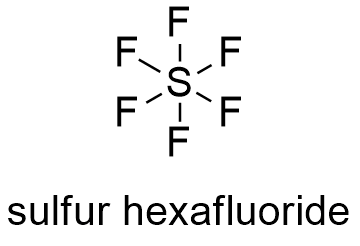
Meanwhile the four fluorine atoms will have 3 lone pairs of electrons in its octet which will further utilize 24 valence electrons. Each sulphur atom in SF 6 molecule creates a covalent bond with 6 fluorine atoms.
Here two fluorine atoms.
Sulfur and fluorine formula. Sulfur in nontechnical British English. Sulphur is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant multivalent and nonmetallicUnder normal conditions sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S 8Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow crystalline solid at room temperature.
Sulfur is the tenth most common element by mass in the universe. A molecular formula helps to know the exact number and type of atoms present in the given compound. Here there is one sulfur atom and four fluorine atoms in the compound which makes it similar to the molecular formula of AX4E.
Molecules having a molecular formula of AX4E have trigonal bipyramidal molecular geometry. Here two fluorine atoms. Sulfur hexafluoride SF 6 or sulphur hexafluoride British spelling is an extremely potent and persistent greenhouse gas that is primarily utilized as an electrical insulator and arc suppressant.
It is inorganic colorless odorless non-flammable and non-toxic. SF 6 has an octahedral geometry consisting of six fluorine atoms attached to a central sulfur atom. Sulfur is abundant multivalent and nonmetallic.
Under normal conditions sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow crystalline solid at room temperature. Chemically sulfur reacts with all elements except for gold platinum iridium tellurium and the noble gases.
The fluorine atom has atomic number 9. The electronic configuration of fluorine is 1S 2 2S 2 2P 5. Each sulphur atom in SF 6 molecule creates a covalent bond with 6 fluorine atoms.
In this way sulfur atom gets total 6 covalent bonds ie. 6 pairs of electrons at its outer shell and each fluorine atom gets 8 electrons in its outer most shell. Ignites in fluorine gas at ordinary temperatures Mellor 211-13 1946-47.
Reacts to incandescence with heated with thorium Mellor 7208 1946-47. Can react with ammonia to form explosive sulfur nitride. Reacts with calcium phosphide incandescently at about 300C.
Reacts violently with phosphorus trioxide Chem. Mixtures with ammonium nitrate or with metal powders. Ionic compounds tend to form crystals with high melting temperatures.
Write the metal first and the non-metal second. Use the atomic number to indicate the number of atoms of each type present in the compound. Change the final.
Sulfur molten appears as a pale yellow crystalline solid with a faint odor of rotten eggsInsoluble in waterA fire and explosion risk above 450 F. Transported as a yellow to red liquid. Handled at elevated temperature typically 290F to prevent solidification and makes transfers easier.
Sulfur is abundant multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow crystalline solid at room temperature.
Chemically sulfur reacts with all elements except for gold platinum iridium tellurium and the noble gases. Sulfur hexafluoride is a sulfur coordination entity consisting of six fluorine atoms attached to a central sulfur atom. It is the most potent greenhouse gas currently known with a global warming potential of 23900 times that of CO2 over a 100 year period SF6 has an estimated lifetime in the atmosphere of between 800 and 3000 years.
A binary covalent compound is composed of two different elements usually nonmetals. For example a molecule of chlorine trifluoride ClF 3 contains 1 atom of chlorine and 3 atoms of fluorine. You can see from its formula that SF 6 is comprised of one sulphur atom and six fluorine atoms.
In this symmetrical form even the very reactive fluorine is locked up tightly. That makes SF 6 a perfect electrical insulator which can effectively extinguish arcs even arcs from a Taser. Of course the fun side of SF 6 is that you can safely inhale small quantities and hear the temporary but.
The formula of the compound often provides a hint as to the skeleton structure. The formula for the chlorate ion for example suggests the following skeleton structure. The third step assumes that the skeleton structure of the molecule is held together by covalent bonds.
The valence electrons are therefore divided into two categories. Bonding electrons and nonbonding electrons. Meanwhile the four fluorine atoms will have 3 lone pairs of electrons in its octet which will further utilize 24 valence electrons.
