
However sarin can evaporate into a vapor gas and spread into the environment. Glyn Volans started working at the Medical Toxicology Unit formerly Poisons Unit in 1975.
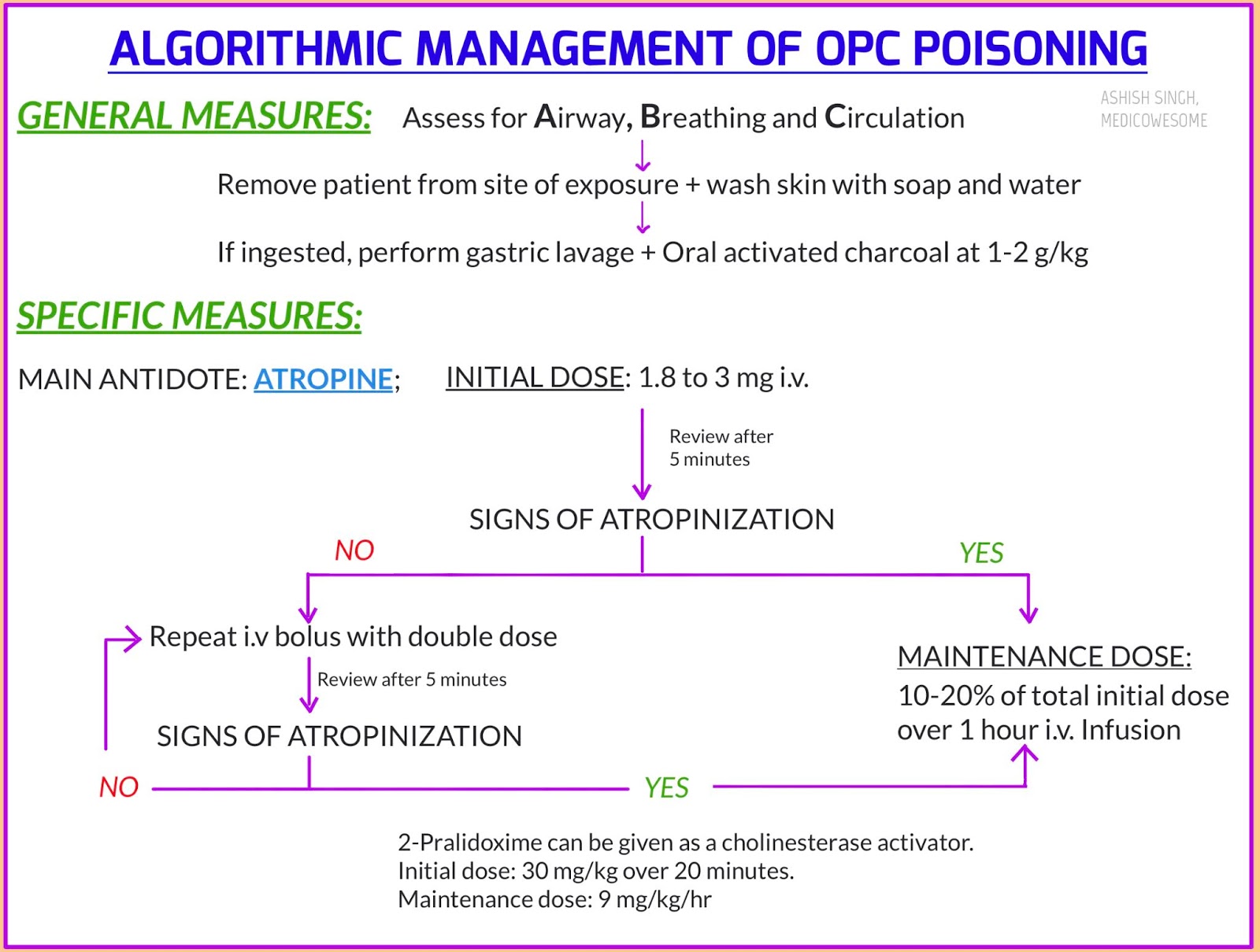
The initial dose for adults is 2 to 5 mg IV or 005 mgkg IV for children until reaching the adult dose.
Organophosphate treatment with atropine. Atropine is not an actual antidote for organophosphate poisoning. However by blocking the action of acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors atropine also serves as a treatment for poisoning by organophosphate insecticides and nerve agents such as tabun GA sarin GB soman GD and VX. Troops who are likely to be attacked with chemical weapons often carry autoinjectors with atropine.
Atropine The endpoint for atropine is dried pulmonary secretions and adequate oxygenation. Tachycardia and mydriasis must not be used to limit or to stop subsequent doses of atropine. The main concern with OP toxicity is respiratory failure from excessive airway secretions.
Start with a 1-2 mg IV bolus repeat q3-5min prn for desire effects drying of pulmonary. Airway control and adequate oxygenation are paramount in organophosphate OP poisonings. Intubation may be necessary in cases of respiratory distress due to laryngospasm bronchospasm bronchorrhea or seizures.
Immediate aggressive use of atropine may eliminate the need for intubation. Succinylcholine should be avoided because it is degraded. Organophosphate poisoning is poisoning due to organophosphates OPs.
Organophosphates are used as insecticides medications and nerve agents. Symptoms include increased saliva and tear production diarrhea vomiting small pupils sweating muscle tremors and confusion. While onset of symptoms is often within minutes to hours some symptoms can take weeks to appear.
Organophosphate poisoning can be short- or long-term. It can be caused by large or small doses. The longer the exposure and the larger the dose the more toxic the effects.
