Pharmacokinetics PK describes the mathematical relationship between the dose of the drug administered and its measured concentration at an easily accessible site of the body. Although the molecular significance of levetiracetam binding to synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is not understood levetiracetam and.
Thus a constant amount of drug is metabolized capacity-limited metabolism and.
Phenytoin saturable protein binding. Phenytoin Dose-Dependent Adverse Effects aka indications of phenytoin toxicity Nauseavomiting early Nystagmus. CNS depression including coma and possible respiratory failure Pod 2. Phenytoin Protein Binding and Volume of Distribution Vd One of the reasons phenytoin is so difficult to predict is because it is highly protein.
Phenytoin is highly protein bound. In the setting of hypoalbuminemia either a corrected phenytoin level should be estimated or a free phenytoin level should be checked. Formulas for adjusting the measured phenytoin level for hypoalbuminemia are population-based and may not be accurate in any given patient.
A large number of conditions including burns sepsis uremia liver disease and many. Mycophenolate decreased phenytoin protein binding from 90 to 87 in vitro. The clinical significance of this interaction is unknown.
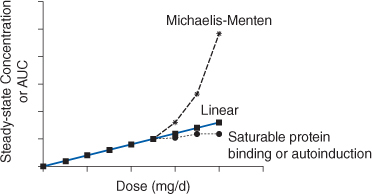
Phenytoin will decrease the level or effect of nimodipine by affecting hepaticintestinal enzyme CYP3A4 metabolism. Phenytoin will decrease the level or effect of nitrendipine by affecting hepatic. Because phenytoin exhibits saturable zero-order or dose-dependent pharmacokinetics the apparent half-life of phenytoin changes with dose and serum concentrations.
This is due to the saturation of the enzyme system responsible for metabolizing phenytoin which occurs at therapeutic concentrations of the drug. Thus a constant amount of drug is metabolized capacity-limited metabolism and. Phenytoin is highly protein bound and extensively metabolised by the liver.
Reduced dosage to prevent accumulation and toxicity may therefore be required in patients with impaired liver function. Where protein binding is reduced as in uraemia unbound phenytoin serum levels will be increased. Due to an increased fraction of unbound phenytoin in patients with renal or hepatic disease or in.
Some examples of drugs which exhibit non-linear kinetic behaviour are phenytoin ethanol salicylate and in some individuals theophylline. What are the practical consequences of saturable protein binding. From equation 3 it can be seen that as f u increases total drug concentration at steady state decreases.
However f u does not affect the steady state concentration of the unbound. As phenytoin is highly protein bound free phenytoin levels may be altered in patients whose protein binding characteristics differ from normal. Most of the drug is excreted in the bile as inactive metabolites which are then reabsorbed from the intestinal tract and excreted in the urine.
Urinary excretion of phenytoin and its metabolites occurs partly with glomerular filtration but more. Because phenytoin is highly protein bound and extensively metabolised by the liver reduced maintenance dosage may be required in patients with impaired liver function to prevent accumulation and toxicity. Where protein binding is reduced as in uraemia total serum phenytoin levels will be reduced accordingly.
However as the pharmacologically active free drug concentration is. Because of potential changes in protein binding during pregnancy the monitoring of phenytoin serum levels should be based on the unbound fraction. Dosage Forms and Strengths.
Dilantin extended phenytoin sodium capsules are available as. Size 4 hemispherical Coni-Snap capsule with a white opaque body and pale pink opaque cap containing a white powder. Protein binding of valproate is reduced in the elderly in patients with chronic hepatic diseases in patients with renal impairment and in the presence of other drugs eg aspirin.
Conversely valproate may displace certain protein-bound drugs eg phenytoin carbamazepine warfarin and tolbutamide. Phenytoin is a barbiturate-like compound that controls seizure activity by decreasing the recovery rate of voltage-activated sodium channels. It is highly protein bound and only the free portion is active.
Phenytoin is metabolized by the liver and has saturable pharmacokinetics. 30 Other medications that can affect protein binding can have significant effects on free phenytoin activity. Overall binding affinity lower Increased free fraction of drug increased availability of active compound Increased adverse effects increased drug clearance Free fatty acids and unconjugated bilirubin displace drugs from protein binding sites Ampicillin sulfonamides phenytoin diazepam.
