9-180 ngmL 9-180 µgL Fibrinogen plasma. 60-75 of total body potassium is found within muscle cells with the remainder in bone.
Adhesions form as a natural part of the bodys healing process after surgery in a similar way that a scar forms.
Potassium chloride 60 mmol. Another meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials found that potassium supplements mostly containing potassium chloride at 6065 mEqday potassium 23462541 mg for 424 weeks in 917 patients with normal blood pressure or hypertension who were not taking antihypertensive medications significantly reduced both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The supplements had the. Potassium Chloride is a metal halide composed of potassium and chloride.
Potassium maintains intracellular tonicity is required for nerve conduction cardiac skeletal and smooth muscle contraction production of energy the synthesis of nucleic acids maintenance of blood pressure and normal renal function. This agent has potential antihypertensive effects and when taken as a nutritional. Manufacturer advises reconstitute 1 sachet with 200mL of water freshly boiled and cooled for infants.
5 sachets reconstituted with 1 litre of water provide Na 60 mmol K 20 mmol Cl 60 mmol citrate 10 mmol and glucose 90 mmol. Manufacturer advises reconstitute 1 sachet with 200 mL of water freshly boiled and cooled for infants. 5 sachets when reconstituted with 1 litre of water provide Na.
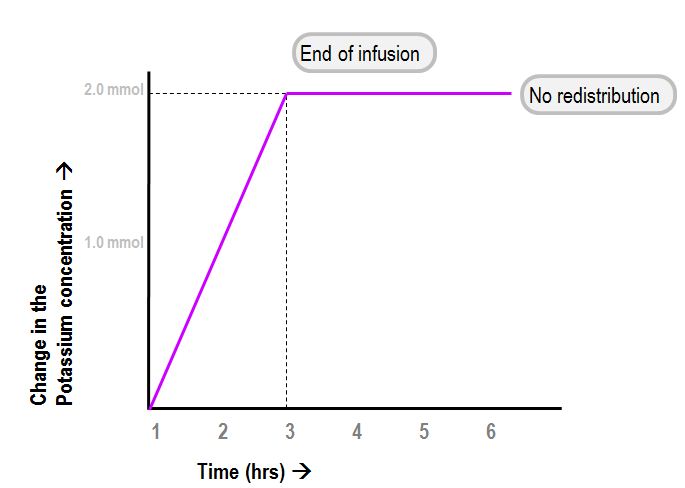
2 The ISPAD definition for DKA with acidosis and a bicarbonate of mmoll or a pH 30 mmol per litre has been adopted. The previous BSPED guideline recommended a bicarbonate of mmoll. 3 This guideline uses pH to categorise the.
Potassium is a chemical element with the symbol K from Neo-Latin kalium and atomic number 19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure.
It was first isolated from potash the ashes of plants from which its name derives. Providing 60 to 80 mmolday in divided doses over days to weeks is usually sufficient. Oral supplementation can irritate GI mucosa leading to bleeding andor ulceration but is associated with a lower risk of rebound hyperkalemia.
It should be taken with plenty of fluids and food. Potassium chloride is the preferred formulation for replacement therapy in most cases. Increasing dietary potassium.
The addition of 18 mmolL of sodium chloride to flavored water triggered an increase of 31 percent in ad libitum drinking of children who exercised in the heat compared with flavored water alone Wilk and Bar-Or 1996. Similar responses have been described for animals Okuno et al 1988 and adult humans Nose et al 1988. 1 mmol potassium 39 mg potassium.
Recommendations by life stage and gender Infants. 400 mgday 10 mmol 7-12 months. 700 mgday 18 mmol Rationale.
The AI for 0-6 months was calculated by multiplying the average intake of breast milk 078 Lday by the average concentration of potassium 500 mgL and rounding. For 7-12 months an average breast milk volume of 06 L. Potassium disorders are common.
Hypokalemia serum potassium level less than 36 mEq per L 36 mmol per L occurs in up to 21 of hospitalized patients and 2 to 3 of outpatients1 3. Potassium intakes have decreased from 150 to 290 mmold to 30 to 70 mmold 600011600 to 12002800 mgd whereas sodium increased from 20 to 40 mmold to 80 to 250 mmold leading to a shift in the dietary potassiumsodium ratio of 3 to. Current recommendations for potassium 4700 mg1175 mmol and sodium 2300 mg100 mmol or 1500 mg65 mmol intakes.
