
Research chemicals are chemical substances used by scientists for medical and scientific research purposes. Fluorine also combines with hydrogen to make hydrogen fluoride a.
A Halogen is a Greek word which means salt-former.
Physical and chemical properties of fluorine. Chemistry End of Chapter Exercises. Classify the six underlined properties in the following paragraph as chemical or physical. Fluorine is a pale yellow gas that reacts with most substancesThe free element melts at 220 C and boils at 188 CFinely divided metals burn in fluorine with a bright flameNineteen grams of fluorine will react with 10 gram of hydrogen.
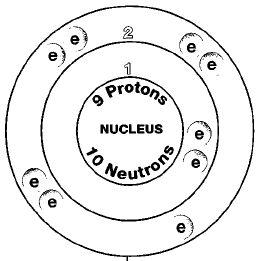
Properties such as the high electronegativity and small size of fluorine lead to a strong C-F bond the strongest covalent bond in organic chemistry The low polarizability of fluorine further leads to weak intermolecular interactions such as Van der Waals interactions and hydrogen bonding These unique properties of fluorine give many PFAS their mutually hydro- and lipophobic stain. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons and 9 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Fluorine is F.
Fluorine is the lightest halogen and exists as a highly toxic pale yellow diatomic gas at standard conditions. As the most electronegative element it is extremely reactive. Classify the six underlined properties in the following paragraph as chemical or physical.
Fluorine is a pale yellow gas that reacts with most substances. The free element melts at 220 C and boils at 188 C. Physical and Chemical Properties of Group 17 Elements Group 17 Elements.
The Halogens The elements in Group 17 are. Fluorine Chlorine Bromine Iodine Astatine These elements are known as halogens. A Halogen is a Greek word which means salt-former.
B This is because halogens are reactive non-metals. They exist naturally in various mineral salts in. Chemical properties of fluorine - Health effects of fluorine - Environmental effects of fluorine.
Electronegativity according to Pauling. 1810-3 gcm-3 at 20C. 0136 nm -1.
Electronic shell He 2s 2 2p 5. Chemical properties of elements and compounds. Atomic number - Atomic mass - Electronegativity according to Pauling - Density - Melting point - Boiling point - Vanderwaals radius - Ionic radius - Isotopes - Electronic schell - Energy of first ionisation - Energy of second ionisation - Standard potential.
Atomic number The atomic number indicates the number of protons within the core of an atom. Chlorine - chlorine - Physical and chemical properties. Chlorine is a greenish yellow gas at room temperature and atmospheric pressure.
It is two and a half times heavier than air. It becomes a liquid at 34 C 29 F. It has a choking smell and inhalation causes suffocation constriction of the chest tightness in the throat andafter severe exposureedema filling with fluid.
Physical and chemical properties. At room temperature fluorine is a faintly yellow gas with an irritating odour. Inhalation of the gas is dangerous.
Upon cooling fluorine becomes a yellow liquid. There is only one stable isotope of the element fluorine-19. Sodium is a chemical element that has been used by humans since the ancient times.
It is the most important metal from a commercial point of view as it is utilized by both organic and inorganic industries. Properties of sodium make it a unique element and here we give you more information about the chemical and physical properties of sodium. Physical Chemical Properties of Tungsten.
Tungsten is one of the important strategic resources. Due to its excellent physical and chemical properties tungsten and its alloys are used to manufacture key armor-piercing components that attack various types of armored targets gyro inertial components for satellites and high-temperature anti-ablation components such as rockets combustion. The halogens show trends in their physical.
The table shows the colour and physical states. Of chlorine bromine and iodine at room temperature and. Changing the state of a pure substance between solid liquid or gas phase is a physical changes since the identity of the matter does not change.
A physical change involves changes in physical properties but not chemical properties. For example physical properties change during tempering steel crystallization and melting. Here are examples.
Physical Properties of Helium. Helium He Physical Properties. 095 K or -2722 o C Boiling Point.
4222 K or -268928 o C Density. 01786 gL at STP. 0145 gcm-3 at its melting point.
Critical Temperature and Pressure. Appearance at STP Colourless gas. Chemical Properties of Helium.
Helium He Chemical Properties. Manganese a chemical element that has a symbol Mn and atomic number 25. This element is not found as a free element in nature but available in combination with iron and other minerals.
It is a metal that has important metal alloy uses and particularly in stainless steel. Chemical Properties Of Manganese. Mixing of ammonia with several chemicals can cause severe fire hazards andor explosions.
Ammonia in container may explode in heat of fire. Incompatible with many materials including silver and gold salts halogens alkali metals nitrogen trichloride potassium chlorate chromyl chloride oxygen halides acid vapors azides ethylene oxide picric acid and many other chemicals. Physical Properties of Hydrogen.
Hydrogen is the smallest chemical element because it consists of only one proton in its nucleus. Its symbol is H and its atomic number is 1. It has an average atomic weight of 10079 amu making it the lightest element.
Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe especially in stars and gas giant planets. However monoatomic hydrogen is. Research chemicals are chemical substances used by scientists for medical and scientific research purposes.
One characteristic of a research chemical is that it is for laboratory research use only. A research chemical is not intended for human or veterinary use. This distinction is required on the labels of research chemicals and is what exempts them from regulation under parts 100-740 in.
The halogens are five non-metallic elements found in group 17 of the periodic table. The term halogen means salt-former and compounds containing halogens are called salts. As an example when boron reacts with fluorine it reacts like metal yet when boron reacts with sodium it reacts like a nonmetal.
The densities boiling points and melting points of the metalloids vary widely. Because metalloids have an intermediate conductivity they typically make good semiconductors. Common Properties Of Metalloids.
In general metalloids share the following. Temperature dependence of physical-chemical properties of selected chemicals of environmental interest. Chlorobenzenes polychlorinated biphenyls polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans.
Fluorides hydrogen fluoride and fluorine are chemically related. Fluorine is a naturally-occurring pale yellow-green gas with a sharp odor. It combines with metals to make fluorides such as sodium fluoride and calcium fluoride both white solids.
Sodium fluoride dissolves easily in water but calcium fluoride does not. Fluorine also combines with hydrogen to make hydrogen fluoride a. Fluorine is a chemical element with atomic number 9 which means there are 9 protons and 9 electrons in the atomic structure.
Caesium has physical and chemical properties similar to those of rubidium and potassium. Alkaline earth metals. Barium is a chemical element with atomic number 56 which.
Dichlorodifluoromethane CCl2F2 CID 6391 - structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature biological activities. Minerals are materials that meet five requirements. 1 naturally occurring 2 inorganic 3 solids 4 with a definite chemical composition and 5 an ordered internal structure.