Finally carboxylic acid side-chains are substituents on aspartic. Environment in which the functional group resides.
Below is the structure of diethyl ether a common laboratory.
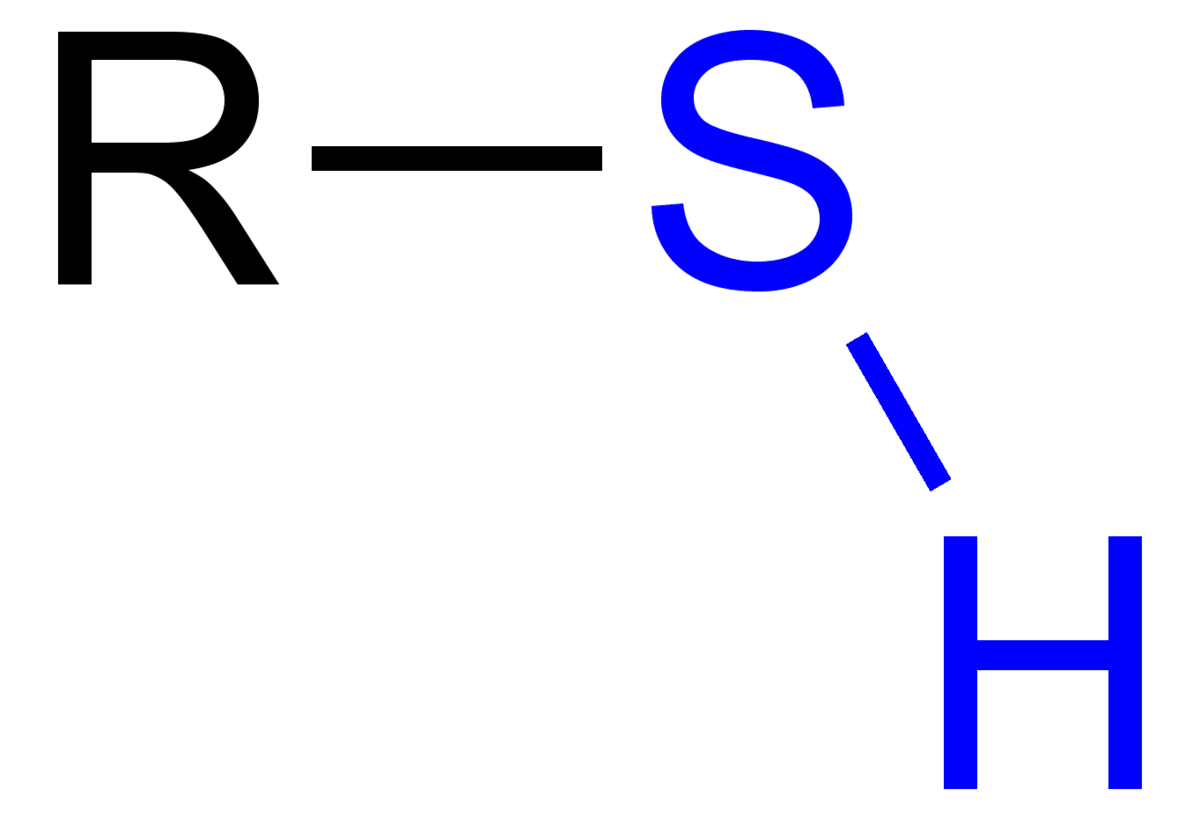
Thiols functional group. The SH functional group itself is referred to as either a thiol group or a sulfhydryl group or a sulfanyl group. Thiols are the sulfur analogue of alcohols that is sulfur takes the place of oxygen in the hydroxyl group of an alcohol and the word is a blend of thio- with alcohol where the first word deriving from Greek θεῖον theion meaning sulfur. Many thiols have strong.
An alcohol is an organic compound with a hydroxyl OH functional group on an aliphatic carbon atom. Because OH is the functional group of all alcohols we often represent alcohols by the general formula ROH where R is an alkyl group. For more information about alkyl groups see Chapter 1 Organic Chemistry Review Hydrocarbons Section 15 IUPAC Nomenclature.
Thiols can be defined as a sulfur analog of alcohols that is in simple it is an organic compound consisting of compounds with a sulfur atom. It is also referred as mercaptan. It consists of sulfhydryl group ie Thiol R-SH.
