Chemicals listed in Column A should not be stored with or used near items in Column B. To collect a liquid sample the glass rod is inserted into the liquid and a finger is placed over the top opening of the rod.

Chapter 4 provides specific guidelines for evaluating the hazards and assessing the.
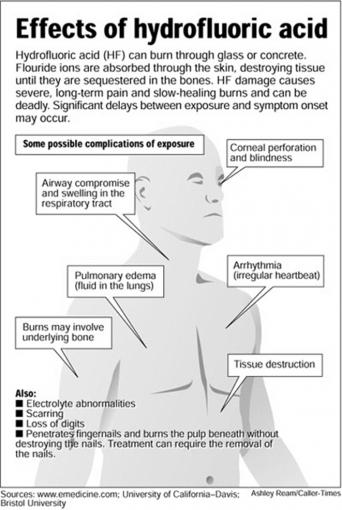
Incompatible glass hydrofluoric acid. Hydrofluoric acid is an irritant to the mucosa of the upper and lower portions of the respiratory tract. As in ocular tissues concentrations as low as 5 mgL 5 ppm may produce irritation to the nasal mucosa. When hydrofluoric acid is present in concentrations greater than 48 the solution fumes adding to the volatile airborne fraction.
Inhalation Exposure Inhalation of hydrofluoric acid vapors may cause severe throat. Dry place away from incompatible materials. HF reacts with many materials therefore avoid contact with glass concrete metals water other acids oxidizers reducers alkalis combustibles organics and ceramics.
Store in containers made of polyethylene or fluorocarbon plastic lead or platinum. Use plastic containers and secondary containment Hydrofluoric acid can result in severe burns to skin and lungs Corrosive Bases-Hydroxylamine Store in separate cabinet Acids Heat Caustic Tetramethylethylamine preferably with ventilation Oxidizers Gas Generation Diamine corrosive cabinet or storage area Flammable Liquids Violent Reaction Triethylamine with a spill tray away from. Hydrofluoric Acid G Not Intrinsically Reactive or Flammable or Combustible Acrylamide.
To provide separation of incompatible materials and to provide information for emergency response personnel. Criteria for Storage Area xStore chemicals inside a closeable cabinet or on a sturdy shelf with a front-edge lip to prevent accidents and chemical spills. XSecure shelving to the wall or floor.
Hydrochloric acid sulfuric acid hydrofluoric acid phosphoric acid. Bases and cyanides. Corrosives Organic Acids.
Store in a corrosive storage cabinet or in secondary containment. Acetic acid trichloroacetic acid lactic acid. Bases and cyanides.
Store in a corrosive storage cabinet or in secondary containment. Not more than 60 gallons may be Category 1 2 or 3 liquids. No more than 120 gallons of Category 4 liquids may be stored in a storage cabinet according to OSHA 29 CFR 1910106d3i.
For ease of locating chemicals many storerooms organize chemicals alphabeticallyHowever chemical storage based upon an alphabetical arrangement of chemicals may inadvertently locate incompatible. Examples of Incompatible Chemicals. The following list is not a complete listing of incompatible materials.
It contains some of the more common incompatible materials. Always research materials you work with in order to work safely in the lab. Chemicals listed in Column A should not be stored with or used near items in Column B.
Chromic acid nitric acid. For example do not use a metal container to store acids do not use a glass container to store hydrofluoric acid do not use glass or metal containers to store organic peroxides and do not use metal containers to store picric acid and solutions of picric acid. Do not use containers that can be confused with consumer commodities like soda bottles or milk jugs.
Do not use metal containers for. Non-corrosive in presence of glass. Special Remarks on Reactivity.
Reacts violently with water and alcohol especially when water is added to the product. Incompatible can react explosively or dangerously with the following. ACETIC ACID ACRYLIC ACID AMMONIUM HYDROXIDE CRESOL CUMENE DICHLOROETHYL ETHER ETHYLENE CYANOHYDRIN.
PVC Polyvinyl chloride Chemical Compatibility Chart. Check the chemical compatibility of Polyvinyl chloride PVC with various chemicals solvents alcohols and other products. The information in this chart has been supplied by reputable sources and is to be used ONLY as a guide in selecting equipment for appropriate chemical compatibility.
