The solubility of the metal compounds thus formed is pH dependent. Ppm to ph chart.
However most heavy metal carbonates precipitate so its a fairly reasonable guess that V 2 CO 3 5 is not soluble.
Solubility chart bicarbonate. Potassium chloride KCl or potassium salt is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorineIt is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water and its solutions have a salt-like tastePotassium chloride can be obtained from ancient dried lake deposits. KCl is used as a fertilizer in medicine in scientific applications and.
The table below provides information on the variation of solubility of different substances mostly inorganic compounds in water with temperature at one atmosphere pressureUnits of solubility are given in grams per 100 millilitres of water g100 mL unless shown otherwise. The substances are listed in alphabetical order. Three components of the mixture will react differently to sodium bicarbonate and sodium.
FIGURE 1 Flow chart for the two-base extraction of benzoic acid 2-naphthol and naphthalene. C pK a Water Sol. G100mL 25 C Appearance benzoic acid 12212 123 417 034 wht.
2-naphthol 14417 123 95 0074 whtbrwn. Naphthalene 12806 80 ntrl. Solubility table From Wikipedia the free encyclopedia See also.
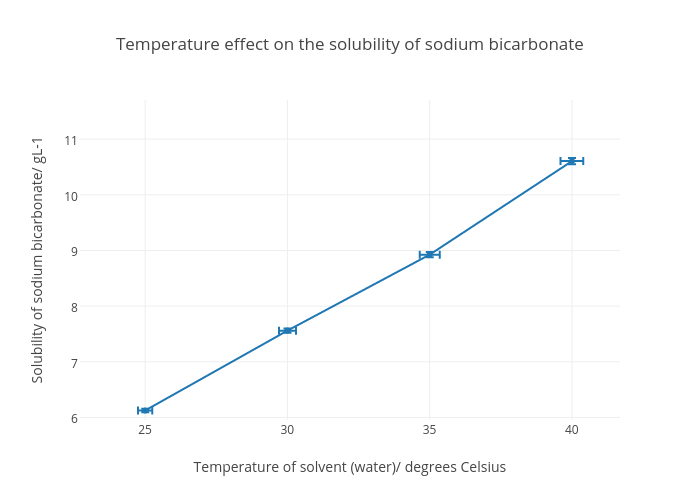
Solubility chart The table below provides information on the variation of solubility of different substances mostly inorganic compounds in water with temperature under 1 atm pressure units of solubility in g100g H2O. The substances are listed in alphabetical order. 3 5 Sodium Bicarbonate Soluble Compounds 4.
5 Hydrochloric Acid Soluble Compounds 5. 96 Sulfuric Acid Soluble Compounds 6. Solubility of Amphoteric Compounds Much information can be obtained about an unknown substance by performing simple solubility and chemical tests.
Determining the solubility behavior of an unknown in water 5 sodium hydroxide solution 5 sodium bicarbonate. Students to determine the solubility of ionic compounds and molecular compounds in both polar and non-polar solvents. Lastly the lab requires allows students to qualitatively compare the melting points of both ionic and molecular compounds.
This lab is strictly qualitative due to the fact that the goal of the lab is to have students collect data on three separate macroscopic phenomena that are. Download Ebook Solubility And Temperature Lab Answers afterward it is not directly done you Page 1223 The solubility product constant is the equilibrium constant for the dissolution of a solid substance intoIn the example of CuIO 3 2 the presence of either Cu 2 or IO 3-in solution should result in a lower molar solubility than in pure water. The reactions of a carboxylic acid and a phenol with bicarbonate ion.
Note that the carboxylic acid has a lower pKa than the conjugate acid of bicarbonate ion carbonic acid. The reaction therefore proceeds to products. The reaction of a phenol however favors the reactants since the pKa of phenol 10 is larger than that of the carbonic acid 64.
Acid-base reactions favor the side with. Adding acid on the other hand lowers pH and alkalinity because in order for it to create carbonic acid acid has to convert bicarbonate alkalinity down into carbonic acid by adding Hydrogen to it. 1 In the chart below acid converts bicarbonate HCO 3 into carbonic acid H 2 CO 3.
When it converts bicarbonate total and carbonate alkalinity are reduced. Difference between solubility and solubility product. Increased temperature usually increases the solubility of solids in liquids.
For example the solubility of glucose at 25 C is 91 g100 mL of water. The solubility at 50 C is 244 g100 mL of water. If we add 100 g of glucose to 100 mL water at 25 C 91 g dissolve.
Nine grams of solid remain on the bottom. We have a saturated solution. If we now heat the mixture to 50 C the remaining 9.
