Due to the cyclic. How to get the most out of spinach.
The links will take you to a page at one of the Web sites at a University Chemistry Department or commercial site in.
Sodium benzene molecule. Benzene in soft drinks is of potential concern due to the carcinogenic nature of the benzene molecule. This contamination is a public health concern and has caused significant outcry among environmental and health advocates. Benzene levels are regulated in drinking water nationally and internationally and in bottled water in the United States but only informally in soft drinks.
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C 6 H 6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon.
Benzene is a natural constituent of crude oil and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Due to the cyclic. The main step wherein the carbon dioxide is fixed condensed with an organic molecule is known as carboxylation reaction.
You must also be familiar with the reverse chemical equation. C 6 H 12 O 6 6O 2 6CO 2 6H 2 O energy. The above chemical reaction describes what occurs in respiration ie the oxidative breakdown of glucose to form water carbon dioxide and energy.
The term aromatic in organic chemistry now means that the molecule contains benzene or its structural relatives. Benzene itself is a clear colorless highly flammable liquid which boils at 801C and melts at 55C. It was used extensively as a solvent for many organic reactions but it is toxic by ingestion and inhalation and may.
Benzene is used to make other chemicals like ethylbenzene cumene and cyclohexane which are then reacted and used in the manufacture of a variety of materials and plastics such as polystyrene ABS and nylon. There can be many steps in the process that starts with the benzene molecule and ends with a completed material or consumer product. Turn off atom manipulation Off.
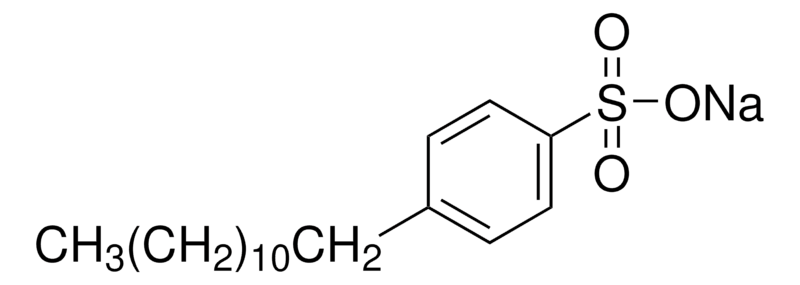
Increase charge of selected atom 1. Decrease charge of selected atom-1. 13 salt C10-13 Alkyl deriv benzene sulfonic acid 14 sodium salt 10-13-sec Alkyl deriv benzene 15 sulfonic acid sodium salt n-Dodecyl 16 benzenesulfonic acid sodium salt isomers 17 Dodecylbenzenesulfonate sodium salt isomers 18 Sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate 2-19 dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid sodium.
2-20 dodecylbenzenesulfonate 3-21 dodecylbenzenesulfonic. There are three benzene rings in the molecule. Every atom involved in a double bond has a p orbital which can overlap side-to-side with similar atoms next to it.
The overlap creates a pi bond which allows the electrons in the p orbital to be found on either bonded atom. These electrons can spread like a cloud over any region of the molecule that is flat and has alternating double and single. Welcome to the Molecule of the Month page.
This is one of the longest running chemistry webpages on the internet. Each month since January 1996 a new molecule has been added to the list on this page which makes this one of the longest running Chemical websites on the internet. The links will take you to a page at one of the Web sites at a University Chemistry Department or commercial site in.
Benzene is widely used in the United States. It ranks in the top 20 chemicals for production volume. Some industries use benzene to make other chemicals which are used to make plastics resins and nylon and synthetic fibers.
Benzene is also used to make some types of rubbers lubricants dyes detergents drugs and pesticides. Natural sources of benzene include volcanoes and forest fires. Also there are many non-benzene kinds of aromatic compounds existing too.
In the living organisms take for example the very common type of aromatic ring is the DNA and RNA bases with double chains. The functional group of an aromatic compound or the substituent of it is known as an aryl group. Molecular formula tells the exact number and type of atoms in a single molecule of a compound.