Atropine systemic is used in the treatment of. Atropisol Isopto Atropine Atropine-Care Ocu-Tropine Drug classes. Mydriatics Atropine ophthalmic is used in the treatment of.
For treatment outside the listed scope of practice requires mandatory approval via the QAS Clinical Consult and Advice Line. Atropine requirements for organophosphate toxicity vary enormously between patients and organophosphates. Target atropinisation for organophosphate toxicity is achieved when the patient has the following endpoints.
- chest clear and no wheeze on auscultation. Organophosphate poisoning symptoms can range from mild to severe and vary widely depending on the type and degree of exposure. In more severe cases it can be life-threatening.
The definitive treatment for organophosphate poisoning is atropine which competes with acetylcholine at the muscarinic receptors. The initial dose for adults is 2 to 5 mg IV or 005 mgkg IV for children until reaching the adult dose. If the patient does not respond to the treatment double the dose every 3 to 5 minutes until respiratory secretions have cleared and there is no.
This material is provided for educational purposes only and is not intended for medical advice diagnosis or treatment. Data sources include IBM Watson Micromedex updated 11 Oct 2021 Cerner Multum updated 1 Nov 2021. Review Adverse reaction to atropine and the treatment of organophosphate intoxication.
Robenshtok E Luria S Tashma Z Hourvitz A. Isr Med Assoc J. Possible mechanisms of anti-cholinergic drug-induced bradycardia.
Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1988 Possible mechanisms of anti-cholinergic drug-induced bradycardia. Meyer EC Sommers DK.
The mainstays of medical therapy in organophosphate OP poisoning include atropine pralidoxime 2-PAM and benzodiazepines eg diazepam. Initial management must focus on adequate use of atropine. Optimizing oxygenation prior to the use of atropine is recommended to minimize the potential for dysrhythmias.
Much larger doses of atropine are often needed for OP pesticide poisoning. Organophosphate or Carbamate Cholinesterase Inhibitors Poisoning Symptoms of organophosphate andor carbamate poisoning. Blurred vision or miosis.
Unexplained excessive lacrimation. Unexplained excessive nasopharyngeal secretions. Chest tightness difficulty breathing wheezing or coughing.
Tremors throughout the body or muscular twitching. Atropine is indicated for the treatment of poisoning by susceptible organophosphorus nerve agents having anticholinesterase activity as well as organophosphorus or carbamate insecticides in adults and pediatric patients weighing more than 41 kg 90 pounds. DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION Important Administration Information.
Three 3 Atropine autoinjectors should be available for use in. An improved treatment combines atropine with the cholinesterase-reactivating oxime 2-pyridine aldoxime methochloride 2-PAM pralidoxime chloride. The dosage of 2-PAM is 2050 mgkg given as a 5 solution IM or by slow IV over 510 min repeated at half the dose as needed.
IV 2-PAM must be given very slowly to avoid musculoskeletal paralysis and respiratory arrest. Atropine a naturally occurring belladonna alkaloid is a racemic mixture of equal parts of d- and l-hyoscyamine whose activity is due almost entirely to the levo isomer of the drug. Atropine is commonly classified as an anticholinergic or antiparasympathetic parasympatholytic drug.
More precisely however it is termed an antimuscarinic. Atropine should be administered every 5 to 10 minutes until secretions begin to dry up. If the military Mark I kits containing autoinjectors are available they provide the best way to administer the antidotes to healthy adults.
One autoinjector automatically delivers 2 mg atropine and the other automatically delivers 600 mg 2-PAM Cl. If the Mark I kit is unavailable or the patientvictim is. Atropineone of the primary active.
The anticholinergic effects of atropine as well as scopolamine and hyoscyamine are particularly useful for treating organophosphate exposure e g. 25 They also offer a basis for research into Alzheimers disease and the development of treatments aimed at replacing depleted acetylcholine. 26 27 28 Scopolamine also has a long.
Malathion is a parasympathomimetic organophosphate compound that is used as an insecticide for the treatment of head lice. Malathion is an irreversible cholinesterase inhibitor and has low human toxicity. 1 Structures Expand this section.
2 Names and Identifiers Expand this section. 3 Chemical and Physical Properties Expand this section. 4 Spectral Information Expand this.
The definitive treatment for organophosphate poisoning is atropine which competes with acetylcholine at the muscarinic receptors. The initial dose for adults is 2 to 5 mg IV or 005 mgkg IV for children until reaching the adult dose. If the patient does not respond to the treatment the dose is doubled every 3 to 5 min until respiratory secretions have cleared and there is no.
003 mgkg Repeat once if needed MAX single dose 05 mg Also used to treat specific toxins eg. 001 mgkg 110000 MAX DOSE 1 mg ET. 01 mgkg 11000 MAX DOSE 25 mg Multiple uses multiple routes Repeat every 3 to 5 min if needed.
05 to 1 gkg. However nerve agents are much more potent than organophosphate pesticides. Sarin originally was developed in 1938 in Germany as a pesticide.
Sarin is a clear colorless and tasteless liquid that has no odor in its pure form. However sarin can evaporate into a vapor gas and spread into the environment. Sarin is also known as GB.
Where sarin is found and how it is used. Sarin is not found. Glyn Volans started working at the Medical Toxicology Unit formerly Poisons Unit in 1975.
He became Director of the Unit in 1980 and leads a multi-disciplinary team of about 80 people. Lakshman Karalliedde is an anaesthetist with an interest in poisoning due to organophosphate pesticides. He joined the Medical Toxicology Unit in 1997.
An ecstasy of fumblingFitting.