For severe hypertension without tachycardia nitroprusside is recommended as it is easily titrated to effect and has a half-life of minutes. Haloperidol should be started at 50 of the target dose on day 1 and increased to the target dose on day 5.
Haloperidol apparent clearance after extravascular administration ranges from 09 to 15 lhkg and is reduced in poor metabolisers of CYP2D6.
Haloperidol half life. The plasma concentrations of haloperidol decanoate reach a peak at about six days after the injection falling thereafter with an approximate half-life of three weeks. The bioavailability is 100 in intravenous IV injection and the very rapid onset of action is seen within seconds. The T 12 is 141 to 262 hours.
Haloperidol increases levels of eliglustat by affecting hepatic enzyme CYP2D6 metabolism. If coadministered with strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors reduce eliglustat dose from 84 mg BID to 84 mg once daily in extensive and intermediate metabolizers. Eliglustat is contraindiated if strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitors are given concomitantly with strong or.
Haloperidol C21H23ClFNO2 CID 3559 - structure chemical names physical and chemical properties classification patents literature biological activities. The half-life of a drug helps us assess the potency and toxicity of a drug over a given amount of time. 8 h Morphinecalc1129 1-7 h.
The terminal elimination half-life of haloperidol is on average 21 hours range 13 to 36 hours after intramuscular administration. Haloperidol apparent clearance after extravascular administration ranges from 09 to 15 lhkg and is reduced in poor metabolisers of CYP2D6. Reduced CYP2D6 enzyme activity may result in increased concentrations of haloperidol.
The terminal elimination half-life of haloperidol is on average 24 hours range of means 15 to 37 hours after oral administration. Haloperidol apparent clearance after extravascular administration ranges from 09 to 15 lhkg and is reduced in poor metabolisers of CYP2D6. Reduced CYP2D6 enzyme activity may result in increased concentrations of haloperidol.
The inter-subject variability. Haloperidol is a highly lipophilic compound and is extensively metabolized in humans which may cause a large interindividual variability in its pharmacokinetics. 3 Studies have found a wide variance in pharmacokinetic values for orally administered haloperidol with 17-61 hours reported for time to peak plasma concentration tmax 145-367 hours reported for half-life t12.
This medicine half life calculator requires the drug dosage measured in mg µg or g and the half time estimated in hours or minutes. The decrease in plasma concentration is followed at 7 stages. The half time or life of a dose is defined as the period of time after administration in either hours of minutes in which the dosage reaches half of its.
The plasma concentrations of haloperidol gradually rise reaching a peak at about 6 days after the injection and falling thereafter with an apparent half-life of about 3 weeks. Steady state plasma concentrations are achieved after the third or fourth dose. The relationship between dose of haloperidol decanoate and plasma haloperidol.
Apparent half-life of about 3 weeks. Steady state plasma concentrations are achieved after the third or fourth dose. The relationship between dose of haloperidol decanoate and plasma haloperidol concentration is roughly linear for doses below 450 mg.
It should be noted however that the pharmacokinetics of haloperidol decanoate following intramuscular injections can be quite variable. Haloperidol used alone is recommended to help calm situations of aggression or agitation for people with psychosis. It is widely accessible and may be the only antipsychotic medication available in limitedresource areas.
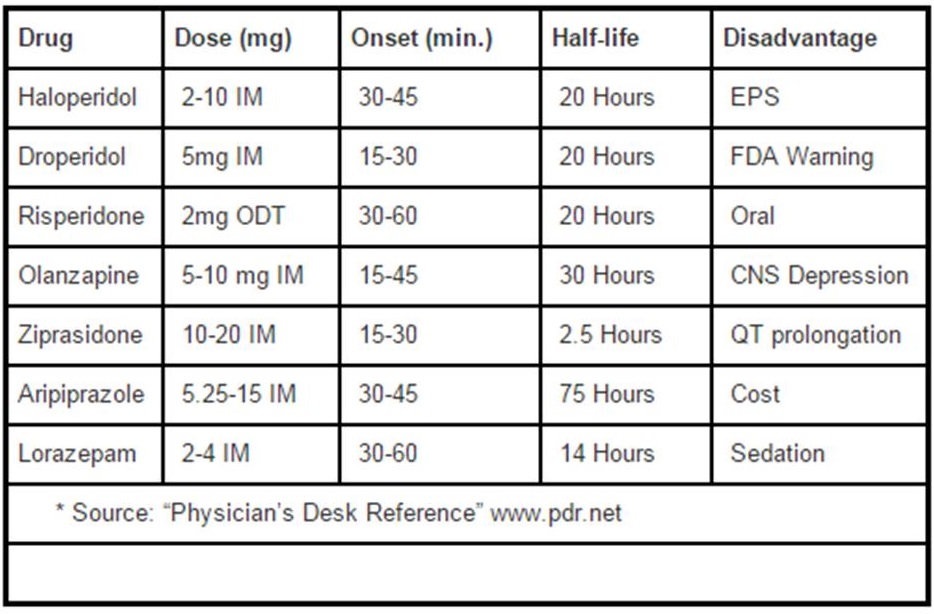
To examine whether haloperidol alone is an effective treatment for psychosisinduced aggression or agitation wherein clinicians are required to intervene to. Droperidol is generally twice as potent as haloperidol so half as much droperidol is needed when compared to the haloperidol doses listed above. Intravenous benzodiazepines midazolam lorazepam back to contents 1 benefits.
