The binding of inhibitors to allosteric sites modifies the structure of the active site thus preventing the binding of substrate to the enzymeThis process is called allostery or allosteric inhibition. Lysozymes are surrounded by a lysosomal membrane that contains the enzymes within the lysosome and protects the cytosol with the rest of the.

Lysozyme is secreted by submucosal glands neutrophils and macrophages.
Lysozyme is an enzyme that. Lysozyme also known as muramidase or N-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase is an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune systemLysozyme is a glycoside hydrolase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of 14-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in peptidoglycan which is the major component of gram-positive bacterial cell. Lysozyme is an enzyme used to break down bacterial cell walls to improve protein or nucleic acid extraction efficiency. Lysozymes muramidases are a family of enzymes with antimicrobial activity characterized by the ability to damage the cell wall of bacteria.
The enzyme acts by catalyzing the hydrolysis of 14-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in. Lysozyme through its dual activities as a lytic enzyme and a small cationic protein damages or kills bacteria by lysing their cell wall peptidoglycan by disrupting bacterial membranes and by activating autolytic enzymes in the bacterial cell wall. Lysozyme is secreted by submucosal glands neutrophils and macrophages.
Against most bacteria lysozyme acts synergistically with other. Lysozyme is an enzyme used to break down bacterial cell walls to improve protein or nucleic acid extraction efficiency. Lysozymes muramidases are a family of enzymes with antimicrobial activity characterized by the ability to damage the cell wall of bacteria.
The enzyme acts by catalyzing the hydrolysis of 14-beta-linkages between. Le lysozyme peut agir comme une opsonine innée ou comme une enzyme lytique capable de lyser des bactéries en particulier celles à Gram positif indépendamment de leur pouvoir pathogène. En revanche les bactéries à Gram négatif sont généralement résistantes à cette enzyme grâce à la couche externe de lipopolysaccharides LPS qui les caractérise.
Lysozyme is a special enzyme found in tears saliva sweat and other body fluids. Other mucosal linings such as the nasal cavity also contain lysozyme. It destroys bacteria that attempt to.
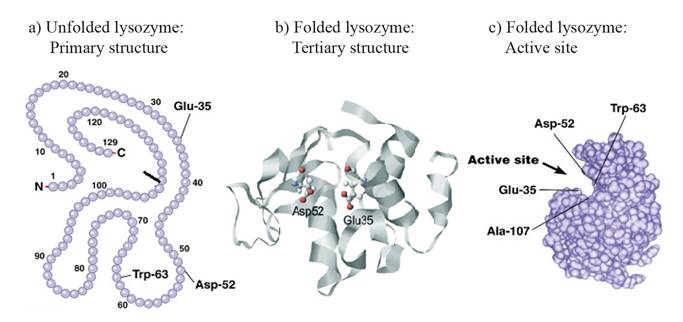
Lysozyme is a small stable enzyme making ideal for research into protein structure and function. Brian Matthews at the University of Oregon has performed a remarkable series of experiments using lysozyme as the laboratory for study. He has performed hundreds of mutations on the lysozyme molecule made by a bacteriophage changing one or more amino acids in the protein chain to a different.
Lysozymes have primarily a bacteriolytic function. Those in tissues and body fluids are associated with the monocyte-macrophage system and enhance the activity of immunoagents. Lyz2 is active against a range of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
More effective than Lyz1 in killing Gram-negative bacteria. Lyz1 and Lyz2 are equally effective in killing Gram-positive bacteria. This gene encodes human lysozyme whose natural substrate is the bacterial cell wall peptidoglycan cleaving the beta1-4glycosidic linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetylglucosamine.
Lysozyme is one of the antimicrobial agents found in human milk and is also present in spleen lung kidney white blood cells plasma saliva and tears. Saliva also contains lysozyme an enzyme that lyses many bacteria and prevents overgrowth of oral microbial populations. In most species the serous acinar cells secrete an alpha-amylase which can begin to digest dietary starch into maltose.
Amylase is not present or present only in very small quantities in the saliva of carnivores or cattle. The enzyme lysozyme is found in many tissues and is known to attack the cell walls of many gram-positive bacteria aiding in defense against infection. Tears are also beneficial to wounds due to the lysozyme enzyme.
However there are also infection risks due to bacteria in the mouth. A dog licking a wounded paw. Oral mucosa heals faster than skin suggesting that saliva may have.
