Children owing to crawling and frequent hand-to-mouth contact ingest settled dust daily. 53 48 Individual exposure dose and risk estimates.

2 People with.
Human exposure assessment for airborne pollutants. The diagram shows specific examples of how climate change can affect human health now and in the futureThese effects could occur at local regional or national scales. The examples listed in the first column are those described in each underlying chapters exposure pathway diagram see Guide to the Report. Moving from left to right along one health impact row the three middle columns.
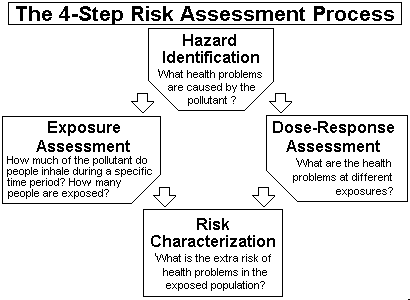
Exposure assessment is the process of measuring or estimating the magnitude frequency and duration of human exposure to an agent in the environment or estimating future exposures for an agent that has not yet been released. An exposure assessment includes some discussion of the size nature and types of human populations exposed to the agent as well as discussion of the. These changes would in turn modify emissions depending on the fuel source and thus further influence air quality.
6 7 Some air pollutants such as ozone sulfates and black carbon also cause changes in climate. 8 However this chapter does not consider the climate effects of air pollutants remaining focused on the health effects resulting from climate-related changes in air pollution exposure. Sources of Human Exposure.
Aluminium and its compounds comprise about 8 of the Earths surface. Aluminium occurs naturally in silicates cryolite and bauxite rock. Natural processes account for most of the redistribution of aluminium in the environment.
Acidic precipitation mobilizes aluminium from natural sources and direct anthropogenic releases of aluminium compounds associated with. The human lung is subjected to airborne pollutants and irritants with each breath. Generally respiratory symptoms result from the inflammation of airway when exposed specifically to allergens toxins or pro-inflammatory agents.
According to the community based follow-up of 422 Canadian children beta-glucan exposure at age 710 years was found to develop and persist atopicnon-atopic. Infectious disease transmission is sensitive to local small-scale differences in weather human modification of the landscape the diversity of animal hosts 71 and human behavior that affects vector-human contact among other factors. There is a need for finer-scale long-term studies to help quantify the relationships among weather variables vector range and vector-borne pathogen.
Worldwide exposure to PM 25 contributed to 41 million deaths from heart disease and stroke lung cancer chronic lung disease and respiratory infections in 2016. Overall ambient particulate matter ranks as the sixth leading risk factor for premature death globally. Some particulates occur naturally originating from volcanoes dust storms forest and grassland fires.
Federal controls on lead in gasoline new paint food canning and drinking water as well as lead from industrial air emissions have significantly reduced total human exposure to lead. The number of children with blood lead levels above 10 micrograms per deciliter µgdL a level designated as showing no physiologic toxicity has declined from 17 million in the late 1980s to 310000 in. 46 Exposure assessment calculations.
52 47 Data analysis and evaluation. 53 48 Individual exposure dose and risk estimates. 54 49 Issues in exposure assessments.
55 410 Exposure assessment of volatile agents. 56 411 Exposure duration. 56 412 Adjustments for sensitive sub-populations.
58 413 Default values for exposure assessments. 58 414 Sources of. In a study conducted by Yale University Environmental Inequality in Exposures to Airborne Particulate Matter Components in the United States Hispanics were exposed to 10 out of the 14 pollutants eg 152 higher than whites for chlorine 94 higher for aluminum African Americans were exposed to 13 out of the 14 pollutants eg 43 higher for zinc 25 for vanadium and Asians had.
Human exposure to MPs could also occur through ingestion for example fibrous MPs can settle on the floor. Children owing to crawling and frequent hand-to-mouth contact ingest settled dust daily. Can we find fibrous microplastics in the atmosphere.
To date and to the best of our knowledge only two studies have demonstrated the presence of fibrous MPs in the atmospheric compartment. More than 12 million people around the world die every year because they live or work in unhealthy environments. 1 Healthy People 2030 focuses on reducing peoples exposure to harmful pollutants in air water soil food and materials in homes and workplaces.
Environmental pollutants can cause health problems like respiratory diseases heart disease and some types of cancer. 2 People with. We would like to show you a description here but the site wont allow us.
The second edition of the Plastic Health Summit will take place on October 21st 2021 in Amsterdam. This year its all about One Health. Because for us theres no doubt about it.
Environmental health and human health are inextricably linked. Join us as we discuss the connection between plastic particles plastic additives and human health environmental justice and meet the next. Soon after exposure to some indoor air pollutants symptoms of some diseases such as asthma may show up be aggravated or worsened.
The likelihood of immediate reactions to indoor air pollutants depends on several factors including age and preexisting medical conditions. In some cases whether a person reacts to a pollutant depends on individual sensitivity which varies tremendously. In most cases natural and anthropogenic human caused air pollution consists of complex mixtures of chemical and biochemical species as well as pathogens and the earth-sourced or earth-hosted component can be difficult to asses Earth Materials and Health pg62 More research can be done to improve human health by finding the sources of airborne pathogens geologically and.
Data necessary for the IPS and an initial hazard assessment are called Hedset and cover issues such as environmental exposure environmental effects exposure to humans and human health effects. At the UNCED meeting on the Environment and Sustainable Development in Rio de Janeiro in 1992 it was decided to create an Intergovernmental Forum on Chemical Safety IGFCS Chapter 19 of Agenda 21. New estimates in 2018 reveal that 9 out of 10 people breathe air containing high levels of pollutants.
Both ambient outdoor and household indoor air pollution are responsible for about 7 million deaths globally per year. In the Western Pacific Region alone. Migration involves exposure to a new set of air pollutants and allergens as well as changes in housing conditions diet and accessibility to medical services all of which are likely to affect migrants health.
Atopy and asthma are more prevalent in developed and industrialised countries compared with undeveloped and less affluent countries and the effect of migration is age and time. Studies show that higher PM 25 exposure can impair brain development in children. Black carbon BC Black carbon is one of the components of particulate matter and comes from burning fuel especially diesel wood and coal.
Most air pollution regulations focus on PM 25 but exposure to black carbon is a serious health threat as well. A Framework for Cumulative Risk Assessment. Exploring the Carcinogenic Effects of Chemical Mixtures.
Most Read The Brain before Birth. Using fMRI to Explore the Secrets of Fetal Neurodevelopment. Environmental Impact of the Clothing Industry.
Air Pollution Includes Gases and Particles. Air pollution consists of gas and particle contaminants that are present in the atmosphere. Gaseous pollutants include sulfur dioxide SO 2 oxides of nitrogen NO x ozone O 3 carbon monoxide CO volatile organic compounds VOCs certain toxic air pollutants and some gaseous forms of metalsParticle pollution PM 25 and PM 10 includes a.