
In the second step of the oxidative phase 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone is hydrolyzed to 6-phosphogluconate a linear molecule. C e-23-diol CH3 Molecular Redox Reactions.
Further since ester A contains eight carbon atoms therefore.
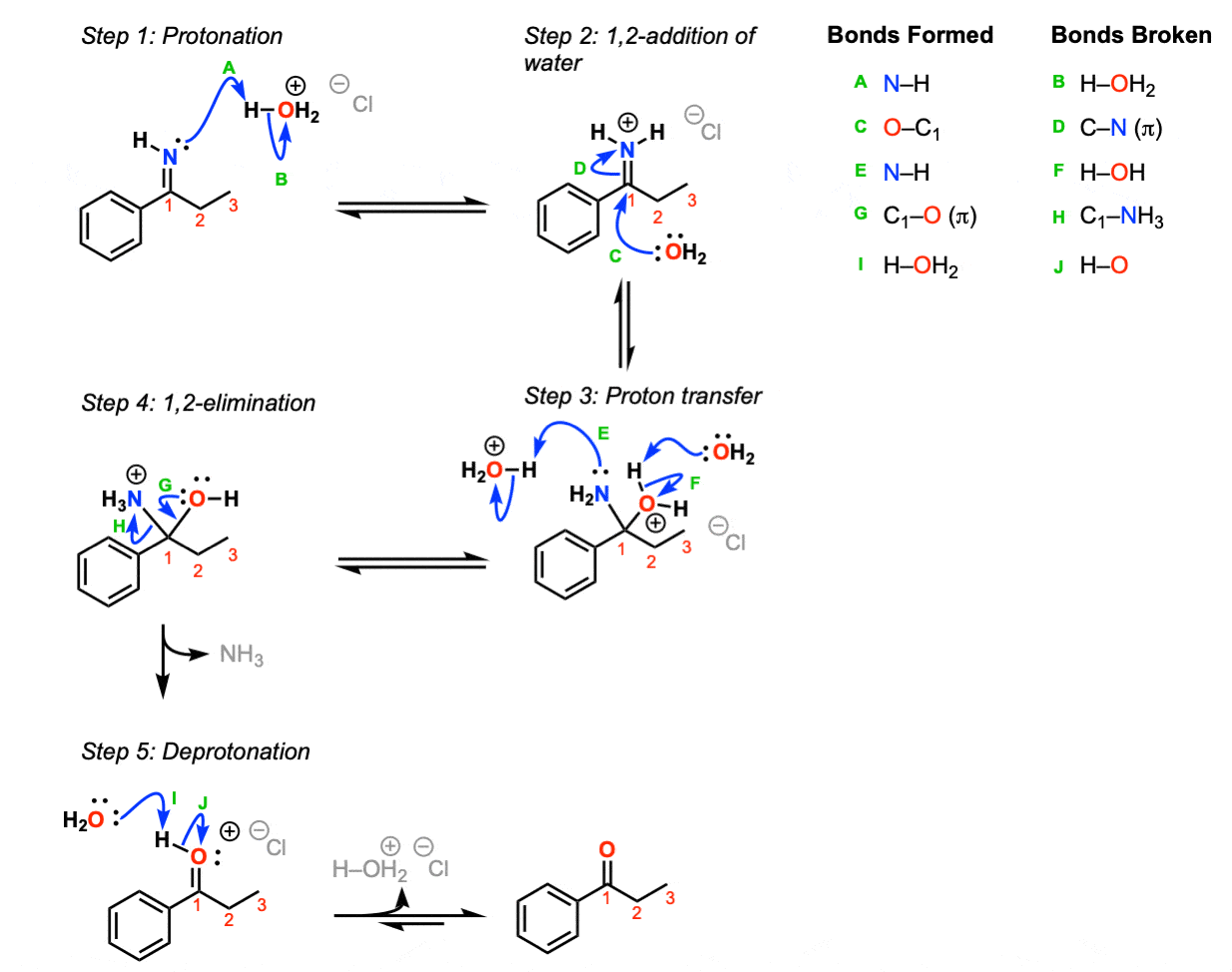
Imine undergoes hydrolysis. Protonation of the imine nitrogen Step 1 arrows A and B results in the formation of the iminium ion which undergoes 12-addition by water Step 2 arrows C and D. Transfer of a proton Step 3 arrows E and F followed by 12 elimination of ammonia Step 4 arrows G and H lead to an oxonium ion which is then deprotonated to give the neutral ketone. The chemical stability of most imine COFs is however still far from satisfactory since they undergo hydrolysis under strongly acidic conditions or exchange with amines due to the reversible nature.
