Zone melting or zone refining or floating-zone method or floating-zone technique is a group of similar methods of purifying crystals in which a narrow region of a crystal is melted and this molten zone is moved along the crystalThe molten region melts impure solid at its forward edge and leaves a wake of purer material solidified behind it as it moves through the ingot. HYDROCHLORIC ACID CAS NO 7647-01-0 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET SDSMSDS SECTION 1.
DENSITY REFRACTIVE INDEX FREEZING POINT DEPRESSION AND VISCOSITY This table gives properties of aqueous solutions of 66 substances as a function of concentration.
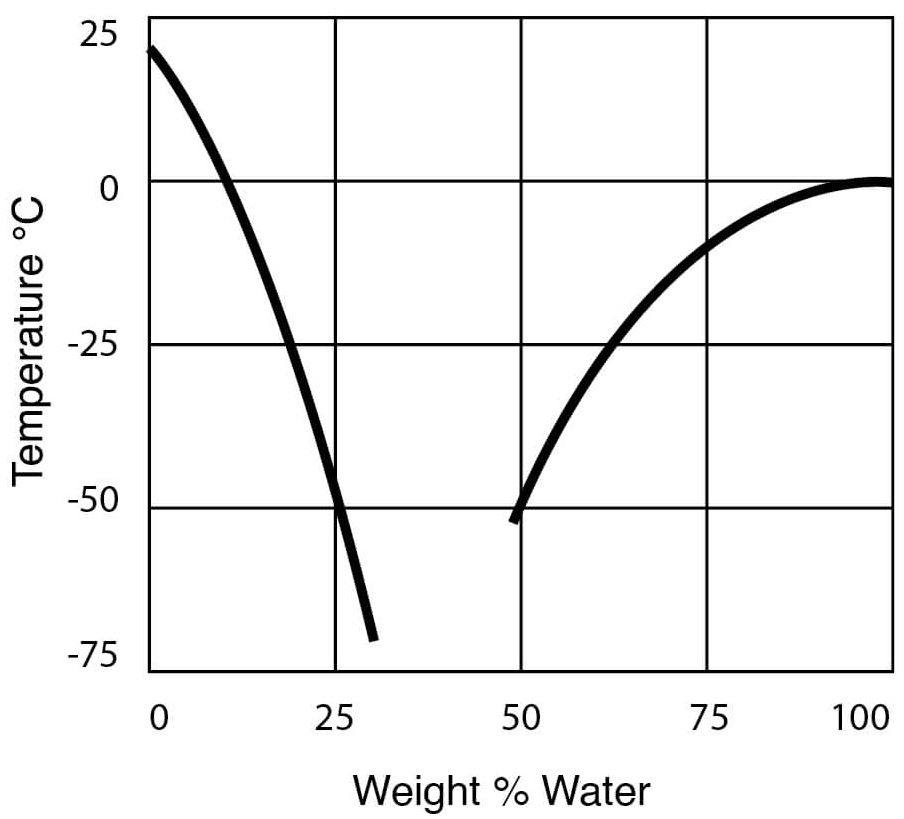
Freezing temperature of hydrochloric acid. The freezing point curve of hydrochloric acid drops significantly from the freezing point of water to a low of -74 o F occurring around 20 concentration and then increases with solution strength to peak at -15 o F at 38. The boiling point shows a high boiling azeotrope at 20 wt HCl. Boiling points decrease with concentrations above 20 HCl decreasing quickly around 30 HCl.
Not pertinent 95 Critical Temperature. Not pertinent 96 Critical Pressure. HYDROCHLORIC ACID HCL 920 SATURATED LIQUID DENSITY Temperature degrees F Pounds per cubic foot 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 74770 74599 74419 74250 74080 73900 73730 73559 73381 921 LIQUID HEAT CAPACITY Temperature degrees F British thermal unit per pound-F 35 40.
Hydrochloric acid has many uses. It is used in the production of chlorides fertilizers and dyes in electroplating and in the photographic textile and rubber industries. Hydrochloric acid is corrosive to the eyes skin and mucous membranes.
Acute short-term inhalation exposure may cause eye nose and respiratory tract irritation and. Hydrochloric Acid 20N 20M Safety Data Sheet. No data available Boiling point.
No data available Flash point. No data available Relative evaporation rate butyl acetate1. No data available Flammability solid gas.
No data available Relative vapor density at 20 C. No data available Relative density. No data available Specific.
HYDROCHLORIC ACID CAS NO 7647-01-0 MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET SDSMSDS SECTION 1. Identification of the substancemixture and of the companyundertaking 11 Product identifiers Product name. 7647-01-0 12 Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture and uses advised against Identified uses.
Laboratorychemicals Industrial for professional use only. Hydrochloric Acid 37 ww 7647 -01 -0 LC50 fish 1 282 mgl LC50. 96 h EC50 Daphnia 1 56 mgl EC50.
Persistence and degradability Hydrochloric Acid 01 N 01M Persistence and degradability Not established. Hydrochloric Acid 37 ww 7647 -01 -0 Persistence and degradability Biodegradability. No test data.
