Two new single bonds are formed C 1-C 6 C 4-C 5 One new pi bond is formed C 2-C 3. A501 Hot Formed Carbon Steel Structural Tubing - Grade B.
This characteristic makes an acetal an ideal protecting group for aldehyde molecules that must undergo further reactions.
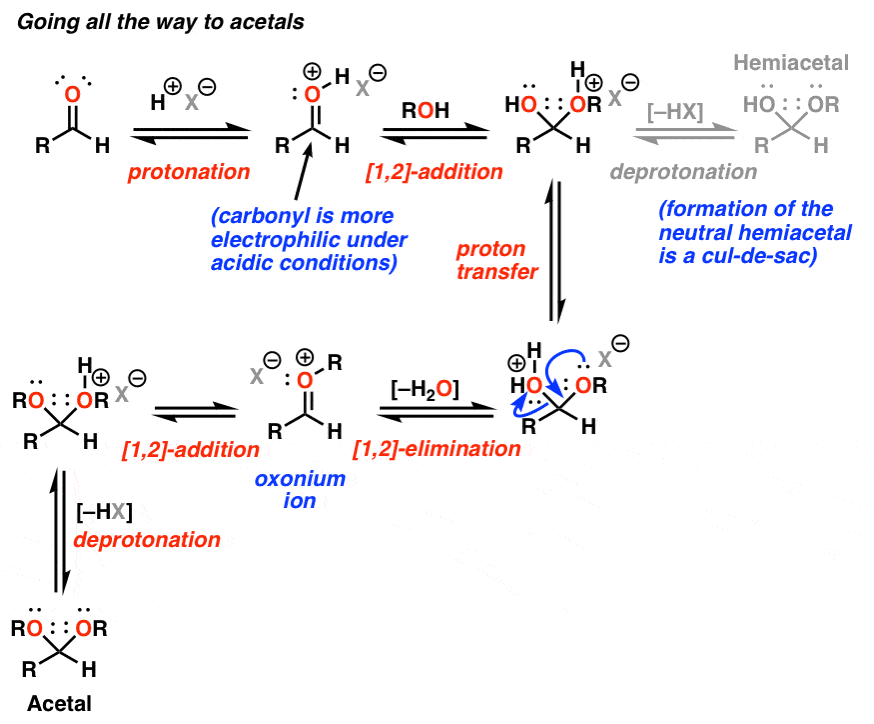
How are acetals formed. Acetals are formed from and convertible to aldehydes or ketones and have the same oxidation state at the central carbon but have substantially different chemical stability and reactivity as compared to the analogous carbonyl compounds. The central carbon atom has four bonds to it and is therefore saturated and has tetrahedral geometry. The term ketal is sometimes used to identify structures.
Acetals are geminal-diether derivatives of aldehydes or ketones formed by reaction with two equivalents of an alcohol and elimination of water. Ketone derivatives of this kind were once called ketals but modern usage has dropped that term. The following equation shows the overall stoichiometric change in acetal formation but a dashed arrow is used because this conversion does not occur on.
Acetals are geminal-diether derivatives of aldehydes or ketones formed by reaction with two equivalents or an excess amount of an alcohol and elimination of water. Ketone derivatives of this kind were once called ketals but modern usage has dropped that term. It is important to note that a hemiacetal is formed as an intermediate during the formation of an acetal.
An Informational Brief on Polymer Machining. Delrin also commonly known as an acetal polyoxymethylene homopolymer is an impact and wear resistant semi-crystalline thermoplastic popular for a broad range of machining applications. Acetals are formed from aldehydes or ketones plus alcohols in the presence of acid We said that a solution of acetaldehyde in methanol contains a new compound.
Weve also said that the rate of formation of hemiacetals is increased by adding an acid or a base catalyst to an alcohol plus aldehyde mixture. But if we add catalytic acid to our acetaldehydemethanol 342 14. The Greek prefix hèmi means half refers to the fact that a single alcohol has been added to the carbonyl group in contrast to acetals or ketals which are formed when a second alkoxy group has been added to the structure.
Cyclic hemiacetals and hemiketals are sometimes called lactols. These ethers again are formed by Williamson-type reactions. However the chloromethyl acetal must be converted in situ to the iodide 111 or activated with Ag.
116 Further methods for MTM introduction consist of a Pummerer rearrangement with dimethyl sulfoxide DMSO and acetic anhydride 117a or treatment of the respective alcohol with dimethyl sulfide in the presence of dibenzoyl peroxide. Acetate-derived TMS and triethylsilyl ketene acetals undergo a mild organoaluminium-catalysed 13-migration 316 of silicon from oxygen to carbon to produce trialkylsilylacetic acid esters Scheme 66. The same rearrangement with TMS enol ethers proved unsuccessful.
2-Chloroalkanoic acids can be prepared with high ee by the diastereoselective halogenation 317 of sugar-derived silyl. Alternatively the imine may be formed in a prior step and then reduced by NaBH 4. Acetic acid may be used as catalyst with ketone reactions.
