Respiratory acidosis ensues due to suppression of the respiratory centre. Signs and Symptoms Clinical Manifestations.

Then the mitochondrial dysfunction induced by salicylate will generate a progressive metabolic acidosis.
Salicylic acidosis alkalosis. Salicylic acid overdose can lead metabolic acidosis with compensatory respiratory alkalosis. In people presenting with an acute overdose a 16 morbidity rate and a 1 mortality rate are observed. Salicylic acid works as a keratolytic comedolytic and bacteriostatic agent causing the cells of the epidermis to shed more readily opening clogged pores and neutralizing.
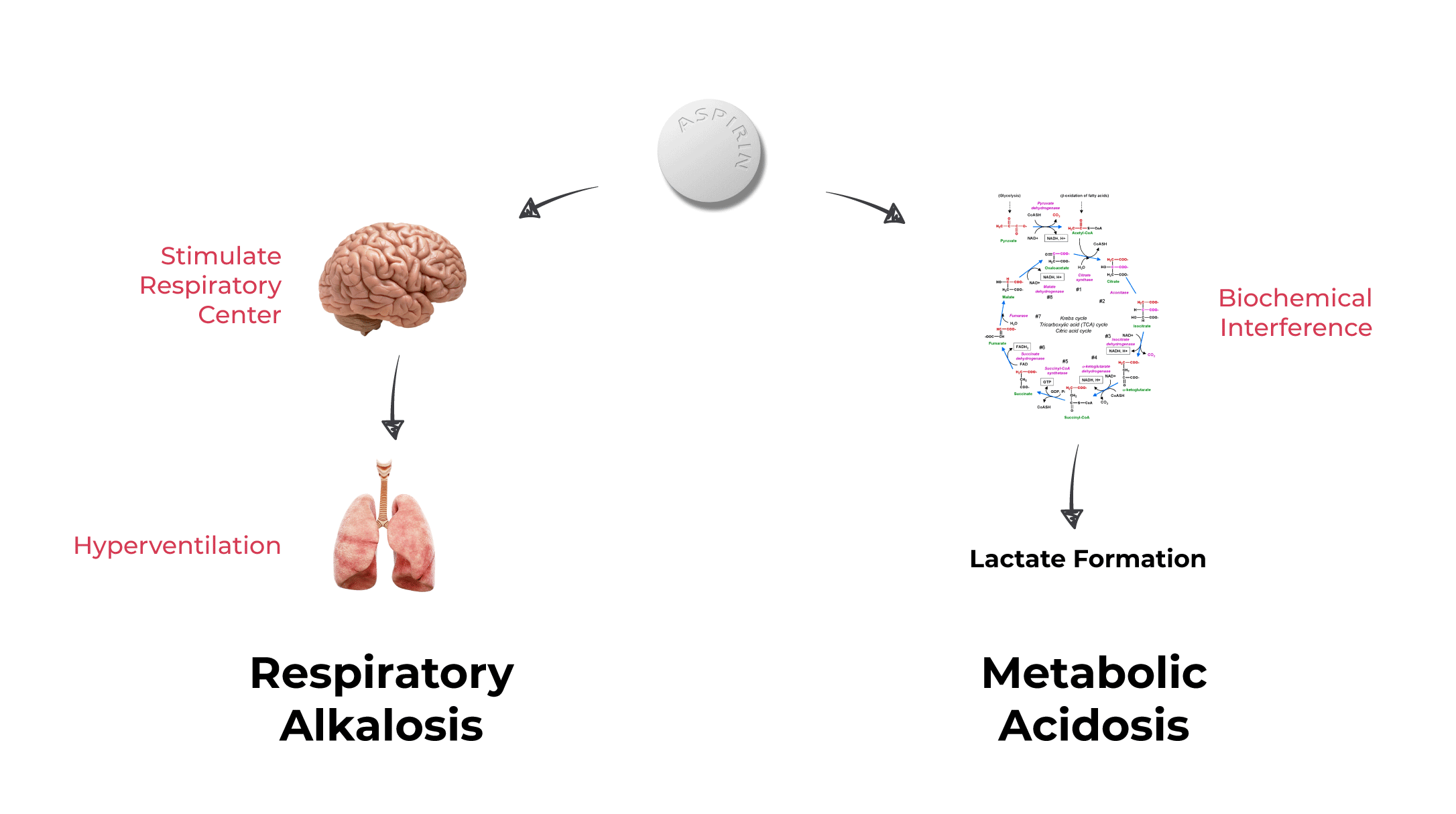
Aspirin causes high anion gap metabolic acidosis and respiratory alkalosis. The high anion gap comes from the addition of salicylic acid as well as the generation of lactic acid due to uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation causing anaerobic respiration. The respiratory alkalosis is due to direct stimulation of the respiratory center.
Salicylate exists in the. Abnormal bicarbonate losses which can occur in loss of fluid from the lower GI tract from surgery drains or severe diarrhea. Signs and Symptoms Clinical Manifestations.
Increased respiratory rate and depth. Diminished cardiac output with pH. Salicylic acid as a peeling agent has a number of indications including acne vulgaris melasma photodamage freckles and lentigines.
The efficacy and safety of salicylic acid peeling in Fitzpatrick skin types IIII as well as in skin types V and VI have been well documented in the literature. This paper reviews the available data and literature on salicylic acid as a peeling agent and its. Salicylate poisoning also known as aspirin poisoning is the acute or chronic poisoning with a salicylate such as aspirin.