Hydrochloric acid 31 36. Muriatic acid Chlorohydric acid Hydrogen Chloride. HCl in aqueous solution CHEMICAL FAMILY.
Description of first aid measures. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor in attendance. Explosion Limits LowerNot available.
FreezingMelting Point-66 deg C Decomposition TemperatureNot available. Specific GravityDensity119 38 Molecular FormulaHClH2O Molecular Weight3646 Section 10 - Stability and Reactivity Chemical Stability. Stable under normal temperatures and pressures.
Conditions to Avoid. FreezingMelting Point-25 C -13 F Boiling Point. 505 C 123 F Flash Point.
Flammable Limits in Air by Volume. Miscible with water. 25 kPa at 25C estimate Vapor Density.
13 estimate Odor threshold ppm. The freezing point may be defined as the temperature at which the liquid and solid states of a substance have the same vapor pressure. It is observed that the freezing point of a solution is always less than the freezing point of the pure solvent.
This is termed as the depression in freezing point of a solution Freezing point depression has very interesting and useful applications in. The freezing point of different sulfuric acid concentrations can vary markedly. 93 wt sulfuric acid has a freezing point below zero at -21ᵒF so many industrial applications can utilize carbon steel tanks with 93 wt H 2 SO 4 uninsulated but 98 wt freezes at 30ᵒF and so much more care is needed for successful storage.
Between the sulfuric acid concentrations of 35 - 75 wt freezing is. What would happen in the calculation in Practice Problem 7 were repeated with a stronger acid such as hydrochloric acid. Explain why an 0100 m solution of HCl dissolved in benzene has a freezing point depression of 0512 o C while an 0100 m solution of HCl in water has a freezing point depression of 0352 o C.
2015present Senior Instructor II University of Oregon. 20132015 Morrill Professor Iowa State University. 1998-2013 Professor of Chemistry Iowa State University.
2013-2014 Visiting Lecturer University of Oregon. 2006 Visiting Professor University of Arizona. 1990-1998 Associate Professor Iowa State University 1988-1990 Associate Professor of Chemistry and Director of Freshman.
Zone melting or zone refining or floating-zone method or floating-zone technique is a group of similar methods of purifying crystals in which a narrow region of a crystal is melted and this molten zone is moved along the crystalThe molten region melts impure solid at its forward edge and leaves a wake of purer material solidified behind it as it moves through the ingot. Xypex Bio-San C500 is a uniquely designed admixture for integral long-term protection of concrete in harsh sewage conditions with high levels of H 2 S that cause Microbial Induced Corrosion MIC. Watch the animation to learn how Bio-San C500s robust dual technology system eliminates the problem.
For the production of aHVP the proteins are hydrolyzed by cooking with a diluted 1520 hydrochloric acid at a temperature between 90 and 120C for up to 8 hours. After cooling the hydrolysate is neutralized with either sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide to a pH of 5 to 6. The hydrolysate is filtered to remove the insoluble carbohydrate fraction and then further refined.
An example of a liquid solution is aqueous hydrochloric acid HCl in water. An example of a gaseous solution is air. Carbon dioxide in soda.
Hydrogen gas in palladium metal. Cite this Article. A strong acid or a strong base completely ionizes dissociates.
H 2 SO 4. Good temperature 72 o F 22 o C Hydrocyanic Acid. Good temperature 72 o F 22 o C Hydrogen Peroxide 10.
Fair temperature 72 o F 22 o C Hydrogen Sulfide. Good temperature 72 o F 22 o C Lead acetate. Tetrahydrofuran THF 990 dimethylformamide DMF 995 ethanol 997 hydrochloric acid HCl roughly 3638 sulfuric acid H 2 SO 4 roughly 9598 potassium.
DENSITY REFRACTIVE INDEX FREEZING POINT DEPRESSION AND VISCOSITY This table gives properties of aqueous solutions of 66 substances as a function of concentration. All data refer to a temperature of 20C. Mass of solute divided by total mass of solution expressed as percent.
M Molality moles of solute per kg of water. C Molarity moles of solute per liter. The LNPs were formulated as originally described and then diluted in PBS that was either pH 74 physiological pH pH 304 or pH 897 with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide respectively.
The final siRNA concentration of the LNP solutions was 0125 mgmL. The LNPs were then stored at either room temperature 25C in the refrigerator 2C or in the freezer 20C for a span of. 001 M HCl is an unsaturated solution of hydrochloric acid in water.
In chemistry an unsaturated solution consists of solute completely dissolved in solute. If no additional solute can dissolve in a solution that solution is said to be saturated. Solubility depends on temperature.
Raising the temperature of a solution may even turn a saturated solution. The combined filtrates are placed in the freezing mixture until they can be worked up as indicated below. The sodium salt still wet with ether is dissolved in 13 liters of distilled water at room temperature the solution cooled to 0C and the nitrile precipitated by adding slowly with vigorous shaking 90 ml of glacial acetic acid while the temperature is kept below 10C.
One rocket fuel uses a mixture of solid ammonium perchlorate NH 4 ClO 4 and aluminum metal Al to produce a solid aluminum oxide hydrochloric acid gas.