In addition two electrons will be kept as lone pair in the sulphur atom. Now we can determine sulphurs hybridization by taking a count of the number of regions of electron density. When bonding takes place there is a formation of 4 single bonds in sulphur and.
The chemical formula of ionic compounds can be quickly calculated using the chemical formula calculator. An ionic compound is composed of a metal and a non-metal. Sodium chloride NaCl and magnesium oxide MgO.
The transfer of electrons between metals and non-metals produces charged particles called ions. Metals lose electrons to produce positve ions called cations. Na Mg 2 Non.
Every compound has its own CHEMICAL FORMULA and its own NAME. The nomenclature naming systems for IONIC and MOLECULAR compounds are different. These consist of any positive ion except H combined with any negative ion.
If H is the positive ion the compound is an acid as we will see later on page 6 The positive ion cation may be a monatomic metal ion such as. A new compound containing xenon and fluorine was isolated. If 0526 g of xenon reacted and 0678 g of the new compound was isolated what is its empirical formula.
A sample of 1256 g of elemental sulfur S is combined with fluorine to give a compound with the formula SF x a stable colorless gas. What is the Hybridization of Sulphur Hexafluoride. To determine the hybridization of sulphur hexafluoride we will look at the orbitals involved and the bonds that are formed during the combination of sulphur and fluorine molecules.
The orbitals involved are 3s 3p y 3p y 3p z and 3dx 2 y2 and 3d z 2During the formation of SF 6 the sulphur atom which is the central atom in its ground. Group 6 metalloids and nonmetals such as oxygen tellurium selenium and sulfur produce 2- anions when they ionize. For instance the stable ionized state of oxygen is given as O2-.
The elements found in group 7 of the periodic table produce anions of -1 when they ionize. For this reason the anion of fluorine would be given as Fl-. Other elements commonly found as diatomic molecules are fluorine F 2 chlorine Cl 2 bromine Br 2 and iodine I 2.
The most common form of the element sulfur is composed of molecules that consist of eight atoms of sulfur. Its molecular formula is S 8. A molecule of sulfur is composed of eight sulfur atoms and is therefore written as S 8.
It can be represented as a a. In a molecular formula it states the total number of atoms of each element in a molecule. For example the molecular formula of glucose is C_6H_12O_6 and we do not simplify it into CH_2O.
And for each compound they all have a molecular formula but some can be similar and those are called isomers which are common in organic chemistry. Fluorine 9 F Neon 10 Ne Sodium 11 Na Magnesium 12 Mg Aluminium 13 Al Silicon 14 Si Phosphorus 15 P Sulfur 16 S Chlorine 17 Cl Argon 18 Ar Potassium 19 K Calcium 20 Ca Scandium 21 Sc Titanium 22 Ti Vanadium 23 V Chromium 24 Cr Manganese 25 Mn Iron 26 Fe Cobalt 27 Co Nickel 28 Ni Copper 29 Cu Zinc 30 Zn Name Atomic no. Symbol Gallium 31 Ga Germanium 32 Ge Arsenic 33 As Selenium 34 Se.
GAS NAME FORMULA COLUMN A COLUMN B Acetylene Ethyne C2H2 137 437 Air 08N2. Fluorine F2 94 1179. Forane 134a Freon134a C2H2F4 35 _____ Freon-11 Trichloro-fluoromethane CCl3F 26 279 Freon-12 Dichloro-difluoromethane CCl2F2 29 325 Freon-13 Chloro-trifluoromethane CClF3 34 257 Freon-14 Tetrafluoro-methane CF4 41 _____ Freon-22 Chloro-difluoromethane CHClF2 41 415.
Molecular oxygen O 2 is a diatomic molecule that is composed of two oxygen atoms held together by a covalent bond. Molecular oxygen is essential for life as it is used for respiration by many organisms. Its also essential for fossil fuel combustion.
Molecular oxygen is very chemically reactive and tends to form oxides by reaction with other elements and compounds quite easily. In this process the CEI is prone to be increasingly functionalized with fluorine and sulfur as well fig. Upon charge a deeper S doping with SF and SO bonds strengthens the corresponding peaks at 6878 eV in F 1s and 5322 eV in O 1s 20.