
This does not imply that the practitioner has no opinion. 2 The blood delivers nutrients and other materials to all parts of the body.
Alcohol intake was reduced from 16469 to 13265 drinks per week 195 reduction.
Reduction of secondary alcohol. The formation of a secondary alcohol via reduction and hydration is shown. With aqueous pK a values of around 1619 they are in general slightly weaker acids than water. With strong bases such as sodium hydride or sodium they form salts called alkoxides with the general formula RO M.
2 R-OH 2 NaH 2 R-O Na 2 H 2 2 R-OH 2 Na 2 R-O Na. 1328 Measure total cholesterol HDL cholesterol and nonHDL cholesterol in all people who have been started on high-intensity statin treatment both primary and secondary prevention including atorvastatin 20 mg for primary prevention at 3 months of treatment and aim for a greater than 40 reduction in nonHDL cholesterol. If a greater than 40 reduction in nonHDL cholesterol is not.
The practitioners goals are secondary to what the client wants. This does not imply that the practitioner has no opinion. Rather the practitioner respects the clients decisions both for and against change.
The harm reduction practitioner frequently uses nonjudgmental but directive techniques including motivational interviewing MI. Miller Rollnick 2002 to allow the client to. Skip to secondary navigation.
Alcohol parks and public health. CISUR researchers develop an evidence-based public-health guide for municipalities considering allowing alcohol consumption on public properties like parks beaches and plazas. BC legal cannabis market growing briskly.
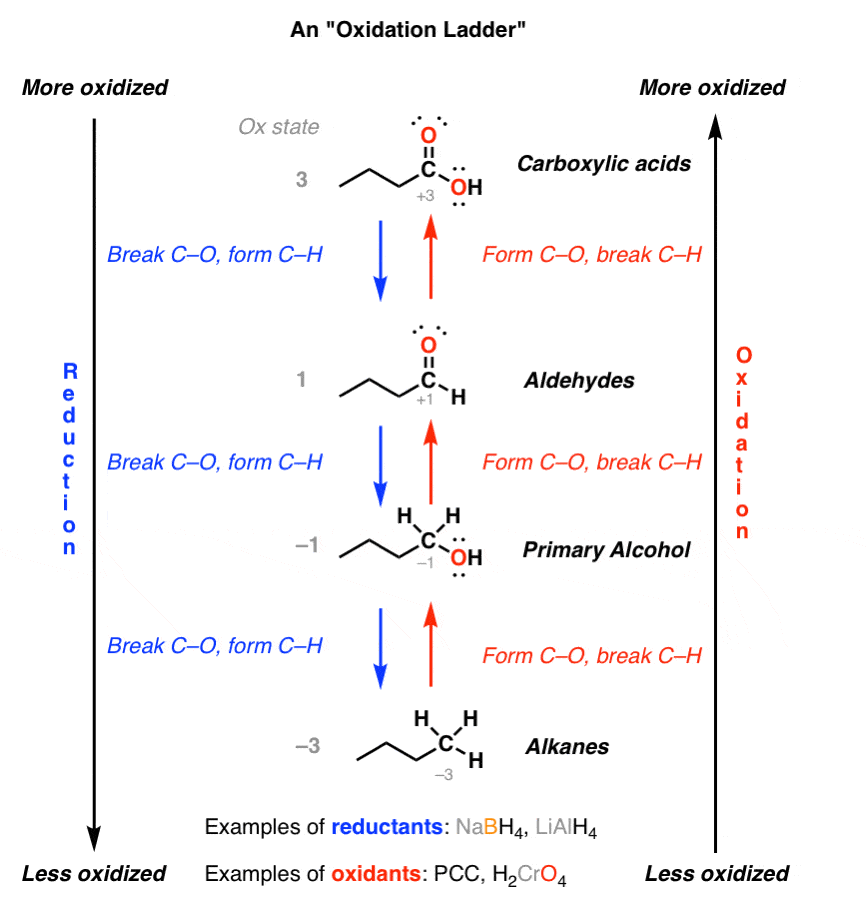
Regulated cannabis market in BC doubled between 2019 and 2020. Products getting cheaper. Reduction of aldehydes and ketones lead to two different sorts of alcohol.
The reduction of an aldehyde. For example with ethanal you get ethanol. Notice that this is a simplified equation - perfectly acceptable to examiners.
The H in square brackets means hydrogen from a reducing agent. In general terms reduction of an aldehyde leads to a primary alcohol. A primary alcohol is one which.
Aldehyde and Ketone reduction by LiAlH 4 to Alcohols. LiAlH 4 is a strong reduction reagent used in organic chemistry. LiAlH 4 can reduce aldehyde and ketone to alcohols.
When aldehyde is reduced by LiAlH 4 primary alcohol is given as the productBut reduction of ketone will give a secondary alcohol. The reduction of a ketone. Again the product is the same whichever of the two reducing agents you use.
For example with propanone you get propan-2-ol. Reduction of a ketone leads to a secondary alcohol. Using lithium tetrahydridoaluminate lithium aluminium hydride Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate is much more reactive than sodium tetrahydridoborate.