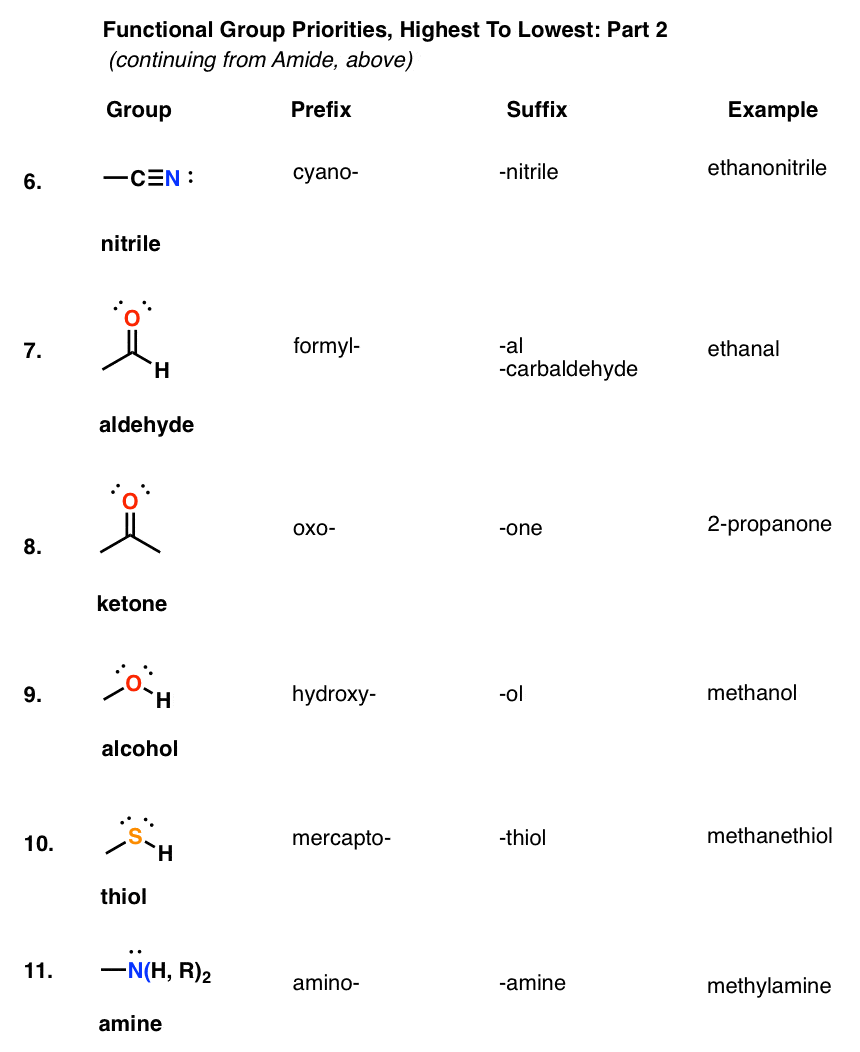
Alcohols and Thiols share some similarity ie. Sulfur emergers to be a larger element compared to that of oxygen the length of CS bond is more than that of CO. The functional group with the highest priority will be the one which gives its suffix to the name of the molecule.
So in example 1 above the suffix of the molecule will be -oic acid not -one because carboxylic acids are given higher priority. However if a ketone is present with an alcohol example 3 then we will use the suffix -one because ketones have a higher. The next functional group we consider the carbonyl group has a carbon-to-oxygen double bond.
Carbonyl groups define two related families of organic compounds. The aldehydes and the ketones. The carbonyl group is ubiquitous in biological compounds.
It is found in carbohydrates fats proteins nucleic acids hormones and vitaminsorganic compounds critical to living systems. Functional groups are specific groupings of atoms within molecules that have their own characteristic properties regardless of the other atoms present in a molecule. Common examples are alcohols amines carboxylic acids ketones and ethers.
In a typical sophomore organic chemistry course theres about 14 functional groups that are key with another group of 8 that make appearances from. The carbonyl group gjr– Carbonyl group CO analogous to alkene Two groups aldehydes RCHO and ketones R2CO Aldehyde 18 H H O methanal formaldehyde H3C H O ethanal acetaldehyde H O benzaldehyde HO O OH OH OH OH H 2R3S4R5R-23456-pentahydroxyhexanal glucose Ketones H3C CH3 O propanone acetone CH3 H O H3C. Thus an alcohol molecule consists of two parts.
One containing the alkyl group and the other containing functional group hydroxyl group. They have a sweet odour. They exhibit a unique set of physical and chemical properties.
The physical and chemical properties of alcohols are mainly due to the presence of hydroxyl group. Some prominent physical and chemical properties of. Created by Alison B.
