SECTION 9 PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Attention. COMPOSITION ETHYLENE GLYCOL 100 107-21-1 4.
Ethylene glycol C 2 H 6 O 2 is a molecular compound that is used in many commercial anti-freezes.
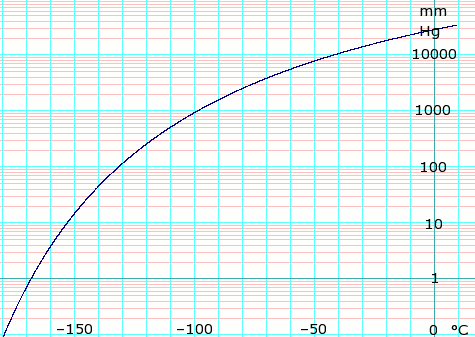
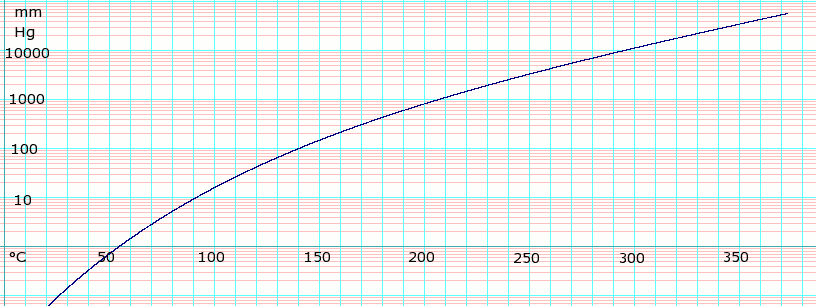
Ethylene glycol vapor pressure. 006 mmHg 20 C Viscosity. Ethylene glycol is widely used to inhibit the formation of natural gas clathrates hydrates in long multiphase pipelines that convey natural gas from remote gas fields to a gas processing facility. Ethylene glycol can be recovered from the natural gas and reused as an inhibitor after purification treatment that removes water and inorganic.
Ethylene glycol has a low vapor pressure. It does not evaporate readily at normal temperatures and therefore high concentrations in air or intoxication are unlikely to occur following inhalational exposures. There may be a slight risk of poisoning where mists or fogs are generated.
If ethylene glycol releases as a vapor it is unlikely to pollute agricultural products. Systemic ethylene glycol toxicity can occur through ingestion. Breathing ethylene glycol vapors may irritate eyes and lungs but is unlikely to cause systemic toxicity.
Ethylene glycol does not absorb well through the skin so systemic toxicity is unlikely. Eye exposure may lead to local. ETHYLENE GLYCOL 1.
HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION HMIS USA. Health - 2 Fire - 1 Reactivity - 0 MATERIAL USE. Antifreeze humectant plasticiser hydraulic fluid solvent 3.
COMPOSITION ETHYLENE GLYCOL 100 107-21-1 4. Ethylene Glycol Page 1 of 4 Ethylene Glycol Section 1 Product Description Product Name. Ethylene Glycol Recommended Use.
Science education applications Synonyms. Carolina Biological Supply Company 2700 York Road Burlington NC 27215 1-800-227-1150 Chemical Information. 800-227-1150 8am-5pm ET M-F Chemtrec.
Ethylene glycol is an odorless colorless sweet-tasting syrupy substance with a molecular weight of 6207 freezing point of -13C and a boiling point of 1976C. It is most commonly encountered as automotive antifreeze. Diethylene glycol behaves similarly to ethylene glycol in an overdose.
The ethylene glycol molecule is incorporated into. If ethylene glycol is heated or misted in work areas that are poorly ventilated vapormist may accumulate and cause respiratory irritation and symptoms such as headache and nausea. Material has a very low vapor pressure at room temperature so inhalation exposures are not expected unless material is heated or misted.
May cause kidney injury. Repeated excessive exposure to. Ethylene glycol is a clear colorless syrupy liquid.
The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Since it is a liquid it can easily penetrate the soil and contaminate groundwater and nearby streams.
Ethylene glycol is a synthetic liquid substance that absorbs water. It is odorless but has a sweet. The total vapor pressure of this solution is 915 mmHg.
Calculate the vapor pressure of pure ethylene glycol at this temperature. Since this solution is only comprised of water and ethylene glycol we can easily calculate the mole fraction of ethylene glycol in this solution by subtracting waters mole fraction from 1. Synonyms Trade Names 12-Dihydroxyethane 12-Ethanediol Glycol Glycol alcohol Monoethylene glycol CAS No.
