Paracetamol also known as acetaminophen and by the brand names of Tylenol and Panadol is usually well-tolerated in prescribed dose but overdose is the most common cause of drug-induced liver disease and acute liver failure worldwide. Damage to the liver is not due to the drug itself but to a toxic metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine NAPQI produced by cytochrome P-450 enzymes in the.
A Guideline Summary has also been published.
Liver injury from paracetamol overdose. Drug induced liver injury DILI is a common cause of acute liver injury. Paracetamol also known as acetaminophen is a widely used anti-pyretic that has long been established to cause liver toxicity once above therapeutic levels. Hepatotoxicity from paracetamol overdose whether intentional or non-intentional is the most common cause of DILI in the United States and remains a global issue.
Paracetamol also known as acetaminophen and by the brand names of Tylenol and Panadol is usually well-tolerated in prescribed dose but overdose is the most common cause of drug-induced liver disease and acute liver failure worldwide. Damage to the liver is not due to the drug itself but to a toxic metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine NAPQI produced by cytochrome P-450 enzymes in the. Paracetamol poisoning also known as acetaminophen poisoning is caused by excessive use of the medication paracetamol acetaminophen.
Most people have few or non-specific symptoms in the first 24 hours following overdose. These include feeling tired abdominal pain or nauseaThis is typically followed by a couple of days without any symptoms after which yellowish skin blood clotting. Paracetamol and have symptoms of acute liver injury eg.
Abdominal pain nausea and vomiting. Diagnosis is somewhat more difficult and a strong clinical suspicion and careful history is key to obtaining the diagnosis. Iatrogenic poisoning or therapeutic error.
Usually with intravenous IV paracetamol where dosing errors are often 10-fold. Initial assessment as. Untreated paracetamol poisoning may cause varying degrees of liver injury over the 2 to 4 days following ingestion including fulminant hepatic failure.
Rarely massive overdose may initially present with coma and severe metabolic acidosis. Presentation with coma may also occur if a combination preparation of paracetamol and opioid is taken in overdose or after an overdose of. The risk that an acetaminophen overdose will cause liver injury correlates with the blood level of acetaminophen relative to the time the drug was taken.
Physicians therefore are able to estimate the patients probability of developing liver injury after an overdose. To make this determination they obtain the patients history of acetaminophen ingestion and measure the blood level of the. However convincing the numerous reports of liver damage following paracetamol overdosage in chronic alcoholics may be 220 they are purely anecdotal and the inescapable fact remains that exactly the same severe and fatal liver damage occurs after overdosage in patients who are not chronic alcoholicsThe doses claimed to have been taken by the chronic.
Table 2 Frequency of liver injury after paracetamol overdose. Patients are grouped by hospital and NAC treatment regimen. RIE Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh.
RVI Royal Victoria Infirmary Newcastle. STH St Thomas Hospital London. 21 h regimen is the conventional NAC treatment 12 h regimen is the SNAP regimen.
Data from the 2 regimens are compared by presenting the absolute. Drug-induced liver injury DILI and herbal-induced liver injury HILI are well-recognized problems and symptomatically can mimic both acute and chronic liver diseases. The probability of an individual drug causing liver injury ranges from 1 in 10000 to 100000 with some drugs reported as having an incidence of 100 in 100000 chlorpromazine isoniazid.
DILI has a worldwide estimated. Fatal liver injury in some patients unpredictable scary 2. Although rare DILI may result in disapproval of a new drug or its removal from the market very costly 3.
It is a troublesome. The liver is one of the only organs in the body that is able to replace damaged tissue with new cells rather than scar tissue. For example an overdose of acetaminophen Tylenol can destroy half of a persons liver cells in less than a week.
Barring complications the liver can repair itself completely and within a month the patient will show no signs of damage. Survival from a paracetamol overdose is generally considered to be 100 in cases receiving NAC within 8 hours of exposure. Efficacy declines after this point.
The threshold for potential paracetamol-induced hepatic injury in adults is 10g or 200 mgkg whichever is less within 24 hours. So 10g is the toxic dose for all those heavier than 50kg. Fortunately N-acetylcysteine NAC is a safe and effective antidote which if used correctly prevents serious hepatic injury after paracetamol overdose.
Updated guidelines for the management of paracetamol poisoning in Australia and New Zealand were released in December 2019. A Guideline Summary has also been published. The ECI have produced this page to give quick access to the.
