Wilson and Green 1985. The test tube on the right contains limewater a solution of.
BUN may be increased as a result of renal dysfunction.
Sodium carbonate base or acid. Sodium carbonate has several uses in cuisine largely because it is a stronger base than baking soda sodium bicarbonate but weaker than lye which may refer to sodium hydroxide or less commonly potassium hydroxide. Alkalinity affects gluten production in kneaded doughs and also improves browning by reducing the temperature at which the Maillard reaction occurs. To take advantage of the.
Sodium carbonate is neither acidic nor basic it is salt made up of a strong base and weak acid. Strong bases dissociate completely in solution and release a larges number of OH ions but the weak acid mostly remain undissociated and release fewer H ions. Soda ash is the trade name for sodium carbonate a chemical refined from the mineral trona or sodium-carbonate-bearing brines both referred to as natural soda ash or manufactured from one of several chemical processes referred to as synthetic soda ash.
It is an essential raw material in glass chemicals detergents and other important industrial products. In 1998 in terms of. The acidbase reaction can be generically represented as follows.
Additionally in the absence of acid thermal decomposition of sodium bicarbonate also produces sodium carbonate which is strongly alkaline and gives the baked product a bitter soapy taste and a yellow color. Since the reaction occurs slowly at room temperature mixtures cake batter etc can be allowed to stand. ACID BASE TITRATION Objective.
To determine pH curve for titration of strong acid-strong base and weak acid-strong base. 1 Theory The process of adding acid to a base or vice versa to produce a salt and water is called neutralization. In the neutralization of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide the reaction that occurs is.
HCl NaOH H 2 O NaCl When an acid and a base are present. Acid-base indicators change colour in acidic or basic solutions. They may be weak acids that dissociate and change colour in alkaline solutions.
Test acid-base indicators with dilute HCl lemon juice vinegar ammonia solution dilute sodium hydroxide solution lime water tap water demineralized water. 563 Prepare bromothymol blue acid-base indicator 3531a Bromothymol blue Bromothymol. This inorganic compound is water-soluble and when dissolved in water it forms carbonic acid and sodium hydroxide.
In its pure form it is white powder and odourless. It is a strong base and acts as an antacid. Sodium carbonate can be produced by four processes Solvay process Labnac process Dual-process Electrolytic process.
Since it is a weak acid it is slightly soluble in. Many personal care and pharmacy products contain a mixture of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate. While sodium bicarbonate is technically an acidic salt it acts as a base in the presence of citric acid.
The two compounds react with one another to produce bubbles leading to an effervescent solution when theyre mixed with water. Coming to the chemistry side sodium bicarbonate and sodium carbonate are basically different type of sodium compounds or salts. One common thing is that they both contain the principal element known as sodium.
As far as the physical appearance goes both are white they are usually solids but often found in powdered form. Further both are classified as a base and these two also have ionic. Add a small amount of sodium carbonate to the acid and seal the test tube with the rubber stopper.
Place the other end of the delivery tube into the test tube containing the lime water. Observe what happens to the colour of the limewater. Repeat the above steps this time using vinegar.
The clear lime water turns milky meaning that carbon dioxide has been produced. You may not. 02M hydrochloric acid standardization against sodium carbonate.
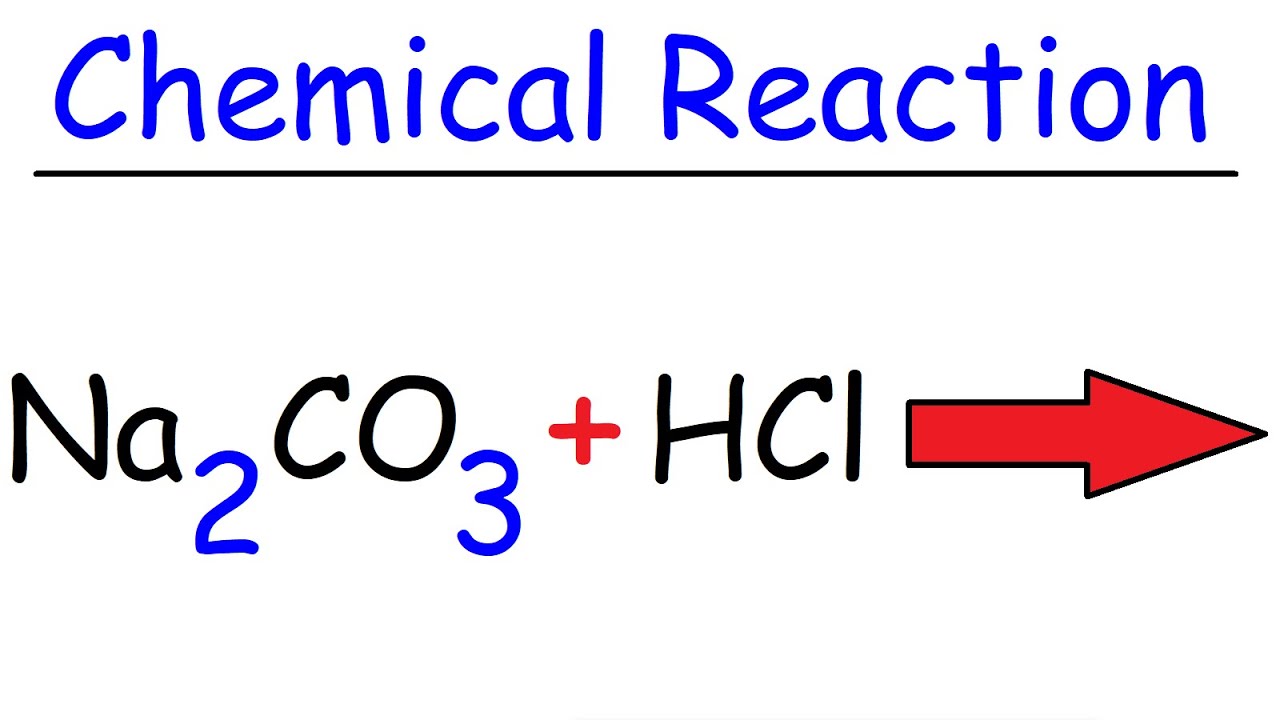
Sodium carbonate is a salt of a weak acid. When titrated with hydrochloric acid carbonate decomposes yielding carbon dioxide and water. Na 2 CO 3 2HCl 2NaCl CO 2 H 2 O.
