
12 764772 2020. The most important organic acids referred in the Annex V are.
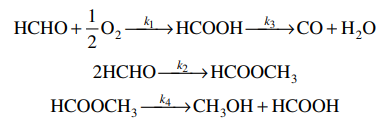
Methanol poisoning occurs because methanol is oxidized to formaldehyde and formic acid which attack the optic nerve causing blindness.
Oxidation of formaldehyde to formic acid. Formic acid is a colorless liquid having a pungent penetrating odor at room temperature comparable to the related acetic acidIt is miscible with water and most polar organic solvents and is somewhat soluble in hydrocarbonsIn hydrocarbons and in the vapor phase it consists of hydrogen-bonded dimers rather than individual molecules. Owing to its tendency to hydrogen-bond gaseous formic. The common name of this substance comes from its similarity and relation to formic acid.
Formaldehyde is an important precursor to many other materials and chemical compounds. In 1996 the installed capacity for the production of formaldehyde was estimated at 87 million tons per year. Photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to formic acid formaldehyde and methanol using dye-sensitized TiO 2 film Appl.
129 2013 pp. Qin G Zhang Y XuebinKe XT Sun Z Mao L Xue S 2013 Photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to formic acid formaldehyde and methanol using dye. Upon the addition of hydrogen the formic acid is converted to formaldehyde.
So formaldehyde is more easily oxidized into formic acid by ambient oxygen. Formic acid is miscible with water and most organic solvents with polarity. Formaldehyde is a colorless poisonous gas synthesized by the oxidation of methanol and used as an antiseptic disinfectant histologic fixative and general-purpose chemical reagent for laboratory applications.
Formaldehyde is readily soluble in water and is commonly distributed as a 37 solution in water. Formalin a 10 solution of formaldehyde in water is used as a disinfectant and to. Although the curing of urea formaldehyde can take place at room temperature using the addition of an acid catalyst such as citric or formic acid to drive the reaction the manufacture of panel products is generally driven by speed or production and therefore the reactions take place in the presence of heat.
During the hot curing of UF resin two condensation reactions take place and a ridged. Solution stabilization is important because formaldehyde solutions oxidize to formic acid and eventually repolymerize to paraformaldehyde. Most protocols requiring methanol-free formaldehyde suggest that the formaldehyde be prepared fresh.
This formaldehyde solution is sealed in ampules immediately after formulation under an inert atmosphere. Ampule packaging stabilizes the preparation. Of formaldehyde to formic acid 37 formaldehyde is usually shipped with 10-15 methanol to inhibit this change.
Our recommendation regarding 37 stock solutions. If a solution of 37 formaldehyde is clear colorless and has no precipitate and has been stored at room temperature in a tightly sealed bottle that has not been exposed to sunlight it should be good. However we still do not.
Formaldehyde is synthesized by the oxidation of methanol. It is among the 25 most abundantly produced chemicals in the world and is used in the manufacture of plastics resins and urea-formaldehyde foam insulation. Formaldehyde or formaldehyde-containing resins are used in the manufacture of chelating agents a wide variety of organic products glass mirrors explosives artificial silk and.
The latter is the oxidation product of formaldehyde so the oxidation chain goes from methanol to formaldehyde to formic acid. Methanol Formaldehyde Formic acid. Formaldehyde is a non-coagulating additive fixative - meaning that while it chemically bonds itself to the tissue it does not form a gel-like matrix that inhibits subsequent reagent penetration.
The portions of the tissue to which. For example oxidation of methanol produces formaldehyde and subsequently formic acid as the formate ion. Both of these products are more toxic than methanol itself.
Ethylene glycol automotive antifreeze is oxidized to oxalic acid as the oxalate ion the toxic compound found in rhubarb leaves and many other plants. Formic acid FA is found to be a potential candidate for the storage of hydrogen. For dehydrogenation of FA the supports of our catalysts were acquired by conducting ZnCl2 treatment and carbonation for biomass waste.
The texture and surface properties significantly affected the size and dispersion of Pd and its interaction with the support so as to cause the superior catalytic performance. Most commercial formaldehyde is prepared from paraformaldehyde PFA polymeric formaldehyde dissolved in distilleddeionized water with up to 10 vv methanol added to stabilize the aqueous formaldehyde. Stabilization is important to prevent oxidation of the formaldehyde to formic acid and its eventual re-polymerization to paraformaldehyde.
To avoid using methanol-stabilized formaldehyde. The centralized methanol and formic acid products in zeolite could be extracted by washing the zeolite catalyst with tetrahydrofuran giving a higher carbon balance for the reaction process table S5. In this case methanol is the predominant extracted product with a small amount of formic acid confirming the hindered overoxidation which might be due to the low methanol concentration at.
Metabolism of methanol occurs in a three-step process initially involving oxidation to formaldehyde by hepatic alcohol dehydrogenase which is a saturable rate-limiting process. In the second step formaldehyde is oxidized by aldehyde dehydrogenase to formic acid or formate depending on the pH. Methanol poisoning occurs because methanol is oxidized to formaldehyde and formic acid which attack the optic nerve causing blindness.
Ethanol is given as an antidote for methanol poisoning because ethanol competitively inhibits the oxidation of methanol. Ethanol is oxidized in preference to methanol and consequently the oxidation of methanol is slowed down so that the toxic by-products do. Iridium single-atom catalyst on nitrogen-doped carbon for formic acid oxidation synthesized using a general hostguest strategy.
12 764772 2020. The most important organic acids referred in the Annex V are. Benzoic acid propionic acid salicylic acid sorbic acid dehydroacetic acid formic acid undecylenic acid citric acid and sodium hydroxymethylaminoacetate.
In 2014 the European Commission added the mixture of citric acid and silver citrate to Annex V and allowed its use as a preservative up to a maximum concentration of 02. With formic acid it may be necessary to use methanol-free solvents and titrants 1. Examples of stable aldehydes are formaldehyde sugars chloral etc.
Formaldehyde polymers contain water as methylol groups. This combined water is not titrated. Addition of an excess of NaOCH 3 in methanol permits release and titration of this combined water after approximate neutralization of.
It is metabolized in the body to produce formaldehyde and formic acid and is toxic if more than 50 mL is consumed. Smaller amounts can cause blindness. Industrially methanol is produced from synthesis gas a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen derived from coke the coal not the soda or methane.
Methanol is used as the fuel in some racing cars and is being investigated as an renewable.