Enzyme and its Active Site. Apart from active sites enzymes have allosteric sites or inhibitor sitesInhibitors may join an enzyme at an active site or allosteric site. The binding of inhibitors to allosteric sites modifies the structure of the active site thus preventing the binding of substrate to the enzymeThis process is called allostery or allosteric inhibition.
An enzymes K m describes the substrate concentration at which half the enzymes active sites are occupied by substrate. A high K m means a lot of substrate must be present to saturate the enzyme meaning the enzyme has low affinity for the substrate. On the other hand a low K m means only a small amount of substrate is needed to saturate the enzyme indicating a high affinity for substrate.
Enzyme An enzyme is a protein or RNA produced by living cells which is highly specific and highly catalytic to its substrates. Enzymes are a very important type of macromolecular biological catalysts. Due to the action of enzymes chemical reactions in organisms can also be carried out efficiently and specifically under mild conditions.
Although enzyme immobilization began over 100 years ago it remains one of the most essential industrial technologies today. This is because immobilized enzymes are highly versatile and have a wide variety of potential applications. Also the enzyme immobilization process has been slowly perfected over the years making it much simpler quicker and efficient than ever before.
This has served. Secondary lysozyme formed by the fusion of primary lysozymes containing engulfed molecules or organelles. The shape of lysozymes is irregular or pleomorphic.
However mostly they are found in the spherical or granular structure. Lysozymes are surrounded by a lysosomal membrane that contains the enzymes within the lysosome and protects the cytosol with the rest of the. An enzyme is a protein or RNA produced by living cells which is highly specific and highly catalytic to its substrates.
Enzymes are a very important type of macromolecular biological catalysts. Due to the action of enzymes chemical reactions in organisms can also be carried out efficiently and specifically under mild conditions. The nomenclature of enzymes is derived from.
Lysozyme C is capable of both hydrolysis and transglycosylation. It shows also a slight esterase activity. It acts rapidly on both peptide-substituted and unsubstituted peptidoglycan and slowly on chitin oligosaccharides.
Hydrolysis of 1-4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between N-acetyl-D. Enzyme activity is measured in units which indicate the rate of reaction catalysed by that enzyme expressed as micromoles of substrate transformed or product formed per minute. An enzyme unit is the amount of enzyme that will catalyse the transformation of 1 μmol of substratemin under specified conditions of pH and temperature.
Enzyme molecules red dots are retained in the dialysis bag and separated from other smaller molecules blue dots. Berg JM Tymoczko JL Stryer L. Section 41 Polarity based separation Like other proteins enzymes can be separated on the basis of polarity more specifically their net charge charge density and hydrophobic.
Lysozyme - A Defensive Enzyme. The illustration on the right shows the protein lysozyme red white blue and gray amino acids which is an important defensive enzyme found in tears saliva and mucus. Lysozymes function is to break down the polysaccharides sugar polymers that are components of bacterial cell walls.
Initially lysozyme is synthesized as a single long polypeptide chain. Lysozyme reacts with peptidoglycan layer and breaks the glycosidic bond. For that reason gram-positive bacteria can be directly exposed to lysozyme however outer membrane of the gram-negative bacteria needs to be removed before exposing the peptidoglycan layer to the enzyme.
Lysozyme treatment is generally conducted at pH 67 and at 35 C. The mass is finally passed to the true stomach the Abomassum where the digestive enzyme lysozyme breaks down the bacteria so as to release nutrients. Use of plant material is thus indirect with primary processing by the bacterial flora maintained in the stomach.
The Perissodactyla including horses rhinoceroses and tapirs have evolved a less efficient form of ruminant digestion. Likewise Na Y zeolite was used to immobilize lysozyme because it had higher activity compared to other supports as reported by Chang and Chu. The heterogeneous surface of zeolites with multiple adsorption sites are considered to be suitable for modulating the enzyme and support interactions Serralha et al.
Une enzyme est une protéine dotée de propriétés catalytiquesPresque toutes les biomolécules capables de catalyser des réactions chimiques dans les cellules sont des enzymes. Certaines biomolécules catalytiques sont cependant constituées dARN et sont donc distinctes des enzymes. Ce sont les ribozymes.
Une enzyme agit en abaissant lénergie dactivation dune réaction chimique ce.