Evolving carbon dioxide acidifies the solution and the end point in its presence is detected too. Answer 1 of 14. If you were foolish enough to put solid NaOH into commercial hydrochloric acid and stir the heat generated would very likely splash a lot of corrosive material around.
If you were to mix a dilute aqueous solution of NaOH with a dilute aqueous solution of HCl you would get a di. Compound Summary for CID 516892 Sodium bicarbonate. Hadzic M Eckstein ML Schugardt M.
The impact of sodium bicarbonate on performance in response to exercise duration in athletes. J Sports Sci Med. The solution in the flask contains an unknown number of equivalents of base.
A small amount of sodium carbonate is added to the acid and the tube is sealed with a rubber stopper. The two tubes are connected. As a result of the acid-carbonate reaction carbon dioxide is produced and the lime water turns milky.
The test tube on the right contains limewater a solution of. Calcium carbonate CaCO 3 Sodium acetate NaOOCCH 3 Potassium cyanide KCN Sodium sulfide Na 2 S Notice that for all of these examples the anion is the conjugate base of a weak acid carbonic acid bisulfate second dissociation step of sulfuric acid acetic acid hydrocyanic acid hydrogen sulfide. Conjugate Bases of Weak vs.
Keep in mind that a salt will only be basic. An acid-base indicator changes its colour depending on the pH eg phenolphthalein. Redox indicators are also frequently used.
A drop of indicator solution is added to the titration at the start. At the endpoint has been reached the colour changes. It is an instrument that measures the electrode potential of the solution.
These are used for titrations based on a redox. Acidbase reaction a type of chemical process typified by the exchange of one or more hydrogen ions H between species that may be neutral molecules such as water H 2 O. Or acetic acid CH 3 CO 2 H or electrically charged ions such as ammonium NH 4.
Or carbonate CO 3 2It also includes analogous behaviour of molecules and ions that are acidic but do not. Acids and bases exist as conjugate acid-base pairsThe term conjugate comes from the Latin stems meaning joined together and refers to things that are joined particularly in pairs such as Brnsted acids and bases. Every time a Brnsted acid acts as an H -ion donor it forms a conjugate baseImagine a generic acid HA.
When this acid donates an H ion to water. Sodium carbonate Sodium acetate etc. Sodium carbonate is formed after the reaction between sodium hydroxide a strong base and carbonic acid a weak acid.
Sodium acetate is formed after the reaction between a strong base sodium. The concentration of the acid we used in class will be sampled with a standardize solution such as sodium hydroxide with an environmentally indicator to show the physical change of color that occurs to the solution by the acid. The equipment necessary for the titration experiment follows.
01M NaOH Acid solution Anthocyanin which is found in red cabbage leaves indicator Burets Ethanol 95. Evaluation of mixed acid-base abnormalities requires an understanding of the anion gap the relationship between the change in serum sodium and chloride concentration and the limits of compensation for the primary acid-base imbalances Saxton and Seldin 1986. Wilson and Green 1985.
Clinical findings and history are also necessary to define the factors that may contribute to the development. For example Sodium hydroxide is a base as well as an alkali as it neutralizes the acids in any acid-base reaction. Secondly it is soluble in water.
On the other hand the Copper oxide is a base but not an alkali as it neutralizes the acid in aqueous solution but does not dissolve in water. A strong base is a chemical compound that gets deprotonated or removes a proton H from a molecule. Of the stronger acid versus the weaker acid.
The weaker base sodium bicarbonate is strong enough to react with the stronger acid benzoic acid but not strong enough to react with the weaker acid 2-naphthol. The sodium salt that forms is ionic highly polarized and soluble in water. Therefore a neutral compound dissolved in diethyl ether can be extracted from the mixture into an aqueous.
Acid-base indicators indicators are natural or synthetic dyes which show a change of colour depending upon the acidity or alkalinity of a solution. The indicator like litmus is red in acidic and blue in basic medium. Methyl orange is red in acidic and yellow in basic medium.
Phenolphthalein is colourless in acidic and pinkish-red in basic medium. Extracellular fluid shifts sodium and water restriction and renal function all affect serum sodium levels. Potassium deficit may occur with kidney dysfunction or diuretic therapy.
BUN may be increased as a result of renal dysfunction. ABGs may reflect metabolic acidosis. Replace potassium losses as indicated.
Potassium deficit may occur especially if the client is receiving potassium.