
Protective antigen PA binds to an appropriate site on the host cell membrane. The toxin is composed of three proteins.
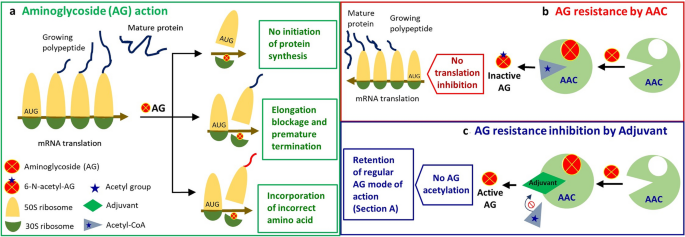
Figure 149 There are several classes of antibacterial compounds that are typically classified based on their bacterial target.
Gentamicin mode of action. Mode of action of Aminoglycosides gentamicin. After entering to the bacterial cell it binds to the 30s ribosomal subunit and results in the misreading of the genetic code. This subsequently leads to the arrest of normal bacterial protein synthesis.
Some examples of Aminoglycosides are Gentamicin tobramycin amikacin etc. Mode of action of Tetracyclines. Once the Tetracyclines enters into.
Gentamicin uptake assays were performed as follows. Baumannii ATCC17978 was grown to OD 06 in Mueller-Hinton II medium. 500 µl culture aliquots were transferred to 2 ml sterile Eppendorf tubes with or without BAC added at 4 µgml 1 and gentamicin-TR was added to each reaction at a final gentamicin concentration of 1 µgml 1.
Reactions were protected from light and. Aminoglycoside is a medicinal and bacteriologic category of traditional Gram-negative antibacterial medications that inhibit protein synthesis and contain as a portion of the molecule an amino-modified glycoside. The term can also refer more generally to any organic molecule that contains amino sugar substructures.
Aminoglycoside antibiotics display bactericidal activity against Gram. Underst anding the mode of action of antimicrobial. All 19 strains of P.
Aeruginosa from urine specimens were susceptible to amoxicillin and gentamicin as completely minimal susceptibility was. Inhibition of protein synthesis. Once inside the bacterial cell aminoglycosides bind to the 30s ribosomal subunit and cause a misreading of the genetic code.
This subsequently leads to the interruption of normal bacterial protein synthesis. Gentamicin tobramycin amikacin streptomycin kanmycin. Spectrum of Activity.
Streptomycin amikacin gentamicin kanamycin tobramycin neomycin Gram -positive gram negative bacteria esp. Pseudomonas spp Binds to bacterial ribosome causing misreading of mRNA resulting in inappropriate amino acid insertion Streptomyces griseus streptomycin Micromonospora spp gentamicin Quinolones. Ofloxacin is a quinolone antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections.
When taken by mouth or injection into a vein these include pneumonia cellulitis urinary tract infections prostatitis plague and certain types of infectious diarrhea. Other uses along with other medications include treating multidrug resistant tuberculosis. LF appears to be a zinc-dependent metalloprotease though its substrate and mode of action have yet to be elucidated.
Mechanism of action of the anthrax toxin. The toxin is composed of three proteins. Protective antigen PA binds to an appropriate site on the host cell membrane.
A cell surface protease cleaves off a 20-kDa piece from the protective antigen and thereby. Function-how the drug works its mode of action. 5 functional groups These are all components or functions necessary for bacterial growth Targets for antibiotics In these discussions we will primarily use the functional classification but will point out where structural similarities also exist.
The indications mode of action side effects and key points of the following antiulcer agents. Histamine 2 receptor antagonists ranitidine famotidine proton pump inhibitors omeprazole pantoprazole mucosal protectant sucralfate antacids aluminum hydroxide and prostaglandins misoprostol. Furanes Nitrofurantoin Mode of Action.
The drug works by damaging bacterial DNA. In the bacterial cell nitrofurantoin is reduced by flavoproteins nitrofuran reductase. These reduced products are are highly active and attack ribosomal proteins DNA respiration pyruvate metabolism and other macromolecule within the cell.