A sulfonic acid or sulphonic acid refers to a member of the class of organosulfur compounds with the general formula RSO 2 OH where R is an organic alkyl or aryl group and the SO 2 OH group a sulfonyl hydroxide. As a substituent it is known as a sulfo groupA sulfonic acid can be thought of as sulfuric acid with one hydroxyl group replaced by an organic substituent. A thiophosphonate group is a functional group related to phosphonate by substitution of an oxygen atom for a sulphur.
They are a reactive component of many pesticides and nerve agentsSubstituted thiophosphonates can have 2 main structural isomers bonding though either O or S groups to give thione and thiol forms respectively. This is a property they share with related functional groups such. R 3 C-NH 2.
A specific example of each general class is provided in the diagram below. In the first two an anionic nitrogen species undergoes an S N 2 reaction with a modestly electrophilic alkyl halide reactant. For example 2 an acidic phthalimide derivative of ammonia has been substituted for the sulfonamide analog listed in the table.
The principle is the same for the two. Here we report the discovery of RedAm activity in an imine reductase enzyme for the direct reductive amination of a cyclic ketone with methylamine. We also investigate engineering the enzyme to.
Another reaction that is often used to produce carboxylic acids is the hydrolysis of nitriles RCN. The nitrile carbon is at the same oxidation state as a carboxylic acid and when treated with aqueous acid or base it undergoes a hydrolysis reaction in just the same way as we have seen on numerous occasions try ityou will see. In this method the lipase enzyme hydrolyzes the triglyceride into glycerol and fatty acids.
Glycerol undergoes phosphorylation then oxidation reaction in which peroxide is generated which condenses with chromogen 4-amino antipyrine 4-AAP4-aminophenazone to form red-colored quinone-imine dye. The absorbance is measured at 505 nm. R 3 C-NH 2.
A specific example of each general class is provided in the diagram below. In the first two an anionic nitrogen species undergoes an S N 2 reaction with a modestly electrophilic alkyl halide reactant. For example 2 an acidic phthalimide derivative of ammonia has been substituted for the sulfonamide analog listed in the table.
The principle is the same for the two. The transdermal patch reduces side effects such as nausea and vomiting. Rivastigmine undergoes extensive metabolism by ChE-mediated hydrolysis to the decarbamylated metabolite without involvement of the major cytochrome P450 CYP450 isozymes.
The metabolite may undergo N-demethylation as well as conjugation. The pharmacokinetic half-life of. The phthalamide undergoes base catalyzed hydrolysis.
The product is decarboxylated with heat and acid to form a chiral amino acid. In this case since the decarboxylation reaction is non-stereospecific but produces a chiral amino acid the product of decarboxylation is also a racemic mixture of L and D amino acids. In other words both the Strecker and Gabriel synthesis reactions result in a.
Sodium borohydride is considered to be a selective reagent 31 which means that it is a weaker reducing agent when compared to LiAlH 4 eg see Section 76Sodium borohydride is useful for the reduction of aldehydes ketones or acid chlorides in the presence of other easily reducible functional groups. 32 The relatively poor reactivity of sodium borohydride is reflected in the solvents. Hydrolysis of the reduction product recreates the original aldehyde group in the final product.
Addition of hydrogen cyanide. The addition of hydrogen cyanide to a carbonyl group of an aldehyde or most ketones produces a cyanohydrin. Sterically hindered ketones however dont undergo this reaction.
