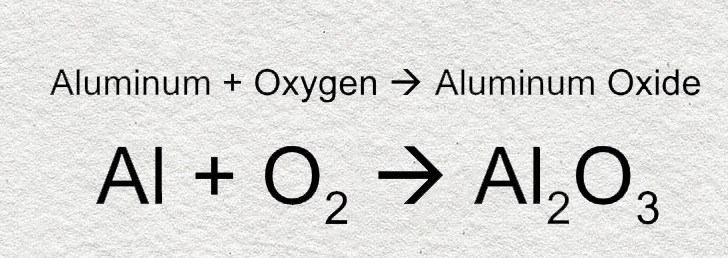
Passivation involves creation of an outer layer of shield material that is applied as a microcoating created by chemical reaction with the base material or allowed to build by spontaneous oxidation in the air. Bauxite consists of 45-60 aluminum oxide along with various impurities such as sand iron and other metals.
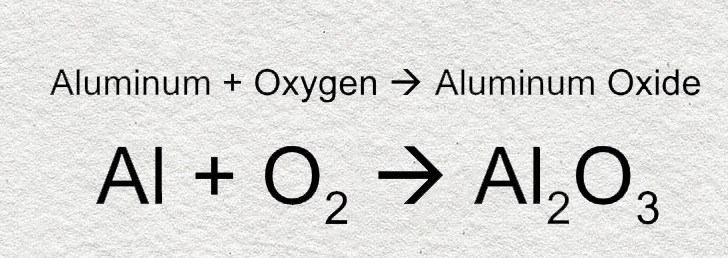
By the end of the 1700s aluminium oxide was known to contain a metal but it defeated all attempts to extract it.
How does aluminum oxide form on metal. Iron oxide rust is a soft red colored metal that begins to expand and flake off as it is chemically transformed which exposes more of the underlying steel or iron to the air and the process continues until the metal is completely transformed to iron oxide. Aluminum oxide is different. It is actually quite hard and serves as a protective coating around the underlying aluminum.
The process of aluminum corrosion is known as oxidation. The resulting aluminum oxide is a thin hard layer that actually protects the metal from further corrosion. Aluminum oxide appears as a powdery white or dull gray coating.
As oxidation occurs it hardens and creates a protective layer over the newly exposed areas of corroded aluminum. Inhalation exposure to 100 mghr aluminium in the form of powder or 92 mg Al per 2 hr as a fume each day for 9-13 months showed a significant retention of aluminium in the lungs of both groups of animals. The aluminium retention in the lungs in rats and hamsters exposed to fume was much greater than when exposed to powder.
Following exposure to fresh air aluminium oxide was cleared. Rather than flaking though aluminum oxide just forms a hard whitish-colored surface skin. When all the aluminum atoms have bonded with oxygen the oxidation process stops.
Scratching this oxide skin exposes bare metal and the process begins again. It wont eat the metal away though except under two conditions. An oxide ˈ ɒ k s aɪ d is a chemical compound that contains at least one oxygen atom and one other element in its chemical formula.
Oxide itself is the dianion of oxygen an O 2 molecular ion. Metal oxides thus typically contain an anion of oxygen in the oxidation state of 2. Most of the Earths crust consists of solid oxides the result of elements being oxidized by the.
ALUMINUM became an economic competitor in engineering applications toward the end of the 19th century. The reason aluminum was not used earlier was the difficulty ofextracting it from its ore. When the electrolytic reduction ofaluminum oxide Al2O3 dissolved in molten cryolite was independently devel oped by Charles Martin Hall in the United States and Paul T.
Heroult in France the. Anodic aluminum oxide AAO typically produced via the electrochemical oxidation of aluminum is a nanostructured aluminum-based material with a very unique structure. AAO contains cylindrical pores that provide for a variety of uses.
It is a thermally and mechanically stable compound while also being optically transparent and an electrical insulator. The pore size and thickness of AAO can. Aluminum is the third most abundant element in the world and the most abundant metal in the earths crust.
Aluminum contributes to more than 8 of the earths core mass. However it is difficult to refine compared to other metals such as iron. For this reason the use of aluminum has lagged behind other metal products while efficient and cost-effective methods were developed to overcome.
Passivation in physical chemistry and engineering refers to coating a material so it becomes passive that is less readily affected or corroded by the environment. Passivation involves creation of an outer layer of shield material that is applied as a microcoating created by chemical reaction with the base material or allowed to build by spontaneous oxidation in the air. Aluminum resists corrosion from the atmosphere if there is an absence of narrow crevices.
