched. Cellulose is an example of an unbranched polysaccharide. Whereas amylopectin a constituent of starch is a highly branched molecule.
Glucose storage in the form of polymers like starch of glycogen makes it slightly less accessible for metabolism. However this prevents it from leaking out of the cell or creating a high osmotic. Unbranched Chains The first four n1-4 unbranched chain saturated hydrocarbons are called methane ethane propane and butane.
After this there is a numerical term of Greek origin followed by the ending -ane. The first twelve members are given in Table 1. The names of the first 12 linear alkanes n Name Molecular formula Constitutional formula 1 methane CH 4 CH 4 2 ethane C 2.
Linear chains of starch are called amylose and when branched they are called amylopectin. Glycogen is similar to amylopectin but is highly branched. It is the major carbohydrate storage form in animals and fungi.
Cellulose is a linear polysaccharide which forms hydrogen bonds among several cellulose chains to form a fibrous structure. It is the major component of the cell wall of plants some. The A chains also known as the unbranched chains are the linear segments joined to other chains by a single 16-α-linkage.
The B chains are those connected to other chains via α-16 linkages and also carry one or more A or B chains attached to them. The C chain is the single central chain that carries the only reducing group of the amylopectin molecule. The linear glucopyranosyl.
The Golgi apparatus or Golgi complex functions as a factory in which proteins received from the ER are further processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations. Lysosomes the plasma membrane or secretion. In addition as noted earlier glycolipids and sphingomyelin are synthesized within the Golgi.
In plant cells the Golgi apparatus further serves as the site at which the. Overall the main ways to change and tune the properties of a polymer include changing the length of the polymer chains creating branched chains from linear polymer chains crosslinking the polymer chains and adding plasticizers into the polymer. The first two mostly rely on the processing conditions whereas the latter two rely more on additives to the polymer be it during polymerization or.
The long polysaccharide chains may be branched or unbranched. Cellulose is an example of an unbranched polysaccharide whereas amylopectin a constituent of starch is a highly branched molecule. Storage of glucose in the form of polymers like starch or glycogen makes it slightly less accessible for metabolism.
However this prevents it from leaking out of the cell or creating a high osmotic. In cellulose glucose monomers are linked in unbranched chains by β 1-4 glycosidic linkages. Because of the way the glucose subunits are joined every glucose monomer is flipped relative to the next one resulting in a linear fibrous structure.
Insects have a hard outer exoskeleton made of chitin a type of polysaccharide. As shown in Figure 4 every other glucose monomer in. Cellulose is an unbranched molecule.
The polymeric chains of glucose are arranged in a linear pattern. Unlike starch or glycogen these chains do not undergo any coiling helix formation or branching. Rather these chains are arranged parallel to each other.
The hydrogen bonds are formed between these chains due to hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl groups which firmly hold the chains together. Simple monosaccharides have a linear unbranched structure but the acyclic form is typically converted into the cyclic form due to its instability. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars.
Glyceraldehyde 3 carbon atoms Erythrose 4 carbon atoms Pentose 5 carbon atoms Glucose 6 carbon atoms What is a Disaccharide. Disaccharides are sugar molecules. As noted earlier HDPE is composed of very long unbranched hydrocarbon chains.
These pack together easily in crystalline domains that alternate with amorphous segments and the resulting material while relatively strong and stiff retains a degree of flexibility. In contrast LDPE is composed of smaller and more highly branched chains which do not easily adopt crystalline structures. Proteins are made up of one or more unbranched chains of _____ _____.
Proteins are polymers made up of how many different amino acids. The covalent bond that joins two amino acids is called a _____ bond. The two major functional groups found in all amino acids are the basic _____ group and the acidic _____ group.
Which of the following accurately describes the. The IUPAC system requires first that we have names for simple unbranched chains as noted above. Because the triple bond is linear it can only be accommodated in rings larger than ten carbons.
In simple cycloalkynes the triple bond carbons are assigned ring locations 1 and 2. Which of the two is 1 may be determined by the nearest substituent rule. Substituent groups containing.
Long chains of carbon atoms make up PVC where every other carbon atom has a chlorine atom attached to it. Polyethylene by contrast is a large chain of carbon atoms with only hydrogen atoms attached. There are no atoms of chlorine oxygen or any other elements.
While PVC always has the same basic structure polyethylene forms into several different types based on the degree of branching from. Lipid - lipid - Saturated fatty acids. The simplest fatty acids are unbranched linear chains of CH2 groups linked by carbon-carbon single bonds with one terminal carboxylic acid group.
The term saturated indicates that the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms are bonded to each carbon in the molecule. Many saturated fatty acids have a trivial or common name as well as a chemically. The primary structure of protein is the hierarchys basic level and is the particular linear sequence of amino acids comprising one polypeptide chain.
Secondary structure is the next level up from the primary structure and is the regular folding of regions into specific structural patterns within one polypeptide chain. Hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl oxygen and the peptide bond amide. In a linear polymer such as polyethylene rotations around carbon-carbon single bonds can allow the chains to bend or curl up in various ways resulting in the spaghetti-like mixture of these different conformations we alluded to above.
But if one of the hydrogen atoms is replaced by some other entity such as a methyl group the relative orientations of the individual monomer units that make. 41 Biological Molecules The large molecules necessary for life that are built from smaller organic molecules are called biological macromoleculesThere are four major classes of biological macromolecules carbohydrates lipids proteins and nucleic acids and each is an important component of the cell and performs a wide array of functions. A They all contain an unbranched carbon chain.
B They all contain unconjugated cis double bonds. C They all are joined to glycerol through an ester bond. D They all are hydrophilic because they contain oxygen.
10_____ What is the proper designation for the unsaturated fatty acids in this lipid. A 182 Δ912 b 182 Δ69 c 172 Δ912. Cellulose is an unbranched chain comprising up to approximately 15000 14-β-D-linked glucose units.
The 14-β-D-linked glucose chains associate by hydrogen bonding both between and within strands conferring strength to the cell wall. The linear polymers aggregate into either amorphous or crystalline regions. Cellulose is present in fungi algae and higher plants ranging from a.
Joins nucleotides to form chains of polynucleotide 1 Question Number Answer Mark 1aiii 1aiii. The only correct answer is C A is. Amylose is linear is unbranched is helical has 14 bonds.
Amylopectin is branched has 14 a nd 16 bonds. Has many terminal ends 3 Question Number Answer Additional guidance Mark 4bi 1. As the percentage of added.
Cellulose unbranched structural support. The formation of a protein is created using a hierarchy of structures. Match each description to its correct level of protein structure Alpha helix.
Major determinant of a proteins characteristics. The formation of a protein is created using a hierarchy of structures. Match each description to its correct level of protein structure Beta.
Alkanes are simplest organic compounds that consist of single bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms with the general formula CnH2n2. Alkanes are solid liquid or gas at room temperature depending on the size of their moleculesTo learn detailed structures formulas and Physical Properties of Alkanes with FAQS and Videos Visit BYJUS for more information.