Aminoglycosides and tetracyclines are inhibitors of protein synthesis. Pharmacodynamics of antibacterial agents as a basis for determining dosage.
If ergosterol synthesis is either completely or partially inhibited the cell is no longer able to construct an intact and functional cell membrane 12 13.
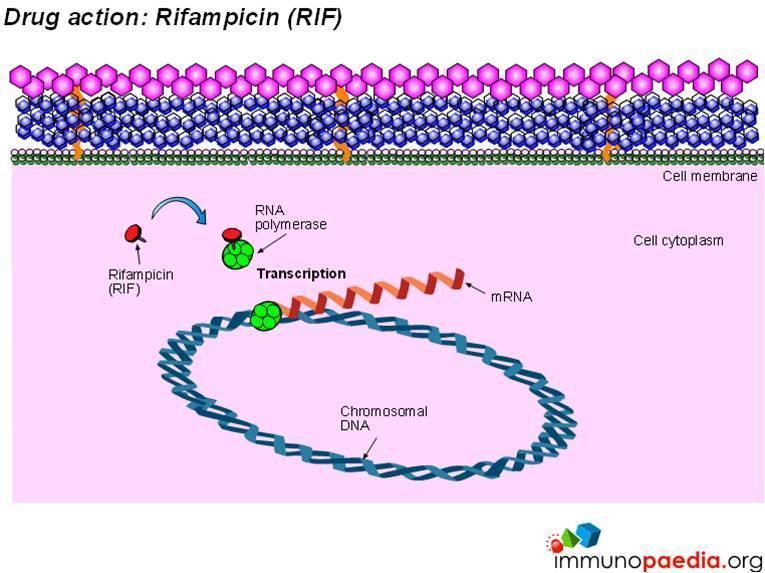
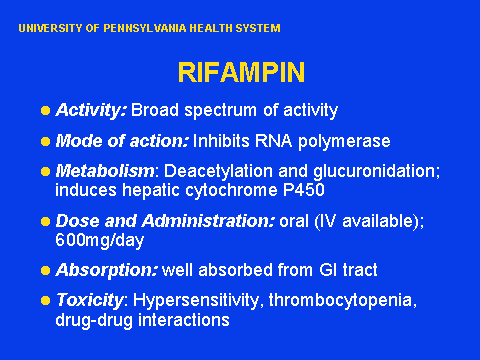
Rifampin mode of action. Mode of action of Rifampin. Rifampin acts via the inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase which is results in the suppression of RNA synthesis and cell death. Inhibition of Mycolic Acids synthesis.
The inhibition of Mycolic Acids synthesis within the bacterial cell is caused by Isoniazid. Mode of action of Isoniazid. Isoniazid is a prodrug and must be activated by bacterial catalase.
Mode of Action Different antibiotics have different modes of action owing to the nature of their structure and degree of affinity to certain target sites within bacterial cells. Inhibitors of cell wall synthesis. While the cells of humans and animals do not have cell walls this structure is critical for the life and survival of bacterial species.
A drug that targets cell walls can therefore. The rifamycin group includes the classic rifamycin drugs as well as the rifamycin derivatives rifampicin or rifampin rifabutin rifapentine rifalazil and rifaximin. Rifamycin sold under the trade name Aemcolo is approved in the United States for treatment of travelers diarrhea in some circumstances.
Streptomyces mediterranei was first isolated in 1957 from a soil sample. In this review the mode of action of antifungals and their mechanisms of resistance are discussed. Additionally an attempt is made to discuss the correlation between fungal and bacterial resistance.
Antifungals can be grouped into three classes based on their site of action. Azoles which inhibit the synthesis of ergosterol the main fungal sterol. Polyenes which interact with fungal.
Rifampin is used as a first-line oral drug treatment for tuberculosis in humans. Link to Wikipedia for more information on Rifamycins. Mode of action.
Inhibition of protein synthesis. Streptogramins irreversibly bind to the 50S ribosomal subunit. Group A streptogramins prevent peptide bond formation during chain elongation step while group B components cause the release of.
It is well established that tetracyclines inhibit bacterial protein synthesis by preventing the association of aminoacyl-tRNA with the bacterial ribosome 44 263. Therefore to interact with their targets these molecules need to traverse one or more membrane systems depending on whether the susceptible organism is gram positive or gram negative. Hence a discussion of the.
Rifampicin causes cholestasis at both the sinusoids and canaliculi of the liver because of defect in uptake by hepatocytes and defect in excretion respectively. Rifampicin may produce liver dysfunction. Hepatitis occurs in 1 or less of patients and usually in the patient with pre-existing liver disease.
Hypersensitivity reactions may occur usually. The short term effects of corticosteroids are decreased vasodilation and permeability of capillaries as well as decreased leukocyte migration to sites of inflammation. 1 Corticosteroids binding to the glucocorticoid receptor mediates changes in gene expression that lead to multiple downstream effects over hours to days.