2 drawbacks contraindications. Perhaps the most deleriogenic sedative agent acting as. Longer half-life 40 hours.
Superior efficacy compared to ondansetron especially the 8-mg dosing of ondansetron. 025 mg palonosetron IV is a commonly used dose for prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting. There are no real contraindications to palonosetron aside from a history of anaphylaxis to the drug.
The main drawback is cost and availability. Opioid or metabolic induced nausea delirium. 2mg to 5mg over 24 hours.
Can also be given as a once daily SC injection. 25mg in 1ml Complex nausea terminal deliriumagitation. 5mg to 15mg over 24 hours anti-emetic.
25mg to 100mg over 24 hours - sedative. Protect from light. A common example of this is the B-52 with its combination of haloperidol 5 mg diphenhydramine 50 mg and lorazepam 2 mg.
For severe hypertension without tachycardia nitroprusside is recommended as it is easily titrated to effect and has a half-life of minutes. Administration of copious intravenous crystalloid is also recommended to enhance urinary elimination. For medium half-life drugs about a day 50 dose reduction for days 1-3 could be followed by reducing to 25 of initial dose for days 4-6 before discontinuing entirely and all offset by the same up-taper.
For the über-short half medications I was able to use an intuitive crosstaper reciprocally decreasingincreasing doses without any consideration for accumulated serum concentration of. Periciazine is a low-to-medium-potency typical antipsychotic with a short half-life so an extended period of reduction is recommended because of the risk of relapse or cholinergic rebound. Haloperidol should be started at 50 of the target dose on day 1 and increased to the target dose on day 5.
38 to 5 hours. 5 to 6 hours Extended release. Use in Specific Populations Special Populations.
There was a 67 decline in albuterol clearance in patients with CrCl 7 to 53 mLminute. Treatment or prevention of bronchospasm in. 1st line for NAUSEA andor VOMITING.
2nd line for NAUSEA Handor VOMITING 1st line for RESTLESSNESS andor AGITATION. 8 hourly PRN. Max PRN dose in 24 hours 30mg equivalent to 3 PRN doses 1 mg subcut.
4 hourly PRN. Max PRN dose in 24 hours 3mg equivalent to 3 PRN doses 30 mg subcut. In 24 hr syringe driver OR plus PRN haloperido l 2 mg subcut in 24 hr syringe.
The half-life of ritalinic acid is about 3-4 hours. The systemic clearance is 040012 Lhkg for d-methylphenidate and 073028 Lhkg for lmethylphenidate. After oral administration of an immediate release formulation of methylphenidate 78-97 of the dose is excreted in the urine and 1-3 in the feces in the form of metabolites within 48-96 hours.
Somnolence alternatively sleepiness or drowsiness is a state of strong desire for sleep or sleeping for unusually long periods compare hypersomniaIt has distinct meanings and causes. It can refer to the usual state preceding falling asleep the condition of being in a drowsy state due to circadian rhythm disorders or a symptom of other health problems. Haloperidol Use with caution.
Consider if agitated delirium. Start low and titrate slowly. Generally safe in cirrhosis.
Oral lorazepam may be given sublingually. Use if agitation severe or oral route not available. Variable half-life 12-60hrs complicated dosing regimen.
Should be used by someone with experience. When changing to methadone from higher doses of morphine the ratio of methadone. Morphine 1000mg 120 Source.
J Pall Med 2003. Bowel Regimen Do not start. 6 unchanged Biliary excretion is a major route of elimination for unchanged drug following oral administration.
Chris is an Intensivist and ECMO specialist at the Alfred ICU in Melbourne. He is also the Innovation Lead for the Australian Centre for Health Innovation at Alfred Health and Clinical Adjunct Associate Professor at Monash University. He is a co-founder of the Australia and New Zealand Clinician Educator Network ANZCEN and is the Lead for the ANZCEN Clinician Educator Incubator programme.