Pharmacokinetics PK describes the mathematical relationship between the dose of the drug administered and its measured concentration at an easily accessible site of the body. PK in particular is a study of what the body does to a drug deals with the processes of absorption distribution metabolism and elimination acronym ADME. Within the PK the steady-state is a concept of.
Protein binding of valproate is reduced in the elderly in patients with chronic hepatic diseases in patients with renal impairment and in the presence of other drugs eg aspirin. Conversely valproate may displace certain protein-bound drugs eg phenytoin carbamazepine warfarin and tolbutamide. See PRECAUTIONS - Drug Interactions for more detailed information on the.
Valproate displaces phenytoin from its plasma albumin binding sites and inhibits its hepatic metabolism. Co-administration of valproate 400 mg TID with phenytoin 250 mg in normal volunteers n 7 was associated with a 60 increase in the free fraction of phenytoin. Total plasma clearance and apparent volume of distribution of phenytoin increased 30 in the presence of.
The process of nephrotoxicity uptake by cells is saturable and the number of insults determines toxicity. It is imperative to minimize the number of insults and allow the tubular cells a relatively drug free period in which to regenerate cells. Amitriptyline plus nortriptyline 80-250 ngmL.
Valproate displaces phenytoin from its plasma albumin binding sites and inhibits its hepatic metabolism. Co-administration of valproate 400 mg TID with phenytoin 250 mg in normal volunteers n7 was associated with a 60 increase in the free fraction of phenytoin. Total plasma clearance and apparent volume of distribution of phenytoin increased 30 in the presence of.
As an example the anti-epileptic drug phenytoin is a highly lipophilic compound. A series of metabolic transformations in the liver convert phenytoin to several inactive water-soluble metabolites that can then be excreted in the urine. In addition excretion of a drug is dependent on intrinsic properties of the drug such as pH and size.
For example weakly acidic drugs display increased. In determining bioequivalence for example between two products such as a commercially available Brand product and a potential to-be-marketed Generic product pharmacokinetic studies are conducted whereby each of the preparations are administered in a cross-over study to volunteer subjects generally healthy individuals but occasionally in patients. Favipiravir is 54 plasma protein-bound.
9 Of this fraction 65 is bound to serum albumin and 65 is bound to ɑ1-acid glycoprotein. 18 Metabolism Favipiravir is extensively metabolized with metabolites excreted mainly in the urine. 10 The antiviral undergoes hydroxylation primarily by aldehyde oxidase and to a lesser extent by xanthine oxidase to the inactive metabolite T705M1.
The binding of the drugs to plasma proteinsegAlbumin results in retention of the drug into the vascular space the drug protein complex can serves as reservoir in the vascular space for sustained drug release to extra vascular tissue but only for those drugs that exhibited a high degree of binding. The main force of attraction are Wander-vals forces hydrogen binding electrostatic binding. A saturable and stereoselective neuronal binding site in rat brain tissue has been described for levetiracetam.
Experimental data indicate that this binding site is the synaptic vesicle protein SV2A thought to be involved in the regulation of vesicle exocytosis. Although the molecular significance of levetiracetam binding to synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is not understood levetiracetam and. 20 - 67 protein bound.
Route of elimination. They are concentrated by the liver in the bile and excreted in the urine and feces at high concentrations in a biologically active form. Improve decision support research outcomes.
With structured adverse effects data including. Low therapeutic index. Poorly defined clinical end point.
Drugs with saturable metabolism. Wide variation in the metabolism of drugs. For diagnosis of suspected toxicity determining drug abuse.
Indications for TDM 8. Drugs with steep dose response curve small increase in dose can result in a marked increase in. There are two drug-binding α 2 δ.
The LAT1 is easily saturable so the pharmacokinetics of gabapentin are dose-dependent with diminished bioavailability and delayed peak levels at higher doses. Conversely this is not the case for pregabalin which shows linear pharmacokinetics and no saturation of absorption. Similarly gabapentin enacarbil is transported not by the LAT1 but by the.