Acid sensitive functional groups such as acetals and ketals and reducible functional groups such as C-C multiple bonds and cyano and nitro groups are tolerated. Acetal formation reactions are reversible under acidic conditions but not under alkaline conditions. This characteristic makes an acetal an ideal protecting group for aldehyde molecules that must undergo further reactions.
A protecting group is a group that is introduced into a molecule to prevent the reaction of a sensitive group while a reaction is carried out at some. A501 Hot Formed Carbon Steel Structural Tubing - Grade B–483. A523 Cable Circuit Steel Piping Grade A–331.
A523 Cable Circuit Steel Piping Grade B–414. A618 Hot-Formed High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Tubing - Grade Ia Ib–483. A618 Hot-Formed High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Tubing - Grade II–414.
A618 Hot-Formed High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Tubing. What is a glycoside. A glycoside is an acetal or ketal formed from the reaction of cyclic monosaccharides with alcohols in the presence of acid.
Generally describe glycoside formation. Hemiacetal sugar alcohol — acetal ring H2O. What is a glycosidic bond.
When two monosaccharide rings are bonded using a C-O-C bond. What is the main difference between glucose and. Acetals are stable to base so this product should not react with Tollens reagent or be reduced by sodium borohydride.
Acid hydrolysis of acetals regenerates the carbonyl and alcohol components and in the case of the glucose derivative this will be a tetramethyl ether of the pyranose hemiacetal. This compound will of course undergo typical aldehyde reactions. By clicking on the diagram a.
A more detailed look at the mode of the cyclization reveals that 4 π electrons are involved in a conrotatory mechanism but any diastereoselectivity involving the new formed σ bond is lost after elimination of the proton. The Nazarov Cyclization is a rare example of a Lewis acid-catalyzed 4-π conrotatory electrocyclic reaction. Acetals that contain different R groups are called mixed acetals.
Acetal is also a common name for the compound 11-diethoxyethane. Acetate Acetate can have several meanings in chemistry. Acetate refers to the ion formed by removing the acidic hydrogen from acetic acid.
The formula for this ion is CH 3 COO. Acetate is a general name for a compound containing the acetate ion. Amines are probably formed mainly by bacterial decarboxylation of amino acids but small amounts may also occur as the result of enzymic reactions of yeast.
1975 showed that the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae can produce the corresponding N -acetylamines from 2-methylbutylamine 3-methylbutylamine and 2-phenethylamine in a fermentation solution. Ketones are formed in the human body as a by-product of lipid metabolism. The two common metabolites produced in humans are the ketone-containing acetoacetic acid and the alcohol metabolite β-hydroxybutyrate.
Acetone is also produced as a breakdown product of acetoacetic acid. Acetone can then be excreted from the body through the urine or as a volatile product through the lungs. Sucrose only has acetal groups and since acetals dont open up to aldehydes under the basic conditions present in the Benedict test sucrose isnt a reducing sugar.
Sucrose gives a negative test blue to the Benedict solution. Another example of a non-reducing sugar are the so-called glucosides of common sugars such as glucose methyl glucoside below. This is obtained by heating.
A501 Hot Formed Carbon Steel Structural Tubing - Grade A. A501 Hot Formed Carbon Steel Structural Tubing - Grade B. A523 Cable Circuit Steel Piping - Grade A.
A523 Cable Circuit Steel Piping - Grade B. A618 Hot-Formed High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Tubing - Grade Ia Ib. A618 Hot-Formed High-Strength Low-Alloy Structural Tubing - Grade II.
33 ketals and acetals comprise more than 700 of the 1323 chemically defined flavoring 34 substances in the United States. Additional structural categories include aromatic 35 heteroaromatic and heterocyclic substances with characteristic organoleptic properties 36 Munro et al 1999. 37 38 Flavors can further be characterized as artificial flavors spices or natural flavors.
Excellent processing stabilizer and antioxidant package for polyacetals. Phenolic based Heat Stabilizer Package with Extended Temperature Range. BRUGGOLEN TP-H1803 Outperforms conventional phenolic based stabilizers.
Improved retention of mechanical performance under heat. Extended heat stabiliza. Two new single bonds are formed C 1-C 6 C 4-C 5 One new pi bond is formed C 2-C 3.
Pay attention to this key pattern because it repeats itself over and over and over. Indeed every Diels-Alder that we learn about will follow this pattern. Three pi bonds are broken.
Two sigma bonds and one pi bond are formed. Alcoholic hydroxyl forms acetals while sulfhydro groups form sulfhydral acetal analogues with formaldehyde. Based on the affinity to combine with formaldehyde proteins could be classified as strong affinity moderate and less affinity ones.
Presences of tyrosine rings in proteins have been identified as an important factor for the affinity of the protein to formaldehyde. In its absence the. At 245 C these newly formed crystals melt.
If the amorphous form of PET were heated from room temperature to the required drying temperature it would agglomerate into one large mass and would then crystallize in that same large mass. To prevent this PET must be constantly agitated while it is heated through its glass-transition temperature and its solid-state recrystallization.