A universal method for easily preparing tough and stretchable materials for biomedical applications has been developed by scientists in Japan. 4262 Ethyl Carbamate Urethane Ethyl carbamate urethane is a chemical naturally formed during food processing especially in alcoholic beverages such as wine beer whisky fruit brandies and fermented foods such as bread and yogurt.
1For example nitrile hydratases are used to make acrylamide on the.
Method for producing acrylamide. On consumers preference for food containing acrylamide Harkness and Areal study peoples willingness to pay for a decrease in the amount of acrylamide in baby food in the United Kingdom. They employ a discreet choice experiment to examine such attributes as packaging production method acrylamide level sugar level and price. The estimation is analyzed by a mixed logit model.
Gel electrophoresis is a method for separation and analysis of macromolecules. Or oligonucleotides the gel is usually composed of different concentrations of acrylamide and a cross-linker producing different sized mesh networks of polyacrylamide. When separating larger nucleic acids greater than a few hundred bases the preferred matrix is purified agarose.
In both cases the gel forms. The method of preparation leads to formations of some important classes of hydrogels. These can be exemplified by the following.
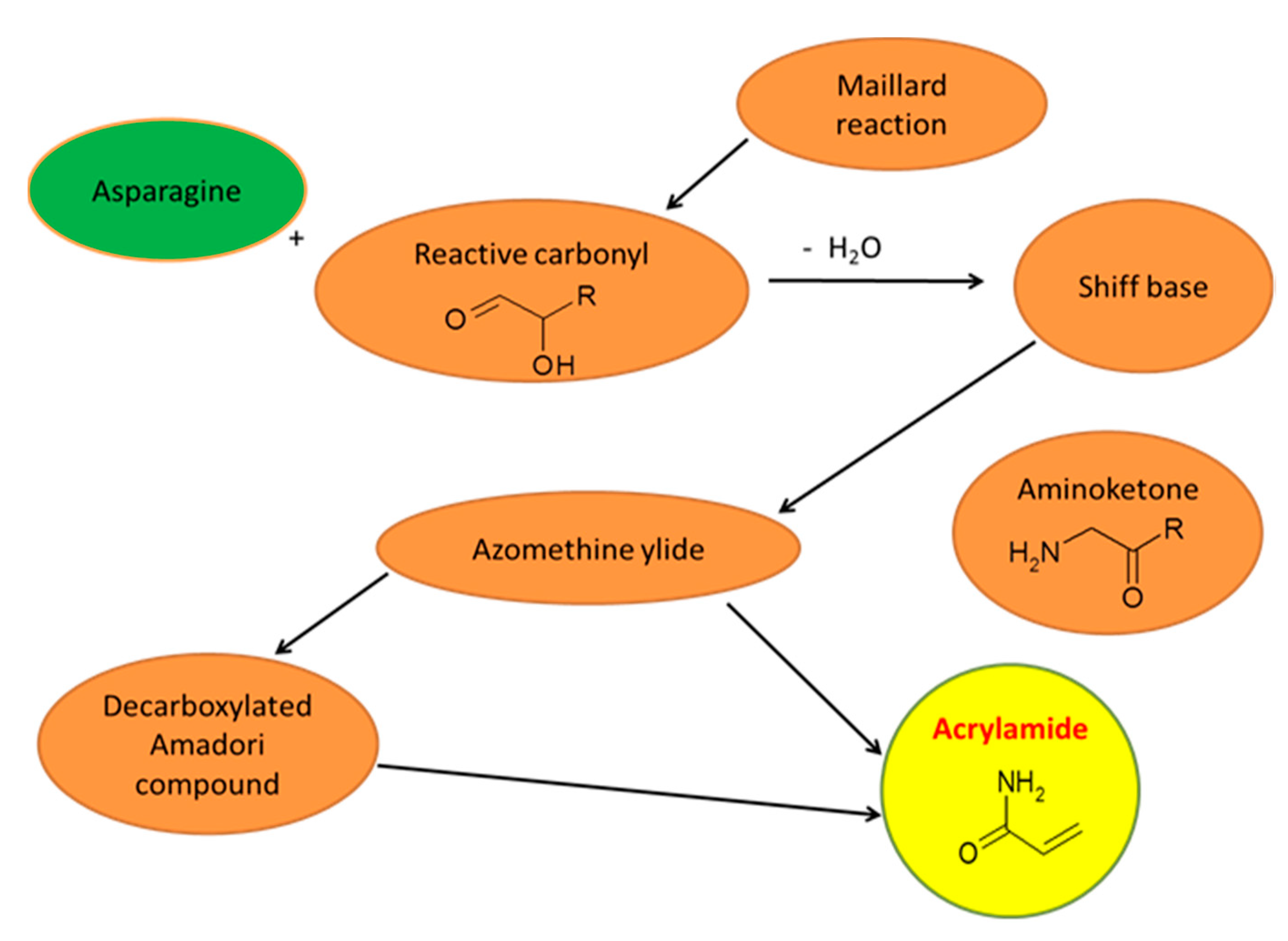
A Homopolymeric hydrogels are referred to polymer network derived from a single species of monomer which is a basic structural unit comprising of any polymer network. Homopolymers may have cross-linked skeletal structure depending on the nature of the. Acrylamide is produced from a chemical reaction between asparagine and a reducing sugar so decreasing the concentration of either is expected to decrease acrylamide.
A potato line was genetically engineered to have low amounts of free asparagine and in early tests had as little as 5 percent of the acrylamide compared with non-GE potatoes when cooked at high temperatures Rommens et al 2008. In chemistry and biology a cross-link is a bond or a short sequence of bonds that links one polymer chain to another. These links may take the form of covalent bonds or ionic bonds and the polymers can be either synthetic polymers or natural polymers such as proteins.
