
Unsaturated fats have at least one double bond in one of the fatty acids. Triglycerides can be both made and broken down through parts of the glucose catabolism pathways.
When starchy foods like rice or potatoes begin to.
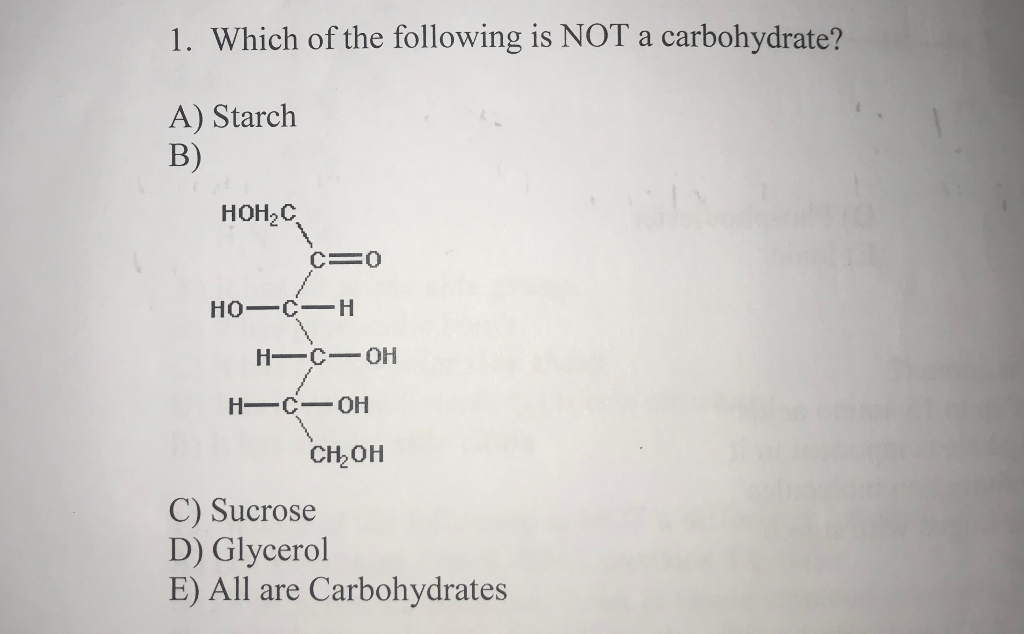
Is glycerol carbohydrate. Glycerol ˈ ɡ l ɪ s ə r ɒ l. Also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English is a simple polyol compound. It is a colorless odorless viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic.
The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glyceridesDue to having antimicrobial and antiviral properties it is widely used in FDA approved wound and burn treatments. Glycerol is a colorless odorless liquid with a sweet taste. It is viscous at room temperature and non-toxic in low concentrations.
Glycerol was discovered in 1779. It is also called glycyl alcohol glycerin or glycerine in some literature. Glycerol is seen in biological systems as an intermediate in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism because surplus carbohydrate can be converted into long.
Glycerol dehydrogenase is a homooctamer composed of eight identical monomer subunits made up of a single polypeptide chain of 370 amino acids molecular weight 42000 Da. Each subunit contains 9 beta sheets and 14 alpha helices within two distinct domains N-terminal residues 1-162 and C-terminal residues 163-370. The deep cleft formed between these two domains serves as the enzymes.
Unfortunately the leading exercise physiology textbook also claims a low-carbohydrate diet sets the stage for a significant loss of lean tissue as the body recruits amino acids from muscle to maintain blood glucose via gluconeogenesis Thus it is certainly time to set the record straight. The Ketone Bodies are an Important Fuel. The hormonal changes associated with a low carbohydrate.
Carbohydrate is also Background The primary role of dietary carbohydrate is the provision of energy to cells particularly the brain that requires glucose for its metabolism. Other nutrients eg fat protein and alcohol can provide energy but there are good reasons to limit the proportion of energy provided by these nutrients as discussed in the chronic disease section. Glycerol which is also known as glycerine glycerin or propanetriol is a polyol compound.
The derivation of the gly- and glu- prefixes for glycerol and for sugars is derived from a Greek word glukus which means sweet. It is a trihydroxy sugar alcohol which acts as an intermediate in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. The formula of glycerol is C 3 H 8 O 3.
PNGase F Glycerol-free is an amidase which cleaves between the innermost GlcNAc and asparagine residues of high mannose hybrid and complex oligosaccharides. Glycerol-free for optimal performance in HPLC and mass spectrometry analysis. 95 purity as determined by SDS-PAGE and intact ESI-MS.
Non-recombinant with no detectable endoglycosidase F1 F2 or F3 contamination. Sports drinks are designed to deliver a balanced amount of carbohydrate and fluid to allow an athlete to simultaneously rehydrate and refuel during and after exercise. Practitioner Fact Sheet.
Athlete infographics have been developed for the information of athletes under the direct guidance of a sports dietitian. Sports dietitians have. Excess acetyl CoA generated from excess glucose or carbohydrate ingestion can be used for fatty acid synthesis or lipogenesis.
Acetyl CoA is used to create lipids triglycerides steroid hormones cholesterol and bile salts. Lipolysis is the breakdown of triglycerides into glycerol and fatty acids making them easier for the body to process. Glycerol can be phosphorylated to glycerol-3-phosphate which continues through glycolysis.
