18 Physical Properties of Amines. Our bodies cant make polyunsaturated fats so they are considered essential and need to be obtained from the foods we eat.
A carboxylic acid is a compound that contains a carboxyl group -COOH.
Foods that contain carboxylic acid. The name carboxylic acid or carboxy can also be assigned for a carboxyl substituent on a carbon chain. An example of such nomenclature is the name 2-carboxyfuran for the compound 2-Furoic acid. Some examples describing the nomenclature of carboxylic acids as per IUPAC guidelines are provided below.
Contain the carboxyl group RCO2H. The tart flavor of sour-tasting foods is often caused by the presence of carboxylic acids. RCOH a carboxylic acid O C O O H the carboxyl group C O H O RCOOH RCO2H condensed ways of writing the carboxyl group.
Chapter 5 Carboxylic Acids and Esters 3 Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids 4 Nomenclature of Carboxylic Acids Select the longest carbon. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid while linoleic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid. Our bodies cant make polyunsaturated fats so they are considered essential and need to be obtained from the foods we eat.
They serve as an important source of energy for the body but the Western diet typically includes very high amounts of. Lactic acid is an organic acid. It has a molecular formula CH 3 CH OHCOOH.
It is white in the solid state and it is miscible with water. When in the dissolved state it forms a colorless solution. Production includes both artificial synthesis as well as natural sources.
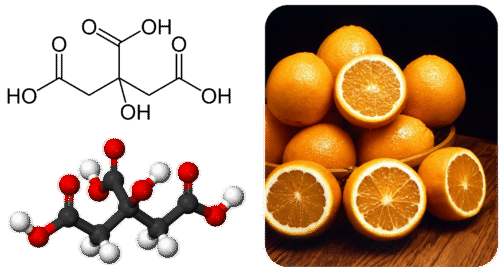
Lactic acid is an alpha-hydroxy acid AHA due to the presence of a hydroxyl group adjacent to the carboxyl group. Tartaric acid is an important component of some commonly used foods like unripened mangoes and tamarind. Natural fruits and vegetables also contain acids.
Citric acid is present in oranges lemon and other citrus fruits. Oxalic acid is present in tomatoes spinach and especially in carambola and rhubarb. Rhubarb leaves and unripe carambolas are toxic because of high concentrations of oxalic.
Niacin is the generic name for nicotinic acid pyridine-3-carboxylic acid nicotinamide niacinamide or pyridine-3-carboxamide and related derivatives such as nicotinamide riboside. Niacin is naturally present in many foods added to some food products and available as a dietary supplement. Number of carbons from the carboxylic acid alpha end to the first carbon in the double bonds.
The figure below shows the fatty acid composition of certain oils and oil-based foods. As you can see most foods contain a mixture of fatty acids. Stick margarine is the only product in the figure that contains an appreciable amount of trans fatty acids.
Corn walnut and soybean are rich. Acetic anhydride is an acyclic carboxylic anhydride derived from acetic acid. It has a role as a metabolite and a reagent.
1 Structures Expand this section. 2 Names and Identifiers Expand this section. 3 Chemical and Physical Properties Expand this section.
4 Spectral Information Expand this section. 5 Related Records Expand this section. 7 Food Additives.
A carboxylic acid is a compound that contains a carboxyl group -COOH. The illustration below is an example of lauric acid which is a saturated fatty acid. The carboxyl group boxed in red is.
Several assays have been used to assess the total antioxidant content of foods eg. The 6-hydroxy-2578-tetramethylchroman-2-carboxylic acid Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity TEAC assay the ferric-reducing ability of plasma FRAP and the. The nitrosated amino acids include N-nitrosoproline N-nitrososarcosine N-nitrosothiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid N-nitrosooxazolidine-4-carboxylic acid and N-nitroso-2-methyl-thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid.
Structures of some important nonvolatile N-nitrosamines are shown in Figure 2. Removal of a carboxylic acid or mineral acid In order to remove an acidic compound from a mixture a base like NaOH or NaHCO 3 is used. The carboxylic or mineral acid and the base react to form a sodium salt which is usually exhibits a higher solubility in aqueous solutions due to its negative charge and higher polarity as indicated by a more negative log K ow value ie CH 3 COOH.
