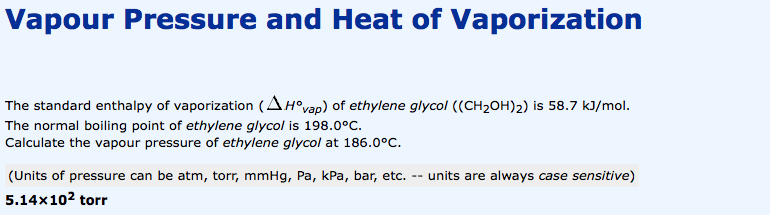
P in mm Hg. B Calculate the heat required to make the conversion described in part a.
If heat is added to an object its temperature will increase.
Ethylene glycol heat of vaporization. Of vaporization Δ vap H o. 460 kJmol Standard molar entropy S o liquid. 1669 JmolK Heat capacity c p.
1495 JmolK Gas properties Std enthalpy change of formation Δ f H o gas. 3944 kJmol Standard molar entropy S o gas. 3118 JmolK Heat capacity c p.
78 JmolK at 25 C Vapor pressure of liquid. P in mm Hg. 760 T in C.
A Paper On Manufacturing Of Ethylene Glycol Ethylene Glycol is nowadays one of the most industrially important chemical. Due to its demand and a vast application area lot of research is going on for improving its production statistics. In 1995 the world capacity for ethylene glycol was about 97 x 106 tonnes per year.
Properties of Ethylene Glycol Ethylene Glycol is specifically colorless. Ethylene glycol is a clear colorless syrupy liquid. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment.
Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Since it is a liquid it can easily penetrate the soil and contaminate groundwater and nearby streams. Ethylene glycol is a synthetic liquid substance that absorbs water.
It is odorless but has a sweet. Ethylene oxide is an organic compound with the formula C 2 H 4 OIt is a cyclic ether and the simplest epoxide. A three-membered ring consisting of one oxygen atom and two carbon atomsEthylene oxide is a colorless and flammable gas with a faintly sweet odor.
Because it is a strained ring ethylene oxide easily participates in a number of addition reactions that result in ring-opening. Heat of vaporization760 mmHg calgm 191 83 99 Thermal conductivity calsec. Ethylene glycol was first prepared by Wurtz in 1859 by the hy-drolysis of ethylene glycol diacetate but was not of commercial in- terest until World War I when it was used in Germany as a sub-stitute for glycerol in explosives production Curme and Johnston 1952.
Later in the 1930s when the commercial. The glycol dehydration process is an example of a process that provides absorption dehydration and in the process a liquid desiccant provides the means to absorb water from the gas stream. Ethylene glycol HOCH 2 CH 2 OH was initially the principal chemical agent in this process has a very strong affinity for water and when the glycol is in contact with a stream of water-wet natural gas.
HOCH 2CH 2OH CAS Registry Number. 1 2-Ethanediol Glycol EG Monoethylene glycol Ethylene glycol is produced from ethylene via the intermediate ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide reacts with water to produce ethylene glycol according to the chemical equation C 2H 4O H 2O HOCH 2CH 2OH This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases or can occur at.
The input energy required to change the state from liquid to vapor at constant temperature is called the latent heat of vaporization. When a liquid vaporize at the normal boiling point the temperature of the liquid will not rise beyond the temperature of the boiling point. The latent heat of vaporization is the amount of heat required to convert a unit mass of a liquid into vapor without a.
Ethylene oxide is a flammable gas with a somewhat sweet odor. It dissolves easily in waterEthylene oxide is a man-made chemical that is used primarily to make ethylene glycol a chemical used to make antifreeze and polyester. A small amount less than 1 is used to control insects in some stored agricultural products and a very small amount is used in hospitals to sterilize medical.
In term of quantity produced ethylene is the most important organic chemical. Ethylene is the feedstock in the manufacture of the most important polymer. It is also converted to ethylene oxide it is a precursor to ethylene glycol ethylbenzene styrene and to various kinds of polyethylene to ethylene dichloride and to vinyl chloride.