Ethylene oxide is a flammable gas with a somewhat sweet odor. It dissolves easily in waterEthylene oxide is a man-made chemical that is used primarily to make ethylene glycol a chemical used to make antifreeze and polyester. A small amount less than 1 is used to control insects in some stored agricultural products and a very small amount is used in hospitals to sterilize medical.
The vapor pressure of a liquid is defined as the pressure exerted by the molecules that escapes from the liquid to form a separate vapor phase above the liquid surface. The pressure exerted by the vapor phase is called the. Vapor or saturation pressure.
Vapor or saturation pressure depends on temperature. If a fluid consist of more than one component a solution components with. The vapor ethylene glycol methanol and other trace hydrocarbons from the prepolymerization and polymerization reactors typically is evacuated through scrubbers spray condensers using spent ethylene glycol.
The recovered ethylene glycol is recirculated in the scrubber system and part of the spent ethylene glycol from the scrubber system is sent to storage in process tanks 13 after. HOCH 2CH 2OH CAS Registry Number. 1 2-Ethanediol Glycol EG Monoethylene glycol Ethylene glycol is produced from ethylene via the intermediate ethylene oxide.
Ethylene oxide reacts with water to produce ethylene glycol according to the chemical equation C 2H 4O H 2O HOCH 2CH 2OH This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases or can occur at. MolaLity 1074 m Molarity 676 M mole fraction 0162 40 ethylene glycol means mass of ethylene glycol 40 g mass of water solvent 60 g 0060 kg mass of solution 100 g 1. Molality Molar mass of ethylene glycol 6207 gmL no.
Of moles 4 g6207 gmol-1 06444 mol Molality no. Of molesmass of solvent in kg Molality 06444 mol0060 kg 107 m. Product Name Ethylene glycol Cat No.
E177-20 CAS-No 107-21-1 Synonyms Monoethylene glycol. 12-Ethanediol Recommended Use Laboratory chemicals. Uses advised against Not for food drug pesticide or biocidal product use Details of the supplier of the safety data sheet Emergency Telephone Number CHEMTRECÒ Inside the USA.
800-424-9300 CHEMTRECÒ Outside the USA. On that basis treatment similar to ethylene glycol intoxication may be of benefit. In cases where several ounces 60 - 100 ml have been ingested consider the use of ethanol and hemodialysis in the treatment.
Consult standard literature for details of treatment. If ethanol is used a therapeutically effective blood concentration in the range of 100 - 150 mgdl may be. Ethylene Glycol ACGIH Vapor fraction 25 ppm 50 ppm – –Ethylene Glycol ACGIH – 01 ppm – – Skin Consult local authorities for appropriate values.
SECTION 9 PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Attention. The data below are typical values and do not constitute a specification. Faint or Mild Odor Threshold.
No data available pH. 33volume 20. The solute lowers the vapor pressure of the solvent resulting in a lowering of the freezing point of the solution compared to the solvent.
Ethylene glycol C 2 H 6 O 2 is a molecular compound that is used in many commercial anti-freezes. A water solution of ethylene glycol is used in vehicle radiators to lower its freezing point and thus prevent the water in the radiator from. 2-24 Total Vapor Pressures of Aqueous Solutions of NH 3.
2-88 2-25 Partial Pressures of H 2 O over Aqueous Solutions of Sodium Carbonate. Ethylene glycol-based fluids are less viscous than propylene glycol-based fluids. Therefore they generally provide superior heat transfer efficiency and better low temperature performance and are preferred for most heat transfer applications.
However in applications where tox-icity is a concern. Speight in Heavy Oil Recovery and Upgrading 2019 62 Pressure Swing Adsorption Units. Pressure swing adsorption units use beds of solid adsorbent to separate impurities from hydrogen streams leading to high-purity high-pressure hydrogen and a low-pressure tail gas stream containing the impurities and some of the hydrogen.
The beds are then regenerated by depressurizing and purging. A gauge range of twice the working pressure is generally selected. The working pressure in all cases should be limited to 75 of the gauge range.
Where alternating pressure and pulsation are encountered working pressure should be limited to 23 of the gauge range. Conditions affecting wear of the system. Chemical and process engineering resources including heat transfer heat exchangers fluid flow pumps cooling towers pressure relief and more.
Fluid Characteristics Chart Table Density Vapor Pressure and Kinematic Viscosity. Hazen-Williams Coefficients Table. Hazen-Williams Water Pressure Drop.
Head loss in a Pipe Darcy - Weisback Equation Calculator. Liquid Temperature Kinematic Viscosity F c K CentiStokes m 2 sec ft 2 sec Enter For Conversion Acetic acid - vinegar 5900 1500 28815 1350 13500e-006 1.