Fatty acids are catabolized in a process called beta-oxidation that takes place in the matrix of the mitochondria and converts their fatty acid chains into two carbon units of acetyl groups. The acetyl groups are picked up by CoA to form acetyl CoA that proceeds into the citric acid cycle. It also is essential in the regulation of acid-base balance amino acid metabolism and synthesis of carbohydrate derived structural components.
Gluconeogenesis occurs in liver and kidneys. The precursors of gluconeogenesis are lactate glycerol amino acids and with propionate making a minor contribution. The gluconeogenesis pathway consumes.
As youll see on the nutrition labels for the food you buy the term total carbohydrate refers to all three of these types. The goal is to choose carbs that are nutrient-dense which means they are rich in fiber vitamins and minerals and low in added sugars sodium and unhealthy fats. When choosing carbohydrate foods.
Eat the most of these. Whole unprocessed non-starchy vegetables. Triglycerides a form of long-term energy storage in animals are made of glycerol and three fatty acids.
Animals can make most of the fatty acids they need. Triglycerides can be both made and broken down through parts of the glucose catabolism pathways. Glycerol can be phosphorylated to glycerol-3-phosphate which continues through glycolysis.
Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of new glucose molecules from pyruvate lactate glycerol or the amino acids alanine or glutamine. This process takes place primarily in the liver during periods of low glucose that is under conditions of fasting starvation and low carbohydrate diets. So the question can be raised as to why the body would create something it has just spent a fair amount.
Amylase is a digestive enzyme that acts on starch in food breaking it down into smaller carbohydrate molecules. The enzyme is made in two places. First salivary glands in your mouth make salivary amylase which begins the digestive process by breaking down starch when you chew your food converting it into maltose a smaller carbohydrate.
When starchy foods like rice or potatoes begin to. Specific Carbohydrate Diet SCD Allowable Foods Additives Baking soda Potassium Sorbate Sulphates Vanillin Alcoholic Beverages Ethanol Gin Mead Scotch whisky Vodka Wine dry red and white Condiments Capers Horseradish sauce Tabasco Brand Pepper Sauce Dairy Asiago cheese Blue cheese Brick cheese Brie cheese Butter Camembert Cheese Cheddar cheese Cheese If a cheese is not a. Glycerol enters into hepatocytes via aquaporin-9 and is phosphorylated by glycerol kinase to generate glycerate-3 phosphate a precursor for gluconeogenesis.
Amino acids are converted to α-ketoacids through deamination reactions catalyzed by glutaminase glutamate dehydrogenase andor aminotransferase. The α-ketoacids are further converted to intermediates of the TCA cycle eg. Glycerol is the basis of all fats and is made up of a three-carbon chain that connects the fatty acids together.
A fatty acid is just a long chain of carbon atoms connected to each other. Saturated and Unsaturated There are two kinds of fats saturated and unsaturated. Unsaturated fats have at least one double bond in one of the fatty acids.
A double bond happens when four electrons are shared. Fatty acids glycerol Volatile fatty acids alcohol Methane carbon dioxide ammonia Hydrolysis Acidogenesis Acetogenesis Methanogenesis Acetic acid Suspended colloidal organic matter protein carbohydrate lipid Hydrogen carbon dioxide Figure 1. Simplified schematic representation of the anaerobic degradation process 1.
Results in a further decrease of pH. If hydrogen pressure becomes. Glycerol accounts for about 20 of total glucose production during prolonged fasting.
The final way we generate pyruvate is throug h lactate. Often incorrectly maligned for its role in muscle soreness and fatigue lactate sometimes incorrectly called lactic acid can actually serve as a fuel source during exercise and also be used in the process of gluconeogenesis. We obtain good denaturation by preparing a sample to a final concentration of 2 mgml protein with 1 SDS 10 glycerol 10 mM Tris-Cl pH 68 1 mM ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid EDTA a reducing agent such as dithiothreitol DTT or 2-mercaptoethanol and a pinch of bromophenol blue to serve as a tracking dye 005 mgml.
We prepare a 2x concentrate of sample buffer consisting of 2. Glycerol is a three-carbon alcohol and each of the carbons bond to one fatty acid. The structure of the fatty acids of a fat determines if a fat is saturated or unsaturated.
Double bonds in one or more alkyl chains of the fatty acids create an unsaturated fat. A fat molecule with no double bonds in any of its alkyl chains is known as a saturated fat. A double bond creates a bend in an alkyl.
2 Carbohydrate should be analysed by a method that allows determination of both available carbohydrate and dietary fibre. For energy evaluation purposes standardized direct analysis of available carbohydrate by summation of individual carbohydrates Southgate 1976. Hicks 1988 is preferred to assessment of available carbohydrate by difference ie.
Total carbohydrate by difference minus. Glycerol molecule and fatty acid chains diff in the length of the chin although the chains have an even number of carbons 0 Comments Posted by Dominique Williams on 1032017 111807 AM Votes 000 Thumps Up Thumps Down. 22 The Percent Daily Values are based on a 2000 calorie diet so your values may change depending on your calorie needs.
The values here may not be 100 accurate because the recipes have not been professionally evaluated nor have they been evaluated by the US. PLAIN BAGEL ENRICHED FLOUR WHEAT.