Such additions to the register are not specified by the WHS. Information is used for classification of all types of chemicals.
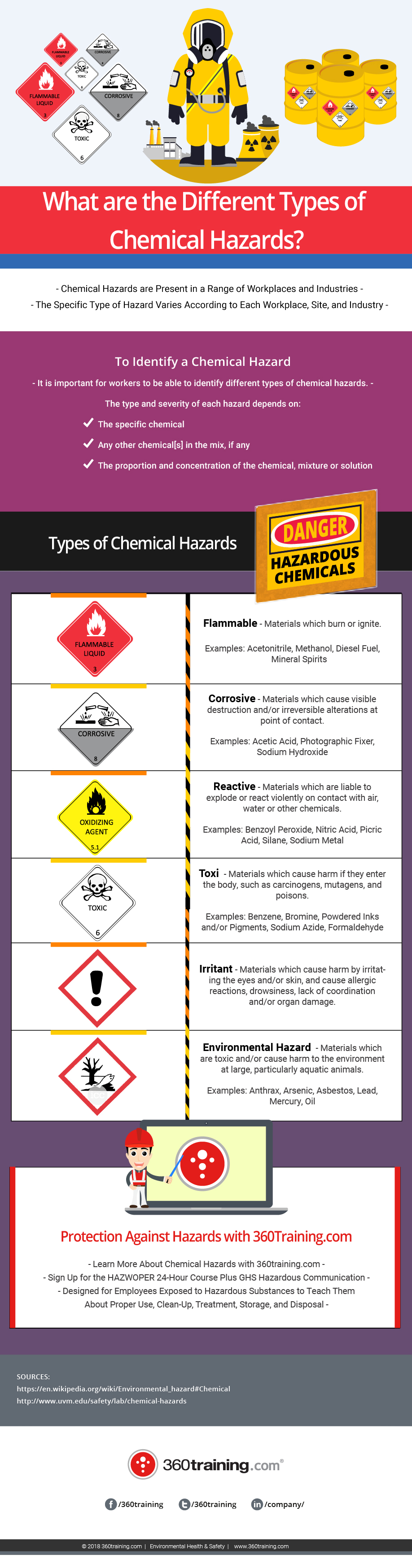
Hazards are placed into one of several categories so that general control strategies appropriate for those categories may be implemented.
The principal types of chemical hazards include. Control banding chemical uses is research laboratories. Hazards are placed into one of several categories so that general control strategies appropriate for those categories may be implemented. A methodical approach to document the.
A chemicals acute toxicity category is based on the amount of chemical needed to cause adverse effects from ingestion skin absorption or inhalation of the chemical ADG. Australian Dangerous Goods ADG Code. Australian Code for the Transport of Dangerous Goods by Road and Rail.
Also referred to as the Australian Dangerous Goods Code administrative control. A method of work a process or a. There are two types of explosive chemicals.
Designed produced or used as an explosive. Include Ethers Tetrahydrofuran Aldehydes and Acetals. Ether is no longer used as an anesthetic agent.
If you need more information on animal anesthesia please contact the ARP at 205 934-3553. Chemical Safety Training OHS_CS101 Course Material. A laboratory characterized as Security Level 2 see Table 102 poses moderate risk for potential chemical biological or radioactive hazards.
The laboratory may contain equipment or material that could be misused or threaten the public. Loss to theft malicious pranks or sabotage would have moderately serious health and safety impact and be detrimental to the research programs and the. Kaolin is an aluminosilicate soft white mineral named after the hill in China Kao-ling from which it was mined for centuries.
In its natural state kaolin is a white soft powder consisting principally of the mineral kaolinite and varying amounts of other minerals such as muscovite quartz feldspar and anatase. The hazards index allows you to search for hazards by name industry and hazard type. Find out how you can manage hazards and keep yourself and your workers safe from harm.
Hazardous chemicals are common in a wide variety of workplaces. Businesses must identify the hazards of all the hazardous. Take precautions to avoid exposure by the principal routes that is contact with skin and.
Or reduce exposure to chemical or physical hazards through the use of various devices. Examples include laboratory chemical hoods and other ventilation systems shields barricades and interlocks. Engineering controls must always be considered as the first and primary line of defense to protect.