The classic symptoms are ringing in the ears nausea abdominal pain and a fast breathing rate. Early on these may be subtle while larger doses may result in fever. Complications can include swelling of the brain or lungs seizures low blood sugar or cardiac arrest.
The anion gap AG is a mathematical construct that compares the blood sodium concentration with the sum of the chloride and bicarbonate concentrations. It is a helpful calculation that divides the metabolic acidoses into 2 categories. High AG metabolic acidosis HAGMA and hyperchloremic metabolic acidosisand thereby delimits the potential etiologies of the disorder.
There is an initial respiratory alkalosis due to central respiratory centre stimulation causing increased respiratory drive. In the later stages a metabolic acidosis develops along side the respiratory alkalosis as a result of direct effect of the metabolite salicylic acid. 1 First finding is respiratory alkalosis.
Salicylate affects the medulla directly increasing respiratory drive. 2 Second an anion-gap metabolic acidosis develops as well creating a mixed picture. Metabolic acidosis reflects increases in ketoacid salicylic acid and lactic acid.
Resulting imbalances include acidosis pH 745 and high or low levels of key electrolyte ions including sodium potassium calcium magnesium chloride hydrogen phosphate and hydrogen carbonate bicarbonate. They may be acute or chronic may occur with varying degrees of severity and may not be sufficiently counteracted by the bodys regulatorycompensatory. More than half of patients with salicylate poisoning have a mixed respiratory alkalosis and increased anion-gap metabolic acidosis.
42 Most affected adults who have ingested salicylates alone. 2-5 mEqkg IV infusion over 4-8 hr depending on the severity of acidosis as judged by the lowering of total CO2 content clinical condition and pH. Severe except hypercarbic acidosis.
90-180 mEqL 75-15 g at a rate of 1-15 L first hour. Adjust for further management as needed. A mixed respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis with normal or high arterial pH normal or reduced hydrogen ion concentration is usual in adults and children over the age of four years.
In children aged four years or less a dominant metabolic acidosis with low arterial pH raised hydrogen ion concentration is common. Acidosis may increase salicylate transfer across the blood brain. In the first instance hyperventilation occurs which results in respiratory alkalosis.
Respiratory acidosis ensues due to suppression of the respiratory centre. In addition metabolic acidosis occurs as a result of the presence of salicylate. Since younger children are often not seen until they have reached a late stage of intoxication they are usually in the stage of acidosis.
Severe metabolic acidosis can lead to impaired myocardial contractility cerebral vasodilatation and coma and several gastrointestinal complications. However rapid alkalinization may result in hypokalemia paradoxical central nervous system acidosis and worsened intracellular acidosis as a result of increased carbon dioxide production with resultant alkalosis. Controlled studies have.
Treatment of acute Poisoning - Aspirin Fatal dose. 15 30 gm Low in case of children Features. Vomiting dehydration acidosis petechial haemorrhage hyperglycaemia hyperpyrexia confusion and coma etc.
Inducing emesis or administering gastric lavage Appropriate infusion measures to correct abnormal electrolyte balance and dehydration Na K HCO3. After ingestion AAS is rapidly transformed into salicylic acid that dissociates into an hydrogen ion plus salicylate. Salicylate is the main form of AAS in the body and produces multiple alterations.
Initially the stimulation of the ventilatory center promotes a respiratory alkalosis. Then the mitochondrial dysfunction induced by salicylate will generate a progressive metabolic acidosis. In young children the initial respiratory alkalosis from salicylate intoxication is transient they often have a predominant metabolic acidosis and in severe cases also respiratory alkalosis on presentation.
What does the label say about Reyes syndrome and Pepto-Bismol. Aspirin and released salicylic acid irritate gastric mucosa cause epigastric distress nausea and vomiting. It also stimulates CTZ.
Aspirin in high dose reduces renal tubular excretion of urate 17 18. Aspirin even in small doses irreversibly inhibits TXA2 synthesis by platelets. Thus it interferes with.
AAS is rapidly transformed into salicylic acid that dissociates into an hydrogen ion plus salicylate. Salicylate is the main form of AAS in the body and produces multiple alterations. Initially the stimulation of the ventilatory center promotes a respiratory alkalosis.
Then the mitochondrial dysfunction induced by sali-cylate will generate a progressive metabolic acidosis due to the. Chronic metabolic acidosis and its side effects. This is a condition where there is too much acid in your bodily fluids.
Depending on severity this can affect your vital organs cardiovascular system kidneys liver pancreas insulin levels and many other parts of your body. There is a large amount of research which suggests an acidic environment promotes tumor growth. Some research gets.
Salicylic acid is treated with acetic anhydride. Salicylates directly stimulate the respiratory drive in the brain stem leading to hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis. Anion gap metabolic acidosis occurs from a buildup of organic acids as well as the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation which results in an imbalance in ATP consumption and production resulting in a net buildup.
The T max of salicylic acid after gastric bypass was observed to be significantly shorter after surgery. C max and AUC 0-24 were also significantly higher Mitrov-Winkelmolen 2016. In a mixed surgery population 80 gastric bypass 20 sleeve aspirin-induced platelet reactivity was significantly reduced and correlated to the extent of weight loss after surgery Norgard 2017.
Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Its quite an experience hearing the sound of your voice carrying out to a over 100 first year.