The mechanism for the addition of hydrogen cyanide is a straightforward nucleophilic addition. Hydrolysis of 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone to 6-phosphogluconate. In the second step of the oxidative phase 6-phosphoglucono-δ-lactone is hydrolyzed to 6-phosphogluconate a linear molecule.
6-Phosphoglucono-δ-lactone is hydrolytically unstable and undergoes a nonenzymatic ring-opening a reaction that occurs at a significant rate. However in the cell this ring-opening reaction an. The first-used COF linking groups based on boroxine and boronated bonds were plagued from poor chemical stability eg cleaved by hydrolysis several others linkers have now been successfully incorporated resulting in more robust frameworks based on imine β-ketoenamine hydrazone azine and imide-type linkages among others Chart 1b.
Ni Nanoparticle-Immobilized Imine-Linked Microspherical Covalent Organic Polymer for Degradation Studies of Organic Dyes. Awasthi ACS Applied Polymer Materials 2021 3 11 5460-5469 Article Publication Date Web. Superhydrophilic Sandwich Structure Aerogel Membrane for Emulsion Separation and Heavy Metal.
Viii Imine ix 24-DNP derivative x Schiffs base. Since an ester A with molecular formula C 8 H 16 O 2 upon hydrolysis gives carboxylic acid B and the alcohol C and oxidation of C with chromic acid produces the acid B therefore both the carboxylic acid B and alcohol C must contain the same number of carbon atoms. Further since ester A contains eight carbon atoms therefore.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Free PDF Download. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids is an excellent source of study material for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry. These NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry are prepared by highly experienced tutors according to the latest term II CBSE Syllabus 2021-22.
The released thiolate undergoes intramolecular 14-addition to the enone triggering a Bergman cyclisation that produces a di-radical. This reactive intermediate is capable of abstracting hydrogen atoms from the deoxyribose backbone to produce double strand DNA breaks which in turn result in cell death Figure 28. The hydrolysis of t-butyl chloride is an example.
Ethyl acetoacetate reacts with strong base forms a resonance-stabilized enolate ion followed by the reaction with propyl bromide forms a substitution product. Of the options given I thought product 1 would be correct seeing as how it has the most stable intermediate cation tertiary and a highly substituted double bond. Hydrolysis of MOF and coordination polymer electrode materials in alkaline electrolyte is inevitableHowever we have found that the hydrolysis of cyanide-bridged nickel-based coordination polymer electrode materials can be suppressed by the introduction of pillared pyrazine ligands.
This optimizes the electrochemical performance. Undergoes violent or explosive reactions with 2-aminoethanol chlorosulfonic acid ethylenediamine mineral acids hydrochloric acid hydrofluoric acid nitric acid sulfuric acid oleum and peroxides Lewis 3rd ed 1993 p. Polymerization initiated by dibenzoyl peroxide in ethyl acetate accelerated out of control ignited and exploded Vervalin 1973 p.
It is prepared by the hydrolysis of ethanal cyanohydrin or through the oxidation of propan-12-diol with dilute nitric acid. An alpha hydroxy carboxylic acid it is produced in the human body from pyruvic acid and ends up in the liver where it is converted to glucose. FTP identify this chemical compound technically known as 2-hydroxypropanoic acid which causes cramping pains when it.
The Lewis acid catalyst AlCl 3 undergoes reaction with the alkyl halide resulting in the formation of an electrophilic carbocation. Gº - RT ln K eq H - T S If Keq 1 energy is released to the surroundings exergonic reaction negative value of Gº reaction favored In organic chemistry the oxy-Cope rearrangement is a chemical reaction. The product 4-4 has been numbered so that the.
Form imine from final ketone. CH3CH2I B t-butyl alcohol 1. 96109 Predict the product for the following reaction.
42 Which of the following reaction series will result in the formation of a new secondary 2 alcohol from the beginning alcohol listed at the top. C e-23-diol CH3 Molecular Redox Reactions. The correct option is.