FlynnDesigned and produced by the University of Ottawa Teaching and Learning Support Service TLSS Centre for e-Learning. Module development was funded by the University of Ottawa the Chemical Institute of Canada Chemical Education Fund and the Ministry of Training Colleges and Universities of Ontario as part of its Ontario Online initiative. In organic chemistry a thiol is a compound that contains the functional group composed of a sulfur atom and a hydrogen atom -SH.
Being the sulfur analogue of an alcohol group -OH this functional group is referred to either as a thiol group or a sulfhydryl groupMore traditionally thiols are often referred to as mercaptans. In organic chemistry sulfide usually refers to the linkage C. In the alcohol functional group a carbon is single-bonded to an OH group the OH group by itself.
The deprotonated forms of alcohols phenols and thiols are called alkoxides phenolates and thiolates respectively. A protonated alcohol is an oxonium ion. In an ether functional group a central oxygen is bonded to two carbons.
Below is the structure of diethyl ether a common laboratory. The deprotonated forms of alcohols phenols and thiols are called alkoxides phenolates and thiolates respectively. A protonated alcohol is an oxonium ion.
In an ether functional group a central oxygen is bonded to two carbons. Below is the structure of diethyl ether a common laboratory solvent and also one of the first compounds to be. The epoxide functional group is also collectively called epoxy.
The IUPAC name for an epoxide group is an oxirane. Epoxy resins may be reacted cross-linked either with themselves through catalytic homopolymerisation or with a wide range of co-reactants including polyfunctional amines acids and acid anhydrides phenols alcohols and thiols usually called mercaptans. An introduction to functional group nomenclature was limited to carbon-carbon double and triple bonds as well as simple halogen groups.
There are however many other functional groups that are covered by the IUPAC nomenclature system. A summary of some of these groups and the characteristic nomenclature terms for each is presented in the following table. Specific examples of their.
Environment in which the functional group resides. Resonance often modifies a peaks position because of electron delocalization CO lower acyl C-O higher etc. IR peaks are not 100 reliable.
Peaks tend to be stronger more intense when there is a large dipole associated with a vibration in the functional group and weaker in less polar bonds to the point of disappearing in some. Acylation of alcohols thiols and sugars were studied with a variety of Lewis acids and it was found that CuOTf 2. The reaction offers broad substrate scope and excellent functional group tolerance.
Lett 2018 20 5622-5625. Carbonylimidazole derivatives are highly active acylation reagents for esterification and amidation in the presence of pyridinium. Alcohols Phenols and Thiols.
In the alcohol functional group a carbon is single-bonded to an OH group the OH group when it is part of a larger molecule is referred to as a hydroxyl group. Except for methanol all alcohols can be classified as primary secondary or tertiary. In a primary alcohol the carbon bonded to the OH group is also bonded to only one other carbon.
In a secondary. Group of atoms which are part of a large molecule that have characteristic chemical behavior. FGs behave similarly in every molecule they are part of.
The chemistry of the organic molecule is defined by the function groups it contains. 2 CC CC CC C CC C HH H HH Alkenes Alkynes Arenes CC Alkanes Carbon - Carbon Multiple Bonds CX X F Cl Br I Alkyl Halide Carbon. The chapter is divided into sections based upon the functional group reactivities of each reagent type such as amine-reactive thiol-reactive carbonyl-reactive and nonspecific photoreactive compounds.
The crossbridges of these reagents also can be designed to provide permanent or cleavable bonds or hydrophilic or hydrophobic properties or to make available long or short linkages between. The last three entries in the left column have hydroxyl functional groups and the first two amino acids in the right column incorporate thiol and sulfide groups respectively. Lysine and arginine have basic amine functions in their side-chains.
Histidine and tryptophan have less basic nitrogen heterocyclic rings as substituents. Finally carboxylic acid side-chains are substituents on aspartic. We would like to show you a description here but the site wont allow us.
PKa Values in DMSO Compilation by Reich and Bordwell A pKa Values in DMSO Compilation by Reich and Bordwell is available as a PDF file. PKa Values in Water Compilation by R. Williams A pKa Values in Water Compilation by R.
Williams is available as a PDF file. PKa Values Compilation by Dave Evans and D. Photolithography is widely used in the semiconductor industry and large-scale mass production of Si-based devices down to several tens of nanometers.
Also in functional oxides it has been applied to the preparation of prototype devices. For example magnetic oxide tunneling junctions field effect transistors and so on 5860Currently this technique is indispensable for oxide electronic.