Empirical formula represents the simplest whole number ratio of all kinds of atoms present in a molecule of a compound. The molecular formula for a compound can be the same as or a multiple of the compounds empirical formula. Molecular formulas are compact and easy to communicate but they do.
When concentrated sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 is added to sodium nitrate NaNO 3 the following reaction occurs. H 2 SO 4 2NaNO 3 Na 2 SO 4 2HNO 3. Then in excess sulfuric acid reactive nitronium ion NO 2 is produced.
HNO 3 H 2 SO 4 NO 2 HSO 4- H 2 O. The nitronium ion NO 2 attacks the benzene ring of phenol to produce a mixture of various structural isomers of. Sodium bicarbonate is a mixture of carbon sodium hydrogen and oxygen.
One molecule contains one carbon atom one sodium atom one hydrogen atom and three oxygen atoms for a molecular formula of NaHCO 3 or CHNaO 3Based on molecular weights sodium bicarbonate is composed of 571 percent sodium 274 percent oxygen 143 percent carbon and 12 percent hydrogen. New Molecule Slows Broad Range of Cancer Types and More–November 15 2019. The fatty acid molecule propionate produced in the gut from fiber shown to protect the cardiovascular system December 282018.
How to get the most out of spinach. Maximizing the antioxidant lutein December 212018. The partially-negatively charged oxygen atom on one alcohol molecule is strongly attracted to the partially positively charged hydrogen atom on another alcohol molecule.
This strong attraction results in much stronger intermolecular forces between alcohol molecules than there are between nonpolar alkanes of the same molar mass. Alcohols are generally more soluble in water than alcohols of the. Sodium Borohydride NaBH 4 For Reduction Of Aldehydes And Ketones And Demercuration.
In a blatant plug for the Reagent Guide each Friday I profile a different reagent that is commonly encountered in Org 1 Org 2. Version 12 just got released with a host of corrections and a new page index. Having just talked about the oxidation ladder it makes sense to start going into.
A monosubstituted benzene when treated with an electrophile could undergo three electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions. Each reaction yields a disubstituted benzene as the organic product which can be identified using the descriptors ortho meta and. Le naphtalène est un bon accepteur délectrons vis à vis dun métal alcalin comme le sodium.
Lorsquon agite de petits morceaux de sodium avec une solution de naphtalène dans le THF anhydre on observe la formation dun anion-radical qui confère à la solution une belle couleur verte. Si lon ajoute un donneur de protons comme léthanol la couleur verte disparaît et il se forme du. Electrophilic Substitution of Disubstituted Benzene Rings.
When a benzene ring has two substituent groups each exerts an influence on subsequent substitution reactions. The activation or deactivation of the ring can be predicted more or less by the sum of the individual effects of these substituents. The site at which a new substituent is introduced depends on the orientation of the existing.
The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the hypothetical charge the atom would have if we could redistribute the electrons in the bonds evenly between the atoms. Another way of saying this is that formal charge results when we take the number of valence electrons of a neutral atom subtract the nonbonding electrons and then subtract the number of bonds. Iodine - iodine - Physical and chemical properties.
Iodine is a nonmetallic nearly black solid at room temperature and has a glittering crystalline appearance. The molecular lattice contains discrete diatomic molecules which are also present in the molten and the gaseous states. Above 700 C 1300 F dissociation into iodine atoms becomes appreciable.
Azobenzene is a molecule whose structure comprises two phenyl rings linked by a NN double bond. The parent compound of the azobenzene class of compounds. 1 Structures Expand this section.
2 Names and Identifiers Expand this section. 3 Chemical and Physical Properties Expand this section. 4 Spectral Information Expand this section.
5 Related Records Expand this section. Gas laws in elucidating the concept of the molecule Boyles law Charles law Gay Lussacs law Avogadros law ideal behaviour empirical derivation of gas equation Avogadro number ideal gas equation. Kinetic energy and molecular speeds elementary idea deviation from ideal behaviour liquefaction of gases critical temperature.
Liquid State Vapour pressure viscosity and.