It reacts violently with. Alcohol is eliminated from the body by various metabolic mechanisms. The primary enzymes involved are aldehyde dehydrogenase ALDH alcohol dehydrogenase ADH cytochrome P450 CYP2E1 and catalase.
Variations in the genes for these enzymes have been found to influence alcohol consumption alcohol-related tissue damage and alcohol dependence. The consequences of alcohol metabolism. A meta-analysis of controlled trials for the primary prevention of alcohol withdrawal seizures demonstrated a highly significant risk reduction for seizures with benzodiazepines and antiepileptic drugs and an increased risk with antipsychotics.
A meta-analysis of randomised placebo-controlled trials for the secondary prevention of seizures after alcohol withdrawal showed lorazepam to be. Reduction and those that are more associated with a war on drugs than is often acknowledged. Globally drug prohibition is universal but with differences in the way that it is implemented see section 34 Depenalisation.
Similarly primary prevention efforts to discourage the use of drugs by young people have remained a feature of the drug policy of countries that have been most. Alcohol any of a class of organic compounds with one or more hydroxyl groups attached to a carbon atom of an alkyl group. Alcohols may be considered as organic derivatives of water H2O in which a hydrogen atom has been replaced by an alkyl group.
Harm Reduction is an evidence-based client-centred approach that seeks to reduce the health and social harms associated with addiction and substance use without necessarily requiring people who use substances from abstaining or stopping. I Included in the harm reduction approach to substance use is a series of programs services and practices. Essential to a harm reduction approach is that.
Several systematic reviews have linked higher alcohol taxes and prices with reduction in alcohol misuse. Carlin J Glover S Bowes G Patton G. Social and school connectedness in early secondary school as predictors of late teenage substance use mental health and academic outcomes.
Journal of Adolescent Health. Wagenaar AC Salois MJ Komro. Notice that LiALH 4 and NaBH 4 reduce aldehydes and ketones to primary and secondary alcohols respectively.
Esters on the other hand are converted to primary alcohols by LiALH 4. LiAlH 4 Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones The Mechanism. As mentioned earlier both reagents function as a source of hydride H which acts as a nucleophile attacking the carbon of the carbonyl CO bond.
Alcohol is a huge contributor to accidents deaths and injuries on the roads each year. Driving requires concentration good coordination and reflexes and the ability to make accurate judgements and decisions. Alcohol reduces all of these abilities.
The risk of serious injury and death from drink driving is greater in regional and rural areas so people who live in those communities should be. An amyl alcohol is any of eight alcohols with the formula C 5 H 12 O. A mixture of amyl alcohols also called amyl alcohol can be obtained from fusel alcoholAmyl alcohol is used as a solvent and in esterification by which is produced amyl acetate and other important products.
The name amyl alcohol without further specification applies to the normal straight-chain form 1-pentanol. Identify and address all modifiable risk factors - smoking diet obesity alcohol intake physical activity blood pressure and HbA1c. Measure full lipid profile again after 3 months non-fasting.
High intensity statin treatment should achieve reduction of non-HDL-C. Alcohol and other drug education programs aim to inform people about the risks of alcohol and other drug use and give them practical skills to make decisions that minimise harm. Depending on its aim a program may seek to delay or reduce the use of alcohol and.
1217 years such as the Australian Secondary Students Alcohol and Drug survey 1029 years such as the Alcohol and Other Drug Treatment Services National Minimum Data Set. The National Drug Strategy Household Survey NDSHS collects data on younger people between 1424 with most data presented in this report relating to young adults aged between 1824. Some data sources can be.
There is a strong scientific evidence that drinking alcohol increases the risk for cancer including cancers of the mouth and throat liver breast in women and colon and rectum and for some types of cancer the risk increases even at low levels of alcohol consumption less than 1 drink in a dayThe evidence indicates that the more alcohol a person drinks the higher his or her risk of. A small reduction in alcohol intake was observed in the control group. Alcohol intake was reduced from 16469 to 13265 drinks per week 195 reduction.
95 CI 19 to. Alcohol consumption increases an individuals risk of cardiovascular disease. How alcohol can damage the cardiovascular system.
The heart and blood vessels form part of the cardiovascular system. 1 Blood is pumped around the body by the heart via these blood vessels through arteries capillaries and veins. 2 The blood delivers nutrients and other materials to all parts of the body.
Alcohol - alcohol - Reactions of alcohols. Because alcohols are easily synthesized and easily transformed into other compounds they serve as important intermediates in organic synthesis. A multistep synthesis may use Grignard-like reactions to form an alcohol with the desired carbon structure followed by reactions to convert the hydroxyl group of the alcohol to the desired functionality.
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome. The primary efficacy outcome was the difference in ICU length of stay LOS between the 2 protocols. Secondary outcomes measured included hospital LOS use of invasive mechanical ventilation and use of adjunctive and sedating agents to control AWS symptoms.
The primary and secondary efficacy end points of ICU and hospital LOS were measured in days.