Hypokalemia defined as a serum potassium level of less than 35 mmolL is one of the most common electrolyte abnormalities encountered in clinical practice with more than 20 of hospitalized patients affected and approximately 40 of ICU patients. Hypokalemia reflects either total body potassium depletion or redistribution from extracellular fluid to intracellular fluid without potassium. 400 mmollitre Other components.
Ca 2 23 mmol phosphate 15 mmol anhydrous glucose 100 g. 700 mmollitre Other components. Acid phosphate 30 mmol.
Net price 500 ml. No price available. Only for use in adults.
Synthamin 17 EF electrolyte-free Baxter Healthcare. Most studies used supplemental potassium doses between 2340 and 2535 mgday 60-65 mmolL. Increased potassium intake resulted in overall reductions of systolic blood pressure by 47 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure by 35 mm Hg.
The blood pressure-lowering effect of supplemental potassium was more pronounced when the analysis was restricted to individuals with hypertension. The dose and administration IV infusion rate for potassium phosphates are dependent upon individual needs of the patient. Phosphorous serum level.
05 mmolkg IV infused over 4-6 hr. Phosphorous serum level 05-1 mgdL. 025 mmolkg IV infused over 4-6 hr.
Moderate hypokalemia serum potassium levels of 25 to 3 mEqL 25 - 30 mmolL may cause muscle weakness tiredness myalgia tremor muscle cramps and constipation. Severe deficits leading to serum potassium levels below 25 mEqL may be life-threatening and lead to electrocardiographic ECG changes such as QRS prolongation ST-segment and T-wave depression and U-wave formation. Hypokalemia is generally defined as a serum potassium level of less than 35 mEqL 35 mmolL.
Moderate hypokalemia is a serum level of 25-30 mEqL and severe hypokalemia is a level of less than 25 mEqL. Hypokalemia is a potentially life-threatening imbalance that may be iatrogenically induced. Hypokalemia may result from inadequate potassium intake increased potassium excretion.
The University of Georgia Agricultural and Environmental Services Laboratories offer soil salinity testing to help farmers and the general public diagnose and manage problems associated with soil salinity. By definition a saline soil contains excess soluble salts that reduce the growth of most crops or ornamental plants. This publication discusses soil salinity testing data interpretation.
09 sodium chloride with glucose and potassium chloride maximum 60 mmolL as required should generally be used for the duration of IV rehydration If a hypotonic solution is later thought to be required discuss this with the paediatric endocrinologist on call. The sodium chloride content should be at least 045 or greater. If measured sodium does not rise as the glucose falls during.
Potassium is the major intracellular cation intracellular K concentration is approximately 140 mEqL and is important for maintaining resting membrane potential of cells particularly muscle and nerves. 60-75 of total body potassium is found within muscle cells with the remainder in bone. Only 5 of potassium is located in extracellular fluid ECF therefore potassium concentration in.
Adhesions form as a natural part of the bodys healing process after surgery in a similar way that a scar forms. The term adhesion is applied when the scar extends from within one tissue across to another usually across a virtual space such as the peritoneal cavityAdhesion formation post-surgery typically occurs when two injured surfaces are close to one another. You want the body to maintain a specific amount of potassium in the blood stream anywhere from 36 - 52 mmolL source.
HealthlineThis obviously isnt going to be possible if you arent getting enough in your diet but if you are eating too much then your body will filter out the excess–or should filter out the excess. Hypokalemia is diagnosed when blood-potassium levels are below 36. 02 mmolL 40 mmolL.
5 40 mmolL. 3 gL 60 gL. 5 60 gL.
3 mmolL 150 mmolL. 2 150 mmolL. 02 mmolL 16 mmolL.
12 16 mmolL. 003 mmolL 038 mmolL. 8 038 mmolL.
05 mmolL 40 mmolL. 12 40 mmolL. Analytical Quality Requirements are a.
136-146 mEqL 136-146 mmolL Chloride. 35-45 mEqL 35-45 mmolL Bicarbonate. 22-29 mEqL 23-29 mmolL Ferritin serum.
27-270 ngmL 27-270 µgL Female. 9-180 ngmL 9-180 µgL Fibrinogen plasma. 200-400 mgdL 59-117 µmolL Follicle-stimulating hormone plasma.
4-25 mIUmL 4-25 IUL Female. 4-30 mIUmL 4-30 IUL. Dosages of potassium mostly in the form of potassium chloride ranged from 60 mmold to greater than 100 mmold.
The results demonstrated that potassium supplementation was associated with a significant reduction in mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure 44 mm Hg and 24 mm Hg respectively.