Fatty acids - one or any mixture of straight chain monobasic carboxylic acids assoc. Fatty acids from edible fats and oils capric caprylic lauric myristic oleic palmitic and stearic acids - MISC REG GMP In foods as a lubricant or binder. Comp in mfr of other food-grade additives - 172860.
REG GMP Defoaming agent comp used in processing beet sugar and yeast - 173340. Carboxylic acid soap Carotene Sometimes made from palm Castile soap often from palm Castor Isostearate Beeswax Succinate Ceteareth 2-100 Ceteareth mbsfl laurethulanate Ceteareth mbhe laurethulanate Cetearyl alcohol Cetearyl ethylhexanote Cetearyl glucoside Cetearyl isononanoate Cetearyl and Sorbitan Olivate Ceteth-20 Ceteth-24 Cetostearyl Alcohol Cetrimonium Bromide. Ethanoic acid CH 3 COOH also known as acetic acid is the most typical example of a carboxylic acid.
A versatile chemical recognised by its acidic smell and taste ethanoic acid is the active ingredient in vinegar. It is also used as a preservative and many foods are stored in it because bacteria is unable to withstand the acidic environment. Fatty acids are long-chain carboxylic acids that may contain one or more carboncarbon double bonds.
With the exception of some specialized fatty acids produced by certain prokaryotes the fatty acid residues in lipids are straight acyl chains with a carboxylic acid group at one end and a methyl group at the other end. The structure of fatty acids varies in any one or more of three ways. Esters derived from carboxylic acids like butyric acid are the most common type of esters.
To increase the production of butyric acid in your body naturally focus on getting more foods that contain butyric acid like ghee and high-quality butter on a regular basis. Also increase your daily intake of fiber-rich foods like vegetables fruits legumes and whole grains. If you can increase.
Specifically a phthalate is any chemical that includes a benzene ring bonded to two carboxylic acid groups via the carbon atom in each group. This chemical can be found in items ranging from plastic food storage containers perfume air fresheners laundry detergent as a component of pesticides and even on plastic toys. Some studies have shown that phthalates can cause damage to.
Leucine is an alpha-amino acid which implies that it contains an alpha-amino group which under biological conditions is in the protonated -NH 3 form an alpha-carboxylic acid group which under biological conditions is in the deprotonated -COO form and a side chain isobutyl group making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. In human beings it is an essential amino acid. 1 and 2 amines have lower boiling points than alcohols of similar molecular weight.
3 amines since they do not hydrogen bond to each other have boiling points similar to hydrocarbons of the same molecular weight. 18 Physical Properties of Amines. Boiling Points Name Molecular weight Boiling point Acetic acid 600 gmol 118C 1-propanol 601 gmol 97C propyl.
The carboxylic acid group is shown in blue the amino group is shown in purple and the central carbon atom is shown in red. The green R represents the side chain which is different for each amino acid. On the right is a two-dimensional ChemDraw model of leucine one of the twenty amino acids available for building proteins.
Leucine differs from the other amino acids only in its side chain. The natural compounds that have been detected in milk are gases alcohol aldehydes ketones carboxylic acid sulfur-containing compounds nucleotide material hormones phosphate esters glucose acetate and citrate. Many of these are products of intermediary metabolism of the mammary gland Davies et al 1983.
Peaker and Faulkner 1983. The reasons for changes in the. Butyric acid n-Butyric acid is a viscous foul-smelling liquid carboxylic acid.
Go To Top C. C60 Fullerene Buckminsterfullerene is a spherical shaped allotrope of carbon discovered in 1985. C70 Fullerene Fullerenes are spherical cagelike molecules consisting of annelated carbon five - and six rings.
Caffeine A stimulant found in drinks and used in pharmaceuticals. Calcite Calcite is the most. Several assays have been used to assess the total antioxidant content of foods eg.
The 6-hydroxy-2578-tetramethylchroman-2-carboxylic acid Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity TEAC assay the ferric-reducing ability of plasma FRAP and the.