In polymer chemistry cross-linking usually refers to the use of cross-links to promote a change in the polymers physical. For example acrylamide is made from acrylonitrile using nitrile hydratase. The conventional method of producing glycolic acid involved reacing formaldehyde with carbon monoxide over an acid catalyst at high temperature and pressure.
Enzymes have offered a more mild alternative. Coli can be made to overexpress nitrilase which when combined with other enzymes such as. Chart compares methods of producing new crop varieties.
Number of genes affected is a measure of the precision. Since only one or a few genes are moveddeletedalltered in genetic engineering last 2 columns transgenics and cisgenics you know what protein will be produced and can test for toxicity and allergenicity. The little r before DNA is for recombinant.
Both apples Arctic. The rst breakthrough in this method came in 1988 when Tanaka et. Methods of the time including sodium dodecyl sulfate poly-acrylamide gel electrophoresis SDS-PAGE and gel permeation chromatography GPC.
The authors supposed that this phenomenon was due to the unique qualities of the cobalt nanocrystals low speci c 2. Heat high photoabsorptivity and large surface area per. Acrylamide is a health concern as based on studies it is a probable human carcinogen.
For more information refer to Health Canadas Acrylamide and Food. 4262 Ethyl Carbamate Urethane Ethyl carbamate urethane is a chemical naturally formed during food processing especially in alcoholic beverages such as wine beer whisky fruit brandies and fermented foods such as bread and yogurt. The total protein content of skin mucosal and serum samples was measured by following the Bradford method Bonjoch and Tamayo 2001 at 595 nm and bovine serum albumin BSA serial dilutions were.
The electrophoretic mobility shift assay EMSA is a rapid and sensitive method to detect protein-nucleic acid interactions 1 6It is based on the observation that the electrophoretic mobility of a protein-nucleic acid complex is typically less than that of the free nucleic acid Fig. 1The current widely-used assay differs little from that originally described by Fried and. A universal method for easily preparing tough and stretchable materials for biomedical applications has been developed by scientists in Japan.
Polyacrylamide-acrylic acid-N-dimethylaminomethyl acrylamide CA. 53800-41-2 produced by reacting 96-164 parts by weight of polyacrylamide with 16 parts dimethylamine and 1 part formaldehyde and containing no more than 02 monomer as acrylamide such that a 20 aqueous solution has a minimum viscosity of 4000 cP at 25 degC as determined by. The gel is made with different concentrations of acrylamide and a cross-linker producing different sized mesh polyacrylamide networks.
Proteins are denatured with SDS that coats the proteins with a negative charge in direct proportion to its mass such that the mass-to-charge mz ratio is constant. N-dimethylaminomethylacrylamide polymer with acrylamide and styrene. NN-Dioleoylethylenediamine NN-dilinoeoyl-ethylenediamine and N-oleoyl-N-linoleoyl-ethylenediamine mixture produced when tall oil fatty acids are made to react with ethylenediamine such that the finished mixture has a melting point of 212deg-228 degF as determined by ASTM method D127-60 and an.
3-monochloropropane-12-diol esters 3-MCPDE and glycidyl esters GE are contaminants that can occur in edible oils such as vegetable oils and foods made from these oils. Weve also taken things a step further from the traditional dumpling method by introducing the latest technology to our processing which makes the wraps even thinner this involved bringing in technology that could mould the dough to a specific shape that would lend to producing the thinnest possible wrap. The meat is also processed and minced at our plant not bought as is as this.
Potting Mix Recipe Method. Pre-soak coir peat in warm water in a large plastic container. To rehydrate a 9L block requires 45L of water so you need a container bigger than a 9L bucket to work in minimum 14L size.
When rehydrated according to the directions for the volume you are making loosen and fluff with your trowel. Mix equal quantities of pre-soaked coir peat and. Cooking is the process of producing safe and edible food by preparing and combining ingredients and in most cases applying heat.
Cooking is a means of processing food without which many foods would be unfit for human consumption. Why do we cook food. Raw foods such as meat fish and eggs may harbour food poisoning bacteria which if consumed are likely to.
Cyclohexanone-formaldehyde resin produced when 1 mole of cyclohexanone is made to react with 165 moles of formaldehyde such that the finished resin has an average molecular weight of 600-610 as determined by ASTM method D2503-82 Standard Test Method for Molecular Weight Relative Molecular Mass of Hydrocarbons by Thermoelectric Measurement of Vapor Pressure which is incorporated by. The NEBNext Multiplex Small RNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina Index Primers 1-48 contains the adaptors primers enzymes and buffers required to convert small RNAs into indexed libraries for next-generation sequencing on the Illumina platform. The novel workflow has been optimized to minimize adaptor-dimers while producing high-yield high-diversity libraries.
There are a number of ways in which allergen information can be provided to your customers. You will need to choose the method which is best for your business and the type of food you serve. Prepacked foods refer to any food put into packaging before being placed on sale while non-prepacked food loose food is unpackaged food.
Enzymes have been employed for a wide variety of chemical processes for decades Fig. 1For example nitrile hydratases are used to make acrylamide on the. Sotirios Longinos currently works as Postdoc Researcher in School of Mining Geosciences Petroleum Engineering Department in Nazarbayev University.
His current project is Cryogenic Fracturing. A carboxymethylated curdlanpolyacrylamide double network hydrogel with high mechanical performance was fabricated by using ionic cross-linking an osmotic pressure method and UV initiation and is employed as a scaffold for cartilage repair.