A chemical formula is a representation of a chemical substance using letters for atoms and subscript numbers to show the numbers of each type of atoms that are present in the substance. In association with Nuffield Foundation.

What is relative formula mass and relative molecular mass.
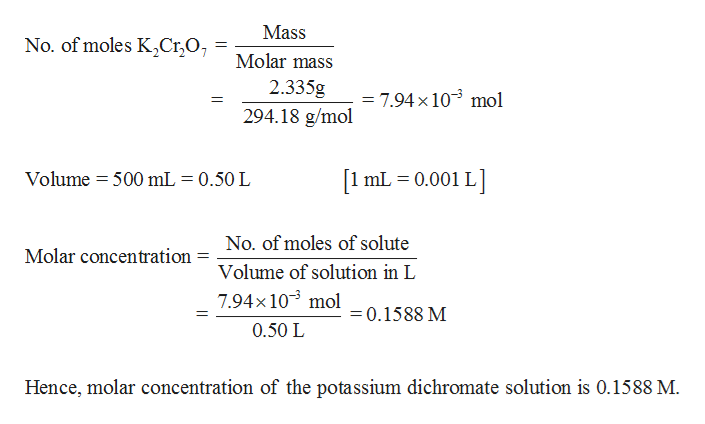
Molecular mass of potassium dichromate. What is Potassium dichromate K 2 Cr 2 O 7. K 2 Cr 2 O 7 is an inorganic chemical reagent with chemical name Potassium dichromate. It is also called as Potassium bichromate or Dipotassium bichromate.
It is crystalline ionic solid with a bright red-orange colour. It is odourless and insoluble in acetone as well as alcohol but dissolves in water. In this experiment you will use a standard solution of potassium dichromate K 2 Cr 2 O 7 to determine the percent by weight of iron as Fe 2 in an unknown solid.
Dichromate ion reduces to two chromiumIII ions. This reaction requires 6 electrons and 14 hydrogen ions. Cr 2 O 7 2- 14H 6 e- 2Cr 3 7H 2 O Only one electron is necessary to reduce FeIII to FeII Fe 3 e- Fe.
Potassium Dichromate Formula and Molecular Structure. The chemical formula for potassium dichromate is K 2 Cr 2 O 7 and the molar mass is calculated to be 294185 gmol. It is an ionic compound with two potassium ions K and the negatively charged dichromate ion Cr2O7- in which two hexavalent chromium atoms with oxidation state 6 are each attached to three oxygen atoms as well.
Potassium dichromate primarily affects the respiratory tract causing ulcerations shortness of breath bronchitis pneumonia and asthma but can also affect the gastrointestinal tract liver kidneys and immune system. This substance is a known human carcinogen and is associated with an increased risk of developing lung cancer and cancer of the. What is relative formula mass and relative molecular mass.
Find the percent composition by mass of potassium dichromate K 2 Cr 2 O 7 Step 1. Find the molar mass of the compound. Divide the total mass of each element by the molar mass and multiply by 100 to find the mass.
Show Video Lesson. How find the percent of an element in a compound. Finding the percent by mass means.
The molar mass of a substance also often called molecular mass or molecular weight although the definitions are not strictly identical but it is only sensitive in very defined areas is the weight of a defined amount of molecules of the substance a mole and is expressed in gmol. It can be calculated by adding the invididual molar mass of every atom that are composing the molecule CH4. Dichromate salts contain the dichromate anion Cr 2 O 2 7.
They are oxyanions of chromium in the 6 oxidation state and are moderately strong oxidizing agents. In an aqueous solution chromate and dichromate ions can be interconvertible. Chromates react with hydrogen peroxide giving products in which peroxide O 2 2.
Potassium is an essential constituent for plant growth and is found in most soils. An alloy of sodium and potassium NaK is used as a heat-transfer medium. Many potassium salts are of utmost importance including the hydroxide nitrate carbonate chloride chlorate.
Im glad you found your way here for chemistry help because youre in the right spot to be enlightened. By the way if its not actually the holidays and I havent updated this recently sorry about that. Here are the rules for using this free website.
I promise that I wont take your. B All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements. C Atoms combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds.