Another state change is involved in vaporization and condensation. The latent heat of vaporization Hv of the substance is the energy required to change a substance from a liquid to a vapor. This same amount of energy is released as the vapor condenses back to a liquid.
Q C or Q D w Hf OR w Hv. Q C Heat Required to MeltVaporize Materials During Heat-Up Wh. Since heat and temperature are both related to the same thing the kinetic energy of the atoms in an object how can we describe this relationship.
If heat is added to an object its temperature will increase. If heat is taken away its temperature will decrease. If an object has more mass it will take more heat to raise its temperature the same.
Generally lower levels of another solvent ethylene glycol average 10 g100 g were detected. 13-Propanediol was detected only in seven samples in the concentration range of 3310 g100 g. 13-Butanediol and diethylene glycol were negative in all samples.
The presence of the major compounds glycerol and PG corresponded to the labeling in the majority of cases except three products. Assume that liquid ammonia NH 3 has a specific heat of 475 Jg-C and that gaseous ammonia has a specific heat of 217 Jg-C. The heat of vaporization for ammonia is 2335 kJmol at its boiling point of 334 C.
A Draw the heating curve for converting 34 g of ammonia from a liquid at -40 C to a gas at 0 C. B Calculate the heat required to make the conversion described in part a. Then subtract latent heat of vaporization per mole of water at the ambient temperature X one half the number of hydrogen atoms per molecule of fuel from the higher heating value per mole to.
Temperature K A B C Reference Comment. Prydz and Goodwin 1972. Coefficents calculated by NIST from authors data.
Heating value is the amount of heat produced by a complete combustion of fuel and it is measured as a unit of energy per unit mass or volume of substance eg. Normal Latent Heat of Latent Heat Specific Boiling Vaporization Freezing of Fusion Temperature Density Heat Substance Point C h fg kJkg Point C h if kJkg C r kgm3 c p kJkgK Ammonia 333 1357 777 3224 333 682 443 20 665 452 0 639 460 25 602 480 Argon 1859 1616 1893 28 1856 1394 114 Benzene 802 394 55 126 20 879 172. The vapor pressure of a liquid is defined as the pressure exerted by the molecules that escapes from the liquid to form a separate vapor phase above the liquid surface.
The pressure exerted by the vapor phase is called the. Vapor or saturation pressure. Vapor or saturation pressure depends on temperature.
If a fluid consist of more than one component a solution components with. Ethylene glycol or propylene glycol make up much of the rest of the mixture preventing freezing but you cant just dump water into your engine if you live in an area that never gets cold. Additives give engine coolant a much longer life than plain water.
Corrosion inhibitors lubricants anti-foaming agents colorants and other additives keep the wateralcohol blend from eating your engine. A counterflow heat exchanger is being used to cool a flow of hot water using a cold 20 ethylene glycol solution. The hot water enters at 80 F with a volumetric flow rate of 400 gpm.
Adding a foreign substance such as salt sugar or ethylene glycol to water lowers the freezing temperature. The foreign substance replaces water molecules in the liquid and there are fewer water molecules to bind to the nuclei. Fast nucleation rates andor slow growth rates result in the formation of many small crystals.
Slow nucleation rates result in the formation of large crystals. New code to calculate heat of formation or the mass flux for a Venturi nozzle. Version 100 includes 147 pure fluids 5 pseudo-pure fluids such as air and mixtures with up to 20 components.
A student has 50 g of each of these liquids at room temperature. The same amount of heat is added to each sample and the final temperature of the liquid is given. Which one has the greatest specific heat capacity.
Liquid Final T A. 481 Carbon tetrachloride C B. 335 Ethylene glycol C C.
348 Acetic acid C D. 301 milk C E. Bromine 676 C —– 16.
The structure of the amino acid. KWheat-up 15012 x 1 x 35 x 1234123. KWmaintain 288 x 14 x 95 x 123412.
KWtotal 64. Calculations for heating air in a duct. Once the volume of air in standard cubic feet per minute SCFM and the required.