
The open hole is called the patent ductus arteriosus. 5 Pharmacological closure Although pharmacological closure of the DA is.
The DA constricts at birth but there is often a small shunt of blood from the aorta to the left pulmonary artery for a few days in a healthy full-term infant.
Premature closure of the ductus arteriosus. The ductus arteriosus also called the ductus Botalli named after the Italian physiologist Leonardo Botallo is a blood vessel in the developing fetus connecting the trunk of the pulmonary artery to the proximal descending aortaIt allows most of the blood from the right ventricle to bypass the fetuss fluid-filled non-functioning lungsUpon closure at birth it becomes the ligamentum arteriosum. Patent ductus arteriosus accounts for 5 to 10 of congenital heart anomalies. The malefemale ratio is 13.
PDA is very common among premature infants present in about 45 with birth weight 1750 g and in 70 to 80 with birth weight 1200 g. About one third of PDAs will close spontaneously even in extremely low birth weight infants. Patent ductus arteriosus PDA is a medical condition in which the ductus arteriosus fails to close after birth.
This allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs by flowing from the aorta which has a higher pressure to the pulmonary arterySymptoms are uncommon at birth and shortly thereafter but later in the first year of life there is often the onset. The increased arterial oxygen tension and decrease in blood flow through the ductus arteriosus causes the ductus to constrict and functionally close by 12 to 24 hours of age in healthy full-term newborns with permanent anatomic closure occurring within 2 to 3 weeks. In premature infants the ductus arteriosus does not close rapidly and may require pharmacologic or surgical closure to.
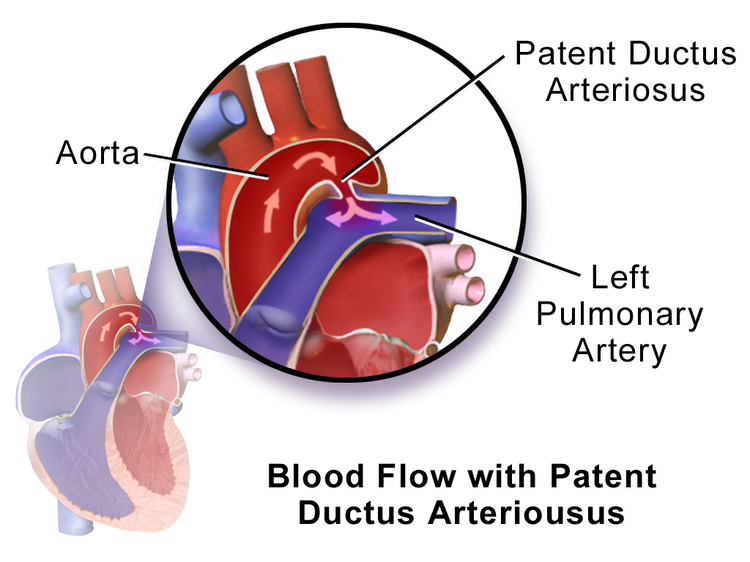
The ductus arteriosus streamlines fetal circulation by flowing blood directly to the aorta bypassing the lungs. After birth the ductus arteriosus usually seals off so that blood from these two vessels does not mix. In patients with PDA the ductus arteriosus stays open patent and blood can flow from the aorta into the pulmonary artery.
Rapid closure of the ductus arteriosus after birth is essential for vascular transition to the mature divided pattern of arteriovenous circulation. Failure of ductus arteriosus closure termed patent ductus arteriosus PDA is primarily an affliction of prematurity with the ductus remaining open at 7 days of age in up to 64 of infants born at 27 to 28 weeks gestation and 87 of infants. Failure of the ductus to close in the early weeks of life as normally occurs results in a Patent or Persistent Ductus Arteriosus PDA.
This allows blood to flow between the aorta and the pulmonary artery leading to an increase in flow in the lung circulation. If the PDA is large the pressure in the lungs may also be elevated. Affected babies may develop heart failure in the early.
The ductus arteriosus is a hole that allows the blood to skip the circulation to the lungs. However when the baby is born the blood must receive oxygen in the lungs and this hole is supposed to close. If the ductus arteriosus is still open or patent the blood may skip this necessary step of circulation.
The open hole is called the patent ductus arteriosus. The ductus arteriosus is a blood vessel that connects the pulmonary artery main vessel supplying the blood to the lungs to the aorta main vessel supplying the blood to the body. This connection is present in all babies in the womb but should close shortly after birth.