The principal constituents that comprise TDS are calcium magnesium potassium sodium bicarbonate sulphates chlorides and nitrate ions. All the above listed principal constituents are macrominerals and do not cause harm to the human body. In fact you need a majority of these minerals for ensuring good health.
However the proportion of these minerals in drinking water is the matter of. Ppm to ph chart. 10 pH 10 mScm 10 ppm TDS RATIO t 0.
8 pH range alkalinity exists as a bicarbonate material. Recheck total alkalinity after pH adjustments. In horticulture EC is the most accurate way to measure nutrient concentration in solution.
University of Minnesota. Pond fish have an average blood pH of 7. Therefore a stronger nutrient solution should be maintained.
The salt is hardly found in nature for its high water solubility. It was first described in 1659 and currently is the most commercially important ammonium compound in production volume and usage terms. Its great importance comes from the fact that the salt incorporates nitrogen and makes it readily available in both of the forms that plants and crops use.
Nitrate ion and ammonia. These sections allow for simple water treatment according to this flow chart. Bicarbonate can be specified as either alkalinity or bicarbonate.
By default a pH of 8 is assumed but if water pH is known it can and should also be entered. An accurate source water pH slightly improves mash pH prediction. If water report is only entered as GHKH general hardness and alkalinity the latter is.
The answer is that you usually cant figure it out from a solubility chart because vanadium is not usually included. However most heavy metal carbonates precipitate so its a fairly reasonable guess that V 2 CO 3 5 is not soluble. And yes this is an unusual problem.
We also predict this to be a double replacement reaction. Li 3 PO 4 aq CrF 3 aq — CrPO 4 s. Vi Dilute Sodium Bicarbonate Solution.
To study the properties of acids and bases dilute HC1 dilute NaOH by their reaction with i Litmus solution BlueRed ii Zinc metal iii Solid Sodium Cabonate 3. To determine the focal length of a a Concave mirror b Convex lens by obtaining the image of a distant object. To trace the path of a.
Calcium carbonate solubility. While the LSI determines when water is oversaturated with calcium carbonate CaCO 3 pH is a major factor on the LSI. And since LSI violations occur locally not universally throughout a pool pH matters a lot.
For instance theres a chart below that shows the equilibria of alkalinity types. When the pH gets to 82 or 83 it becomes very difficult for calcium. Solubility switch exists for basic organic compounds.
A water insoluble organic base can be protonated by reaction with an acidic solution and can thus move from the ether layer into the aqueous layer in a separatory funnel. Many of the carboxylic acids are strong enough that they can be deprotonated by a saturated solution of sodium bicarbonate a relatively weak base. Phenols on the.
Which substance is likely to be baking soda sodium bicarbonate. At 30 o C exactly 95 grams of this salt dissolved completely in 100 grams of water. According to the solubility chart the salt is.
Solubility of salts in water is temperature dependent. Consider the solubility curve of the salts seen here. Which salts solubility changed the least from 0 - 100oC.
Sotred in the form of bicarbonate ions C. Disolved in plasma D. Disolved in the cytosol of red blood cells.
The common pathway shared by the respiratory and digestive systems is the A. What determines the direction of respiratory gas movement. Muscle contraction in the alveoli B.
Some bases are soluble in water. Physical Properties of Acid. The word acid comes from the Latin word for sour.
This distinguishable property helps identify acids from other compounds such as salt and bases. Many acids can be hazardous if ingested and shouldnt be tasted. Once the acid binds to the base it becomes a neutral substance.
Often this reaction. 91 Exercise 1 Observing Photosynthesis via CO 2 Consumption 1. Label 4 screw cap tubes 1 2 3 and 4 with a marker and line them up in order in a test tube rack.
Obtain 3 pieces of Elodea about 6 cm in length and 2 pieces of aluminum foil. Fill a 250 ml Erlenmeyer flask to the 100 ml line with tap water then add 5 ml of phenol. The maximum amount of a substance that can be dissolved in a given volume of solvent is called solubility.
Often the solubility in water is expressed in gram100 mL. A solution that has not reached its maximum solubility is called an unsaturated solution. This means that more solute could still be added to the solvent and dissolving would still occur.
A solution that has. The solubility of the metal compounds thus formed is pH dependent. Most tend to be least soluble in alkaline solutions.
Since the optimal pH for precipitation depends both on the metal to be removed and on the counter ion used hydroxide carbonate or sulfide the best treatment procedure must be determined on a case- by-case basis. Metal solubility data are available in Benefield and Morgan.