Hepatotoxicity is the injury or liver damage caused by exposure to drugs. The symptoms of poisoning depend on the substance and the amount you take. Liver damage and less frequently renal damage can occur following overdose.
Nausea and vomiting the only early features of poisoning usually settle within 24 hours. Persistence beyond this time often associated with the onset of right subcostal pain and tenderness usually indicates development of hepatic necrosis. Get emergency help immediately if any of the following symptoms of overdose occur while taking acetaminophen.
Kaysen GA Pond SM Roper MH Menke DJ Marrama MA Combined hepatic and renal injury in alcoholics during therapeutic use of acetaminophen Arch Intern Med 145 1985. Johnson GK Tolman KG Chronic liver disease and acetaminophen Ann Intern. Symptoms of paracetamol overdosage in the first 24 hours are pallor nausea hyperhidrosis malaise vomiting anorexia and abdominal pain.
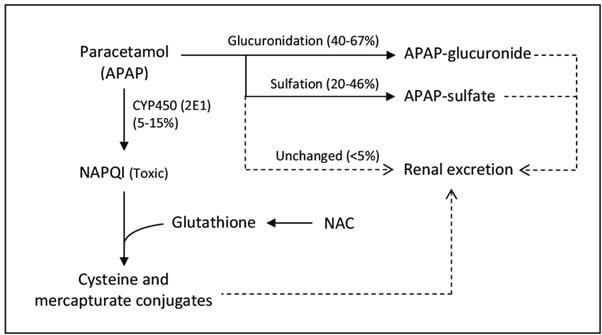
Liver damage may become apparent 12 to 48 hours after ingestion. This may include hepatomegaly liver tenderness jaundice acute hepatic failure and hepatic necrosis. APAP toxic metabolite NAPQI usually quickly detoxified by glutathione stores in liver In overdose glutathione runs out NAPQI accumulates liver injury.
NAC increases availability of glutathione NAC is a precursor. Clinical Features Stage 1 first 24hr Mild nausea and vomitingmalaise. Hypokalemia associated with high 4-hr level Massive Ingestion 500 mgkg may present with acidemia.
Overdose of paracetamol leads to paracetamol toxicity which mainly results into liver injury but is also one of the most common causes of poisoning all over world. Many people who develop paracetamol toxicity may feel no symptoms at all in the first 24 hours that follow overdose of paracetamol. Others may initially experience nonspecific complaints like vague abdominal pain and nausea.
An overdose of acetaminophen can damage your liver or cause death. Call your doctor at once if you have nausea pain in your upper stomach itching loss of appetite dark urine clay-colored stools or jaundice yellowing of your skin or eyes. Aspirin may cause stomach or intestinal bleeding which can be fatal.
Call your doctor at once if you have symptoms such as bloody or tarry stools or. Tylenol liver damage acetaminophen can occur from accidentally ingesting too much acetaminophen or intentionally. Signs and symptoms of acetaminophen-induced liver damage may include.
Nauseau vomiting kidney failure bleeding disorders coma and death. Acetaminophen is a drug contained in over 200 OTC and prescription medications from. If there are risk factors for hepatotoxicity and inadvertent paracetamol overdose including.
Body weight less than 50 kg. Severe liver disease pharmacokinetics of paracetamol is altered in severe liver disease and the hazards of overdose are greater in people with non-cirrhotic alcoholic liver disease. Increasing age andor frailty.
Overdose 75 g or more of paracetamol in a single administration in adults or 140 mgkg of body weight in a single administration in children causes hepatic cytolysis likely to induce complete and irreversible necrosis resulting in hepatocellular insufficiency metabolic acidosis and encephalopathy which may lead to coma and death. Simultaneously increased levels of hepatic transaminases. Harmless at low doses acetaminophen has direct hepatotoxic potential when taken as an overdose and can cause acute liver injury and death from acute liver failure.
Even in therapeutic doses acetaminophen can cause transient serum aminotransferase elevations. Acetaminophen is a p-aminophenol derivative with analgesic and antipyretic activities. Although the exact mechanism through.
Poisoning paracetamol overdose Infection Hepatitis A and B Liver ischaemia. Common causes of chronic hepatocellular injury include. Alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Chronic infection Hepatitis B or C Primary biliary cirrhosis. Less common causes of chronic hepatocellular injury include.
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.