HCNaq Hydrocyanic acid. If the two concentrations are the same the equivalent pH value is neutral.
Chemistry is all about learning chemical elements and compounds and how these things work together to form several chemical equations that are hard to understand.
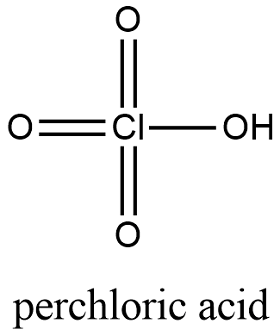
Perchloric acid in solution formula. Perchloric acid is a mineral acid with the formula H Cl O 4. Usually found as an aqueous solution this colorless compound is a stronger acid than sulfuric acid nitric acid and hydrochloric acid. It is a powerful oxidizer when hot but aqueous solutions up to approximately 70 by weight at room temperature are generally safe only showing strong acid features and no oxidizing properties.
PERCHLORIC ACID 50 BUT. May react vigorously or deflagrate when mixed with oxidizable material Merck. This includes but is not limited to alcohols amines boranes dicyanogen hydrazines hydrocarbons hydrogen nitroalkanes powdered metals silanes or thiols Bretherick 1979.
Perchloric acid ignites on contact with. PH of a strong acidbase solution. This online calculator calculates pH of the solution given solute formula and solution molarity.
The solute is assumed to be either strong acid or strong base. Articles that describe this calculator. PH of a solution calculator.
PH of a strong acidbase solution. Digits after the decimal point. The examples of strong acids are sulfuric acid H2SO4 perchloric acid HClO4 nitric acid HN3 hydrobromic acid HBr hydrochloric acid HCl hydroiodic acid HI and many more.
Differ from strong acid the weak acid will partially dissolve in the water solution. Write balanced molecular and net ionic equation for the following reaction and identify the gas formed. Solid magnesium carbonate reacts with an aqueous solution of perchloric acid.
HYDROCHLORIC ACID is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride an acidic gas. Reacts exothermically with organic bases amines amides and inorganic bases oxides and hydroxides of metals. Reacts exothermically with carbonates including limestone and building materials containing limestone and hydrogen carbonates to generate carbon dioxide.
Reacts with sulfides carbides borides and. Acid dissociation constant K a. Sometimes referred to as the acid-ionization constant or simply acid constant K a is the quantifiable strength of an acid in an aqueous solution.
While pH power of Hydrogen specifies the level of basicity the acidity of any solution acid dissociation constant tells us about the concentration of hydrogen ions H or hydronium ions H3O in a solution. When a weak acid reacts with a weak base the equivalence point solution is alkalinebase if the base is strong and acidic if the acid is strong. If the two concentrations are the same the equivalent pH value is neutral.
However weak acids cannot usually be titrated with weak bases because the color change is short-lived and therefore difficult to observe. Acid strength is the tendency of an acid symbolised by the chemical formula to dissociate into a proton and an anion The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete except in its most concentrated solutions. Examples of strong acids are hydrochloric acid perchloric acid nitric acid and sulfuric acid.
A weak acid is only partially dissociated with. Mass percentage and densities of common solution Substance Formula Mass percentage Density. Glacial acetic acid CH3COOH 995 1050 methanoic acid HCOOH 90 1200 hydrochloric acid HCl 10 1050 nitric acid HNO3 71 1420 nitric acid HNO3 61 1370 perchloric acid HClO3 60 1540 sulphuric acid H2SO4 96 1840 potassium hydroxide KOH 50 1520 sodium hydroxide NaOH 50 1530 ethanoic acid.
PH -log1H Where. Hydrogen ion concentration in the solution H concentration of acid is depended on its pKa for strong acid like HCl its pKa1 thus H concentration of 1 M HCl is also 1 M. For weak acid such as acetic acid its pKa00000175 thus H concentration of 1 M acetic acid is.