Many statues erected over a hundreds of years ago have not deteriorated badly which is in contrast with aluminum cables used in seawater. The corrosion resistance of aluminum is due to its tendency to form a compact oxide layer over the surface. The metal oxide semiconductors which operate at low.
Solid solutions can be formed by the dopants and the host metal oxides. Dopants can either form solid solution by substitution of the host atoms from the lattice or these can be interstitially present in the host lattice. Interstitially dissolved foreign atoms may change the strain in the lattice and when ionized their charge affects.
The focus of this document is on aluminium metal aluminium oxide and aluminium hydroxide. However in order to more fully understand their toxicity and related human health effects other pertinent studies involving aluminium compounds were reviewed. The basis for this is that the chemistry and biochemistry of the aluminium ion Al 3 dominate the pathways that lead to toxic outcomes.
The analysis of a curious metal ornament found in the tomb of Chou-Chu a military leader in 3 rd century China turned out to be 85 aluminium. How it was produced remains a mystery. By the end of the 1700s aluminium oxide was known to contain a metal but it defeated all attempts to extract it.
Humphry Davy had used electric current to extract sodium and potassium from their so-called. Bauxite consists of 45-60 aluminum oxide along with various impurities such as sand iron and other metals. Although some bauxite deposits are hard rock most consist of relatively soft dirt that is easily dug from open-pit mines.
Australia produces more than one-third of the worlds supply of bauxite. It takes about 4 lb 2 kg of bauxite to produce 1 lb 05 kg of aluminum metal. Alloying element in bronze brass aluminum and other metal alloys for zinc die casting alloys for zinc dry cell and zincair batteries for the production of zinc sheet for architectural and coinage applications as a reducing agent in organic chemistry and for other chemical applications.
In the form in which it is sold this product. Aluminum for example forms a thin very tough sapphire-like oxide coat. It slows down the diffusion of oxygen to the metal so its self-limiting.
Its very protective for most purposes but its electrically insulating which is why there are big problems with aluminum wiring. Most other oxide layers arent so tough but I dont know of any others that are as loose and flaky as rust. Aluminum and its alloys have a great affinity for oxygen.
Pure aluminum melts at 1200F 650C and the oxide that protects the metal melts at 3700F 2037C. Because the oxide melts at a temperature approximately 2500F 1370C higher than the aluminum itself the oxide must be cleaned from the metal before welding can begin. Contrasted to an applied coating which bonds to the metal but does not react chemically A black oxide conversion coating is applied to ferrous alloys when oxidizing salts react with the iron to form magnetite Fe 3 O 4 the black oxide of iron.
Though standard Black Oxide is set up for steel it can be done on other substrates including stainless steel copper and brass among others. Aluminum is lightweight conducts heat well and is fairly inexpensive making it a popular choice for cooking. Canadians normally take in about 10 milligrams of aluminum daily mostly from food.
Aluminum pots and pans provide only one or two milligrams of the total. While aluminum has been associated with Alzheimers disease there is no definite link proven. The World Health Organization.
They react with oxygen and form metal oxides. For example sodium is a very reactive. When sodium is cut or scratched its freshly exposed shiny surface rapidly turns dull as a thin layer.
The first two are corundum ie. Aluminium oxide Al 2 O 3 in crystal form. Its naturally transparent and in terms of strength its only second to diamonds.
Sapphire is used in bullet proof glass aeroplane windows scratch resistant smartphone screens. In the meantime one of the less precious corundum minerals emery is used as an abrasive for example in sand cloth. Molten salts or other non-aqueous media like ionic liquids provide an alternative electrolyte in which aluminum does not form the surface oxide film and can be successfully electrodeposited from the electrolyte Li and Bjerrum 2002.
However the major obstacle in using ionic liquids is the lack of oxidatively stable inexpensive current collectors that can operate in chloroaluminate ionic. The exposed surface of aluminum combines with oxygen to form an inert aluminum oxide film only a few ten-millionths of an inch thick which blocks further oxidation. And unlike iron rust the aluminum oxide film does not flake off to expose a fresh surface to further oxidation.
If the protective layer of aluminum is scratched it will instantly reseal itself. The thin oxide layer itself. Aluminum alloys contain almost no iron and without iron the metal cant actually rust but it does oxidize.
When the alloy is exposed to water a film of aluminum oxide forms quickly on the surface. The hard oxide layer is quite resistant to further corrosion and protects the underlying metal. The flow dependent chemical dissolution of the oxide.
Cathodic protection does not stop this phenomenon and coatings have to be used. Aluminum corrosion cathodic protection seawater hydrodynamics Introduction Use of aluminum alloys in seawater is of continuous interest because of the need for light-weight structural materials. As long as galvanic contact with more noble.