More clinically significant signs and symptoms may include rapid. Your veterinarian will base a diagnosis of this poisoning on a history of eating grapes raisins currants or the presence.

Its also important to watch for signs of diabetes or renal failure.
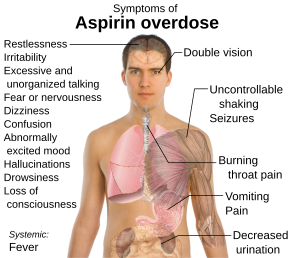
Salicylate poisoning symptoms. Salicylate poisoning also known as aspirin poisoning is the acute or chronic poisoning with a salicylate such as aspirin. The classic symptoms are ringing in the ears nausea abdominal pain and a fast breathing rate. Early on these may be subtle while larger doses may result in fever.
Complications can include swelling of the brain or lungs seizures low blood sugar or cardiac arrest. In an acute salicylate overdose the onset of symptoms will occur within 3 to 8 hours. The severity of symptoms is dependent on the amount ingested.
For mild ingestions salicylate levels 40 to 80 mgdL nausea vomiting and generalized abdominal pain are common. Tachypnea is usually present. Headaches and dizziness may also occur.
The classic finding of tinnitus may also be present. The earliest symptoms of acute aspirin poisoning may include ringing in the ears and impaired hearing. More clinically significant signs and symptoms may include rapid.
Salicylate Toxicity This review focuses on risk factors for salicylate poisoning the pathophysiology of both acute and chronic toxicity hidden sources of salicylate that may result in. Aspirin is the most common type of salicylate. Popular brand name aspirins include Bayer and Ecotrin.
Aspirin and other salicylates are most. You may need this test if you have symptoms of acute or gradual aspirin poisoning. Symptoms of acute aspirin poisoning usually happen three to eight hours after an overdose and may include.
Nausea and vomiting. Rapid breathing hyperventilation. Methyl salicylate oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil is an organic ester naturally produced by many species of plants particularly wintergreens.
The compound was first extracted and isolated from plant species Gaultheria procumbens in 1843. It can be manufactured synthetically and it used as a fragrance in foods beverages and liniments. It forms a colorless to yellow or reddish liquid.
Salicylate aspirin poisoning in adults. Serotonin syndrome serotonin toxicity Severe nonexertional hyperthermia classic heat stroke in adults. General measures for acute poisoning treatment.
Treatment of acute poisoning caused by specific agents other than drugs of abuse. Tricyclic antidepressant poisoning. Follow salicylate levels and clinical symptoms following dialysis.
In some cases multiple dialysis runs may be necessary. Lab monitoring back to contents lab monitoring. Cycle labs at least q2hr initially.
Target potassium 45 mM. Alkalinization if patient has symptoms or a salicylate level 40 mgdL 29 mM Serum pH. NAPQI also known as NAPBQI or N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine is a toxic byproduct produced during the xenobiotic metabolism of the analgesic paracetamol acetaminophen.
It is normally produced only in small amounts and then almost immediately detoxified in the liver. However under some conditions in which NAPQI is not effectively detoxified usually in the case of paracetamol overdose it. Unfortunately the symptoms of grape or raisin poisoning are non-specific and early signs are similar to a variety of things including simple dietary indiscretion eating foods that should not be eaten.
More severe signs are similar to kidney failure from other causes. Your veterinarian will base a diagnosis of this poisoning on a history of eating grapes raisins currants or the presence. Poisonings - Acute Guidelines for Initial Management Poisonings - Antihistamines antihistamine-decongestant poisoning Poisonings - Tricyclic antidepressant poisoning.
Key Points Many medications may have anticholinergic effects and interaction between two or more of these medications can lead to symptoms such as an agitated delirium mydriasis dry mouth and tachycardia. Poisoning acute guidelines for initial management Resuscitation Hydrocarbons Poisoning Eucalyptus oil Poisoning Camphor Poisoning Salicylates Poisoning. Mucous membrane irritation and gastrointestinal symptoms usually develop first followed by CNS depression which increases the risk of aspiration pneumonitis.
Acetaminophen. Ethylene glycol. Biochemistry back to contents Ethylene glycol and methanol themselves arent very toxic.
However alcohols are metabolized by alcohol dehydrogenase and aldehyde dehydrogenase producing toxic metabolites. Ethylene glycol oxalic acid calcium-oxalate precipitation in the. The main features of salicylate poisoning are hyperventilation tinnitus deafness vasodilatation and sweating.
Coma is uncommon but indicates very severe poisoning. The associated acid-base disturbances are complex. Treatment must be in hospital where plasma salicylate pH and electrolytes can be measured.
Absorption of aspirin may be slow and the plasma-salicylate concentration may. The main features of salicylate poisoning are hyperventilation tinnitus deafness vasodilatation and sweating. Coma is uncommon but indicates very severe poisoning.
The associated acid-base disturbances are complex. Treatment must be in hospital where plasma salicylate pH and electrolytes can be measured. Absorption of aspirin may be slow and the plasma-salicylate concentration may.
Consider hemodialysis based on symptoms. Salicylate level of 100 mg per dL or more in acute toxicity or 60 mg per dL or more in chronic toxicity. Or if patient requires intubation.
Salicylate poisoning is usually associated with plasma concentrations 350 mgL 25 mmolL. Most adult deaths occur in patients whose concentrations exceed 700 mgL 51 mmolL. Single doses less than 100 mgkg are unlikely to cause serious poisoning.
Common features include vomiting dehydration tinnitus vertigo deafness sweating warm extremities with bounding. Consuming a small amount is unlikely to have any effect on you but a larger amount could have an intoxicating effect. Also consider obtaining acetaminophen and salicylate levels to rule out co-ingestions.
An increased anion gap metabolic acidosis is expected in patients with cyanide poisoning. It is also advisable to get a carboxyhemoglobin level in patients where this is a concern such as fire or smoke inhalation victims. The symptoms of celiac disease and gluten intolerance typically improve when a person eliminates gluten from the diet but return when they reintroduce it.
Patients are often asymptomatic or have only mild gastrointestinal symptoms at initial presentation. Untreated paracetamol poisoning may cause varying degrees of liver injury over the 2 to 4 days following ingestion including fulminant hepatic failure. Rarely massive overdose may initially present with coma and severe metabolic acidosis.
Presentation with coma may also occur if a. Salicylate poisoning is usually associated with plasma concentrations 350 mgL 25 mmolL. Most adult deaths occur in patients whose concentrations exceed 700 mgL 51 mmolL.
Single doses less than 100 mgkg are unlikely to cause serious poisoning. Patients should be given supportive therapy or treatment for salicylate poisoning as necessary. This may include treatment like.
The symptoms of food poisoning usually last less than 24 hours. With some bacteria the toxins are produced in the food before it is eaten while with other bacteria the toxins are produced in the intestine after the food is eaten. Symptoms usually appear within several hours when food poisoning is caused by toxins that are formed in the food before it is eaten.
It takes longer for symptoms. This is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that functions to reverse anticholinergic toxicity by increasing extracellular levels of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. In essence this substance is counteracting the effects of the anticholinergic drugs that were ingested.
Physostigmine is not only the most common treatment for anticholinergic toxicity it is the most. The symptoms of high anion gap metabolic acidosis are usually non-specific though dyspnea and dysfunction of central respiratory center stimulation are common symptoms that are observed. As a result it is important to test for harmful ingestions such as aspirin and acetaminophen overdoses.
Its also important to watch for signs of diabetes or renal failure. Other than an anion blood test.