In some babies especially in those born prematurely this vessel may remain open. This is called a patent or persistent. A dilator of the ductus arteriosus and delays ductal closure.
The risk of PDA is greater with furosemide compared with chlorothiazide. Furosemide is associated with nephro- and ototoxicity. - Use chlorothiazide and not furosemide for management of PDA-associated left heart volume overload and pulmonary oedema.
5 Pharmacological closure Although pharmacological closure of the DA is. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs use in pregnant women at 30 weeks gestation and later may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. NSAID use at 20 weeks gestation or later may cause fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and in some cases neonatal renal impairment.
Patent ductus arteriosus PDA is a heart defect found in the days or weeks after birth. The ductus arteriosus is a normal part of fetal blood circulation before a baby is born. Its an extra blood vessel that connects 2 arteries.
The pulmonary artery and the aorta. The pulmonary artery carries blood from the heart to the lungs. The aorta carries blood from the heart to the body.
Patent ductus arteriosus symptoms vary with the size of the defect and whether the baby is full term or premature. A small PDA might cause no signs or symptoms and go undetected for some time even until adulthood. A large PDA can cause signs of heart failure soon after birth.
Your babys doctor might first suspect a heart defect during a regular checkup after hearing a. Patent ductus arteriosus PDA is a heart defect found in the days or weeks after birth. The ductus arteriosus is a normal part of fetal blood circulation.
All babies are born with this opening between the aorta and the pulmonary artery. But it usually closes on its own shortly after birth. If it stays open it is called patent ductus arteriosus.
Treatments for a patent ductus arteriosus depend on the age of the person being treated. In a premature baby a PDA often closes on its own. The doctor will monitor your babys heart to make sure the open blood vessel is closing properly.
Premature constriction or closure may lead to right heart failure resulting in fetal hydrops. Histology and Mechanisms of Normal Closure. Grossly the constitution of the fetal ductus arteriosus appears to be similar to the contiguous main pulmonary artery and descending aorta.
There are important histological differences however. 49 Whereas the mediae of surrounding aorta and. The DA constricts at birth but there is often a small shunt of blood from the aorta to the left pulmonary artery for a few days in a healthy full-term infant.
In premature infants and in those with persistent hypoxia the DA may remain open for much longer. Your childs doctor may prescribe medicines to help close patent ductus arteriosus in premature infants. Indomethacin or ibuprofen triggers the patent ductus arteriosus to constrict or tighten which closes the opening.
Acetaminophen is sometimes used to close patent ductus arteriosus. Procedures - Congenital Heart Defects. Cardiac catheterization is a common procedure that is sometimes used.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs NSAIDs use in pregnant women at 30 weeks gestation and later may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. NSAID use at 20 weeks gestation or later may cause fetal renal dysfunction leading to oligohydramnios and in some cases neonatal renal impairment. Failure of closure of the ductus arteriosus leads to hemodynamic changes similar to those seen in VSD.
The direction and extent of the shunt in the PDA depends on the size of the PDA and the relative systemic and pulmonary vascular resistances. PDA is more common in females premature infants patients with Down Syndrome and congenital rubella syndrome. The child was diagnosed with Patent Ductus Arteriosus or PDA a common condition detected in premature babies.
Doctors performed a minimally invasive treatment procedure using a. Show All 145Most Common 2Technology 23Government Military 40Science Medicine 40Business 24Organizations 42Slang Jargon 11 Acronym Definition PDA Personal Digital Assistant electronic handheld information device PDA Public Display of Affection PDA Personal Data Assistant PDA Progressive Democrats of America PDA. The mission of The Annals of Thoracic Surgery is to promote scholarship in cardiothoracic surgery patient care clinical practice research education and policy.
As the official journal of two of the largest American associations in its specialty this leading monthly enjoys outstanding editorial leadership and maintains rigorous selection standards. Risk of Myocardial Infarction and Death After Noncardiac Surgery Performed Within the First Year After Coronary Drug-Eluting Stent Implantation for Acute Coronary Syndrome or Stable Angina Pectoris. The Journal of Pediatrics is an international peer-reviewed journal that advances pediatric research and serves as a practical guide for pediatricians who manage health and diagnose and treat disorders in infants children and adolescentsThe Journal publishes original work based on standards of excellence and expert review.
The Journal seeks to publish high quality original articles that are.