The principal metabolite from hepatocytes and in the urine was 2-methoxyethoxyacetic acid MEAA. This metabolite accounted for approximately 36 of the radioactivity in the 48-hr culture medium and about 67 of the administered dose in the 48-hr urine. Other prominent metabolites common to both systems included 2-2-methoxyethoxyethanol methoxyacetic acid MAA 2-methoxyethanol and.
The register template format can also be amended to include additional information to assist the business such as. The issue date of the SDS. Name of the manufacturersupplier of the hazardous chemical.
The location on-site where the chemical is usedstored. Any codes or numbers used to identify the chemicals at your workplace. Such additions to the register are not specified by the WHS.
Earth systems include the lithosphere atmosphere hydrosphere and biosphere. Human activities influence many of the processes that shape these systems Crutzen 2002 Zalasiewicz et al 2010 Goudie 2013 Lewis and Maslin 2015Of particular concern to the disaster risk community are the anthropogenic influences on the occurrence frequency and intensity of natural. The principal advantage of Carbon Dioxide.
The fire extinguishing agent used in these devices is a powder composed of very small particulates. Types of agents available include sodium bicarbonate base and potassium bicarbonate base. Dry chemical type extinguishers have special treatments that ensure proper flow capabilities by providing.
In addition to the chemical hazards found in laboratories there are also numerous physical hazards encountered by laboratory staff on a day-to-day basis. As with chemical hazards having good awareness of these hazards good preplanning use of personal protective equipment and following basic safety rules can go a long way in preventing accidents involving physical hazards. These hazards and associated risks must be managed to ensure the safety of staff students and others.
Information about managing common hazards is included in this section. Each of the following topics include departmental procedures and guidelines resources legislation and related links. Click on the subject area for more information.
Honey is a sweet viscous food substance made by honey bees and some other bees. Bees produce honey from the sugary secretions of plants floral nectar or from secretions of other insects such as honeydew by regurgitation enzymatic activity and water evaporation. Honey bees store honey in wax structures called honeycombs whereas stingless bees store honey in pots made of wax and resin.
Hazard in three principal categories health flammability and instability. Health Risks Posed by Hazardous Materials Hazardous materials vary greatly in the types of health risks they pose to humans. Emergency responders contend with the following potential health risks.
4 from hazardous materials. Thermal Radiological Asphyxiation Chemical Etiological or Mechanical TRACEM. Consult this chart for an overview of commonly used glove types for laboratory use and their general advantages and disadvantages.
Glove Selection and Usage above for more information on how to select the right glove for a job. Once selected glove use requirements for your lab should be posted in your Chemical Hygiene Plan flipchart under theStandard. Other hazards could be knives wet floors even bullying behaviors.
Think about hazards as categories. They could be biological such as bacteria or animal excrement chemical ergonomic such as. Information is used for classification of all types of chemicals.
The GHS is testing and test-method neutral for health and environmental hazards and is designed to permit self-classification to the maximum extent possible. Law recognizes that pesticides which are intended to be biologically active and have effects on living organisms should be subject to testing and approved by a. Examples of control measures to manage the psychological hazards that can result in work-related stress and possible injury or workers compensation claims include.
High and low job demands. High and low job demands include too much or too little work responsibility and excessive or. The following are types of distribution reservoirs.
Chemical hazards are those of disinfection by-products leaching of piping materials and fittings and water treatment chemicals. Physical hazards include turbidity of water odors colors scales which are buildups of materials inside the pipes from corrosions and sediment resuspension. There are several bodies around the world that.
Some examples include benign salts like sodium chloride and non-toxic non-corrosive cleaning chemicals. Contact EHS prior to disposing any chemical into a sink or via the trash. The most important question to answer when managing a chemical waste.
Does my chemical waste have to be collected and managed as a hazardous. The principal contractor must draw up a construction phase plan and this should include the fire safety and emergency procedures for the site. See Appendix 3 of L153 for further details of the plan.
The plan must include suitable and sufficient arrangements for dealing with any foreseeable emergency including.