Hydrofluoric Acid Concentrated solutions of HF will remove just about everything from glass and will even etch the surface of the glass itself. It should not be used on calibrated volumetrics. HF causes severe painful burns that do not heal well and prolonged or intense exposure can lead to a very slow painful death.
It is notto be used by any students at Truman under any circumstances. One can use manual shaking using a glass stirring rod. The magnetic stirrer makes the dissolving process easy and convenient.
If you want you can heat the solution 60C to accelerate the dissolving process. Do not dissolve in 1000 ml of deionized Milli-Q water. In most cases solution volume increases when a large amount of solute dissolves in a solvent.
Adjust pH to. Mixing in equal molar portions with any of the following substances in a closed container caused the temperature and pressure to increase. 2-aminoethanol ammonium hydroxide 28 chlorosulfonic acid ethylenediamine ethyleneimine ethylene cyanohydrin hydrochloric acid 36 hydrofluoric acid 487 isopropyl alcohol nitric acid 70 2-nitropropane propiolactone propylene oxide.
Never mix incompatible materials together in a single container see Section 5241. Wastes must be stored in containers compatible with the chemicals stored. For example hydrofluoric acid waste must not be stored in glass containers corrosive chemicals must not be stored in metal containers etc.
In 1893 Gruber adapted this cameo process to stained glass by etching with hydrofluoric acid the same process touted as original when introduced by Charles Marq as a way to fabricate Marc Chagalls designs. Father Alain Couturier an artist spent the years of World War II in New York where he met many ex-patriot artists. After the war he returned to France and began work on the.
Powerful oxidizers such as fluorine chlorine trifluoride and oxygen difluoride and hydrofluoric acid. Silica will dissolve in hydrofluoric acid and produce a corrosive gas silicon tetrafluoride. Acute effects of exposure.
Examples of incompatible chemicals include. A acidbase pairs redox pairs. B picric acid trinitrotolueneCH 3 N 2.
Organic solvents are potential hazards because. A most organic solvents are volatile and flammable. B most organic solvents absorb directly through the skin.
C most organic liquids burn. D all of the above. Solvents such as THF and.
Acid-based cleaning products may be used on non-acid sensitive masonry which generally includes. Granite most sandstones slate unglazed brick and unglazed architectural terra cotta cast stone and concrete. Most commercial acidic cleaners are composed primarily of hydrofluoric acid and often include some phosphoric acid to prevent rust-like stains from developing on the masonry after the.
Chen et al. Took yet another approach investigating microfluidic devices based on a glassPDMSglass sandwich configuration. The main advantage of such devices is the possibility to dismount and reuse them in various applications.
Their proposed sandwich configuration could exceedingly increase the sealing strength of reversibly adhered devices being also able to withstand. Prudent execution of experiments requires not only sound judgment and an accurate assessment of the risks involved in the laboratory but also the selection of appropriate work practices to reduce risk and protect the health and safety of trained laboratory personnel as well as the public and the environment. Chapter 4 provides specific guidelines for evaluating the hazards and assessing the.
Are sinks equipped with glass traps to be used with all chemicals except when using hydrofluoric acid 42 Housekeeping and maintenance. Is the laboratory kept in a neat orderly arrangement. 10142c Are benches floors shelves and hoods kept free of reagents and equipment not in use.
1011 Do all laboratory employees clean their working areas regularly. Quantitative Chemical Analysis 7E Daniel C. Glass sample collection rods are commonly used to retrieve liquid samples from closed top drums.
To collect a liquid sample the glass rod is inserted into the liquid and a finger is placed over the top opening of the rod. Rubber aspirator bulbs are also available to assist with this process. Liquid sampling often results in small spills and plastic sheeting and splash protection may be.
Academiaedu is a platform for academics to share research papers. Mixing with any of the following substances in a closed container caused the temperature and pressure to increase. Glacial acetic acid acetic anhydride acrolein chlorohydrin chlorosulfonic acid ethylene cyanohydrin glyoxal hydrochloric acid 36 hydrofluoric acid 487 nitric acid 70 oleum propiolactone sulfuric acid 96 NFPA 1991.
Accidental contact between a caustic.