1 00000175 00000175 M. For more information or to place an order contact. The Nest Group Inc 17 Hayward St Ipswich MA 01938-2041 USA Tel.
1-508-485-5736 For your convenience we accept Mastercard VISA and American Express credit cards. HClO₄ perchloric acid HClO₃ chloric acid 2. The aqueous solution is one of the examples that include a base and its conjugate acid.
Neutral Base It is the one that forms a bond with a neutral acid. Super Base This type of base is formed by alkali metal with its conjugate acid and even better in comparison to a strong base. One of the examples of the super base is sodium.
Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. What volume of a 0248 M perchloric acid solution is required to neutralize 107 mL of a 0155 M calcium hydroxide solutio. Chemical formula plays an important role in understanding different concepts of chemistry.
Chemistry is all about learning chemical elements and compounds and how these things work together to form several chemical equations that are hard to understand. Sulfuric Acid H3BO3 Boric Acid H3PO2 Hypophosphorous Acid H3PO3 Phosphorous Acid PhosphoricIII Acid H3PO4 Phosphoric Acid HBr Hydrobromic Acid HCl Hydrogen Chloride HClO4 Perchloric Acid HCN Cyanic Acid HgNO32 MercuryII Nitrate HgCl2 MercuryII Chloride HgO MercuryII Oxide HgS MercuryII Sulfide HNO2 Nitrous Acid HNO3 Nitric Acid K2C2O4. HC 2 H 3 O 2.
H 2 Saq Hydrosulfuric acid. HCNaq Hydrocyanic acid. Important Bases All of the Group IA and IIA hydroxides Name of Base.
XP Vista 7 8 10 single user license price. 2495 - approximately 33 Buy Now. By clicking Buy Now.
You will continue to the FastSpring checkout page where payment will be taken and your order fulfilled by FastSpring our. Gram equivalent number of solute in 1L solution. Expressed as N for capacity analysis.
Concentration indirectly expressed by the volume ratio of diluting the liquid reagent. It is used in JIS and others. Sulfuric acid 1 2 Sulfuric acid is shown diluted with 2 volumes of water.
We are a leading supplier to the global Life Science industry with solutions and services for research biotechnology development and production and pharmaceutical drug therapy development and production. The strongest acid is perchloric acid on the left and the weakest is hypochlorous acid on the far right. Notice that the only difference between these acids is the number of oxygens bonded to chlorine.
As the number of oxygens increases so does the acid strength. Again this has to do with electronegativity. Oxygen is a highly electronegative element and the more oxygen atoms present the.
In some cases particularly in situations involving acid-base chemistry the solution concentration is expressed in normality N or C NNormality is defined as the number of equivalent weights or simply equivalents eq of solute dissolved per liter of solution equivalentsL N Equation 1Normality is used in place of molarity because often 1 mole of acid does not neutralize 1 mole of. Acid in aqueous solution. HClO 4 H 2 O H 3 O ClO 4 Hydroiodic.
HI H 2 O H 3 O I Hydrobromic. HBr H 2 O H 3 O Br Hydrochloric. HCl H 2 O H 3 O Cl Nitric.
HNO 3 H 2 O H 3 O NO 3 Sulfuric. H 2 SO 4. H 2 SO 4 2H 2 O 2H 3 O SO 4 2-Iodic.
HIO 4 H 2 O H 3 O. The strongest acid is perchloric acid on the left and the weakest is hypochlorous acid on the far right. Notice that the only difference between these acids is the number of oxygens bonded to chlorine.
As the number of oxygens increases so does the acid strength. Again this has to do with electronegativity. Oxygen is a highly electronegative element and the more oxygen atoms present the.
The chemical formula for hydrochloric acid HCl represents the ionic bond between the elements of hydrogen and chlorine to form the compound hydrogen chloride a gas in its anhydrous form. HCl is an aqueous solution made from this hydrogen chloride gas dissolved in water. One of the most stable industrial acids HCl still presents significant corrosion hazards and storage difficulties.