It is not known which of the actions of nitrofurantoin is primarily. As a rule antimicrobial agents are of most use in medicine when the mode of action of the antimicrobial chemicals involves biochemical features of the invading pathogens not possessed by normal host cells. Antibiotics represent a major class of antimicrobial agents.
By definition antibiotics are biochemicals produced by microorganisms that inhibit the growth of or kill other microorganisms. Mechanism of Action Drug Class Specific Drugs Bacteriostatic or Bactericidal Spectrum of Activity. Causes mismatches between codons and anticodons leading to faulty proteins that insert into and disrupt cytoplasmic membrane.
Streptomycin gentamicin neomycin kanamycin. Each class of antibacterial drugs has a unique mode of action the way in which a drug affects microbes at the cellular level and these are summarized in Figure 149 and Table 141. Figure 149 There are several classes of antibacterial compounds that are typically classified based on their bacterial target.
Common Antibacterial Drugs by Mode of Action. Mode of Action Target Drug Class. Glucocorticoids inhibit neutrophil apoptosis and demargination and inhibit NF-Kappa B and other inflammatory transcription factors.
1 They also inhibit phospholipase A2 leading to decreased formation of arachidonic acid derivatives. 1 In addition glucocorticoids promote anti-inflammatory genes like interleukin-10. Corticosteroids like betamethasone can act through.
Cefotetan or cefoxitin plus doxycycline clindamycin plus gentamicin ofloxacin plus metronidazole. Typically two antibiotics are prescribed. Human Papillomavirus HPV Topical Preparations creams and solutions that the patient applies directly to the affected area.
La gentamicina es un antibiótico del grupo de los aminoglucósido producido por la Micromonospora purpurea 1 utilizado como antibiótico de amplio espectro y acción bactericida para el tratamiento de infecciones causadas por bacilos gramnegativos como Pseudomonas aeruginosa Klebsiella pneumoniae o Proteus mirabilisAunque también es activo en menor medida para bacterias. Adequate understanding of the mode of action of antibiotics is therefore an. With the discoveries of antibiotics such as Gentamicin Neomycin T obramycin a nd Am ikacin.
G entamicin is les s. Inhibition of protein synthesis B. Drugs that act on the 50S subunit LINCOSAMIDES Clindamycin Source.
Streptomyces lincolnensis resembles macrolides in binding site anti- bacterial activity and mode of action Bacteriostatic vs. Anaerobes gram bacteria C. Perfringens and gram bacteria Bacteroides fragilis 32.
The action of clotrimazole is fungistatic at concentrations of drug up to 20 mcgmL and may be fungicidal in vitro against Candida albicans and other species of the genus Candida at higher concentrations Label. Unfortunately resistance to clotrimazole which was rare in the past is now common in various patient populations 2. Novel therapies which have met with some success in animal studies include use of gentamicin.
Pathogens were eradicated from sputum more frequently using this mode of therapy no significant difference was seen in clinical outcome. Pneumoniae pneumonia should be for at least 10 days. Computed tomography of the chest may be useful in the patient who is slow to respond in.
Penicillin has an interesting mode of action. It prevents the cross-linking of small peptide chains in peptidoglycan the main wall polymer of bacteria. Pre-existing cells are unaffected but all newly produced cells grow abnormally unable to maintain their wall rigidity and they are susceptible to osmotic lysis.
This morphogenetic effect of penicillin can be demonstrated by growing either. Gentamicin and levofloxacin were used as two representatives for antibiotics to help verify the reliability of our assay protocol by checking whether resistance emerges after repeated treatment. Discuss the mode of action of the 4 different classes of antibiotics studied.
Prevents the enzyme necessary catalyzing the final step in cell wall biosynthesis Tetracyclines. Inhibit the initiation of transition in protein synthesis by inhibiting the binding of tRNA to mRNA. Start studying MicroBio Ch 20.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.