Glucocorticoids inhibit neutrophil apoptosis and. Polyenes Amphotericin nystatin Fungi Interfere with fungal plasma membrane Streptomyces nodosus Streptomyces noursei Rifamycins Rifampin Gram -positive gram negative bacteria M. Tuberculosis Inteferes with bacterial DNA.
Function - how the drug works its mode of action. 5 functional groups These are all components or functions necessary for bacterial growth Targets for antibiotics. Inhibitors of cell wall synthesis Inhibitors of protein synthesis Inhibitors of membrane function Anti-metabolites Inhibitors of nucleic acid synthesis 3.
Narrow spectrum Broad Spectrum In these discussions. Each class of antibacterial drugs has a unique mode of action the way in which a drug affects microbes at the cellular level and these are summarized in Figure 149 and Table 141. Figure 149 There are several classes of antibacterial compounds that are typically classified based on their bacterial target.
Common Antibacterial Drugs by Mode of Action. Mode of Action Target Drug Class. Practice Mode Questions and choices are randomly arranged the answer is revealed instantly after each question and there is no time limit for the exam.
Exam Mode Questions and choices are randomly arranged time limit of 1min per question answers and grade will be revealed after finishing the exam. Text Mode Text version of the exam 1. Nurse Rita is giving instructions to her.
On the basis of mode of action. Bacteriostatic antibiotics Tetracycline Chlorampenicol Erythromycin Lincomycin Bacteriocidal antibiotics Cephalosporin Penicillin Erythromycin Aminoglycosides Cotrimoxazole 9. CYP3A inducers nevirapine rifampin efavirenz.
Decreased serum levels and loss of effectiveness of maraviroc. Loss of antiviral effect of maraviroc. This antiretroviral drug was released in late 2007.
The desired and beneficial action of this antiretroviral drug is. Same mode of action as other beta-lactam antibiotics. Disrupt the synthesis of the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls.
Targocid UK Active against aerobic and anaerobic Gram-positive bacteria including MRSA. Vancomycin is used orally for the treatment of C. Mode of transmission is similar with HBV.
The desired and beneficial action of this anti-hepatitis drug is. Anti-hepatitis B agents inhibit reverse transcriptase in hepatitis B virus and cause DNA chain termination leading to blocked viral replication and decreased viral load. Anti-hepatitis agents are.
Mode of action of fluoroquinolones. Serumbactericidal activity of rifampin in combination with other antimicrobial agents against Staphylococcus aureus. Bayston R Ashraf W Bhundia C.
Mode of action of an antimicrobial biomaterial for use in hydrocephalus shunts. Pressure mmH 2 0 Average Pressure settings Settings Flow rate mlhr 250 200 150 100 50 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 215 180 145 110 80 50 25 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 Codman Shurtleff Inc. 325 Paramount Drive Raynham MA 02767 For Customer Service.
Injectable drugs have more rapid onset of action Chronic conditions malnutrition of patients leads to poor oral absorption of drugs. Providers Misunderstanding between patients and prescribers leading to injection overuse 80-95 of patients do not prefer injections O v e r-p re sc r i p t i o n D e m a n d Patients perception that providers prefer injections 5-20 of patients. Observations on mode of action of erythromycin.
Comparison of clindamycin rifampin tetracycline metronidazole and penicillin for efficacy in prevention of experimental gas gangrene due to Clostridium perfringens J Infect Dis 1987 vol. Pharmacodynamics of antibacterial agents as a basis for determining dosage. Which of the following choices correctly matches the class of antibiotic and its mode of action.
Select all that apply. Aminoglycosides and tetracyclines are inhibitors of protein synthesis. Penicillins and cephalosporins inhibit nucleic acid synthesis.
Sulfonamides inhibit the synthesis of essential metabolites. Lipopeptides inhibit cell wall synthesis. Aminoglycosides and tetracyclines are.
The Rifampin class drugs are often utilized because Doxycycline really should not be used in second round treatment because the Borrelia get so resistant to it. Unfortunately there is a small minority of patients but that may be 20 of patients that have untoward reactions to the Rifampin class. And it is really difficult to tell Herxing from drug reaction in these folks.
Rifampin rifamycin rifampicin. Mode of Action of the Tetracyclines and the Nature of Bacterial Resistance to Them. In an introductory chapter to a symposium on.
Clotrimazole acts primarily by damaging the permeability barrier in the cell membrane of fungi. Clotrimazole causes inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis an essential constituent of fungal cell membranes. If ergosterol synthesis is either completely or partially inhibited the cell is no longer able to construct an intact and functional cell membrane 12 13.
Rifapentine has similar activity to rifampin but persists in the blood at therapeutic levels for longer 72. Mode of Action of Clofazimine and Combination Therapy with Benzothiazinones against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59 2015 pp.
View Record in Scopus Google Scholar. The history of tuberculosis. Respir Med 100 2006 pp.