D Most of the atoms mass and all of its positive charge is contained in a small core called the nucleus. E All of the above are part of the atomic. The same goes for potassium tartrate at 1 g and for potassium cyanide at only 50 mg.
Potassium dichromate is lethal at between 6 and 8 g and 30 g of potassium nitrate causes severe intoxication which may result in death. Because of its strongly corrosive mechanism potassium hydroxide concentrations between 10 and 12 ml in a 15 caustic may be lethal. Potassium is a chemical element with the symbol K from Neo-Latin kalium and atomic number 19.
Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to form flaky white potassium peroxide in only seconds of exposure. It was first isolated from potash the ashes of plants from which its name derives.
These molecular compounds covalent compounds result when atoms share rather than transfer gain or lose electrons. Covalent bonding is an important and extensive concept in chemistry and it will be treated in considerable detail in a later chapter of this text. We can often identify molecular compounds on the basis of their physical properties.
Under normal conditions molecular. Aqueous Potassium Dichromate K2Cr207 Solution. NanoDrop CF-1 Calibration Check Fluid.
Showing 1 of 1. For use with Thermo Scientific NanoDrop Spectrophotometers. Ten times more concentrated compared to other K 2 Cr 2 O 7 calibration solutions.
Packaged in 05mL snap-top glass ampules. Intended for single use only. Molecular formula Molar mass gmol Density Range of concentration.
C 2 H 4 O. C 2 H 5 NO. C 3 H 6 O.
C 2 H 3 N. Free radical scavenging. Searching and identifying natural and safe antioxidants especially of plant origin have been notably increased in recent years 26 27Assays based on the use of O 2 and OH DPPH ABTS and NN-dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride cation radical DMPD are among the most popular spectrophotometric methods for determination of the antioxidant.
Determining relative molecular mass by weighing gases. In association with Nuffield Foundation. Use this demonstration to determine the relative molecular masses of different gases using the ideal gas equation.
Includes kit list and safety instructions. Determining the relative atomic mass of magnesium. In association with Nuffield Foundation.
Use this practical to determine the relative. The molecularformula mass is numerically equal to the mass of one mole of the substance. For example the molecular weight of water would be obtained by the following process.
Molecular mass of H 2 O 2 x atomic mass of H 1 x atomic mass of O 2 x 100797 1 x 159994 amu 1802 amu. A reaction in which a reducing agent loses electrons while it is oxidized and the oxidizing agent gains electrons while it is reduced is called as redox oxidation reduction reaction. An unbalanced redox reaction can be balanced using this calculator.
Use this demonstration to calculate the relative molecular mass of butane using simple apparatus. Includes kit list and safety instructions. Ammonia and hydrogen chloride.
In association with Nuffield Foundation. A demonstration to show the diffusion of gases using ammonia solution and hydrochloric acid. Includes kit list and safety instructions.
Dyeing three colours from. Lewis structures can play a vital role in understanding oxidation-reduction reactions with complex molecules. Consider the following reaction for example which is used in the Breathalyzer to determine the amount of ethyl alcohol or ethanol on the breath of individuals who are suspected of driving while under the influence.
The chemical formula of Methanol is CH 3 OH. Since its chemical structure is a linkage between a methyl CH 3 group and a hydroxyl group OH it is sometimes also written as MeOH where Me stands for MethylThe molecular weight or molar mass of Methanol is 3204 gmol. Stool specimens may be preserved in 10 buffered formalin see Laboratory Safety or suspended in a storage medium composed of aqueous potassium dichromate 25 wv final concentration.
Formalin-based fixatives are not recommended if molecular testing will be performed. Because the number of oocysts can vary even in liquid stools samples multiple stool specimens should be tested. How do you know the Order of Elements in a Chemical Formula What is Chemical Formula.
A chemical formula is a representation of a chemical substance using letters for atoms and subscript numbers to show the numbers of each type of atoms that are present in the substance. Based on the chemical formula of a substance we know the composition of the substance. The COD is often measured using a strong oxidant eg.
Potassium dichromate potassium iodate potassium permanganate under acidic conditions. A known excess amount of the oxidant is added to the sample. Once oxidation is complete the concentration of organics in the sample is calculated by measuring the amount of oxidant remaining in the solution.
This is usually done by titration using an.