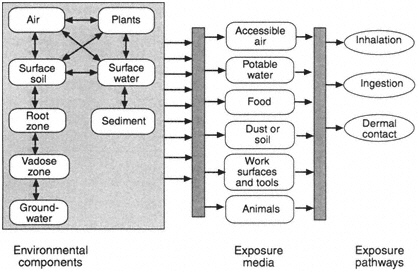
The final exposure scenario defines the operational conditions and risk management measures required to ensure the safe use of the substance for each exposed. As Section 64 reviews this is the specific locations where people might come into contact with a contaminated medium.
Pesticides can enter the body by any one or all three of these routes.
Environment and exposure routes. Scarce knowledge is available on the relationship between maternal chemical exposure during pregnancy and foetal deaths. We studied the association of spontaneous abortions and stillbirths with occupational or daily maternal exposure to chemicals commonly used by pregnant women. Data from the Japan Environment and Childrens Study JECS a nationwide prospective birth cohort study.
The Case Studies in Environmental Medicine CSEM are self-instructional continuing-education primers designed to increase primary care providers knowledge of hazardous substances and aid in the evaluation of patients potentially exposed to hazardous substances. The main routes of exposure to cadmium are via inhalation or cigarette smoke and ingestion of food. Skin absorption is rare.
Human exposure to cadmium is possible through a number of several sources including employment in primary metal industries eating contaminated food smoking cigarettes and working in cadmium-contaminated work places with smoking being a major contributor 91 92. Environment International is a multi-disciplinary Open Access journal publishing high quality and novel information within the broad field of Environmental Health Sciences. Coverage includes but is not limited to the following research topics.
Consumer exposure may also occur via other routes such as via floor wood stone and car polishing and cleaning products. Groups that may be exposed to high concentrations of PFAS include workers and people eating or drinking water and foods contaminated via PFAS treated food contact materials Susmann et al 2019. Though PFAS are used in drugs and medical equipment there is little.
A number of recent studies suggest that dietary intake is one of the main routes to human exposure to PBDEs. In recent years PBDEs have become widespread environmental pollutants while body burden in the general population has been increasing. The results do show notable coincidences between the China Europe Japan and United States such as dairy products fish and seafood being a cause.
Also general population exposure may occur through contact with contaminated environment media particularly in the vicinity of wood-treatment facilities and hazardous-waste sites. In addition some other important routes of exposure seem to be the inhalation of contaminated air ingestion of contaminated ground water used as a source of drinking water ingestion of contaminated food and. Concentrations that are actually measured in the environment.
The third section of this chapter includes the effects of the duration and frequency of exposure interspecies variation and intraspecies variation on toxicity. Finally toxic responses associated with chemical exposures are described according to each organ system. Routes of Exposure There are four routes by which a substance can.
There are four main routes of exposure. Percutaneous though broken or damaged skin. Mucous membranes of the eyes nose and mouth.
The biosafety levels range from BSL-1 to BSL-4. Each biosafety level builds on the controls of the level before it. Every microbiology laboratory regardless of biosafety level follows standard microbiological practices.
Other Routes of Exposure. Systemic Toxicity Systemic fluoride toxicity may result from ingestion inhalation or extensive dermal burns. Hypocalcemia hypomagnesemia hyperkalemia potassium pulmonary edema metabolic acidosis ventricular arrhythmias and death are possible.
Eye Exposure May result in severe ocular damage with concentrations greater than 05. An exposure scenario is a set of conditions that describe how a substance is manufactured or used and the measures necessary to control exposure to humans and releases to the environment. The final exposure scenario defines the operational conditions and risk management measures required to ensure the safe use of the substance for each exposed.
The main routes of aluminium consumption by humans are through inhalation ingestion and dermal contact and sources of exposure are drinking water food beverages and aluminium containing drugs. Aluminium is naturally present in food. Aluminium and its compounds are poorly absorbed in humans although the rate at which they get absorbed has not been clearly studied.
They also calculated the mortality percentage of bees via the two exposure routes. Using data from the VarroaPop Pesticide model and Monte Carlo simulation which is a method that distributes a wide range of possible outcomes scientists simulated all combinations of pesticide application methods and routes of exposure. They used four different sets of Monte Carlo.
Many species of Cryptosporidium exist that infect humans and a wide range of animals. Although Cryptosporidium parvum and Cryptosporidium hominis formerly known as C. Parvum anthroponotic genotype or genotype 1 are the most prevalent species causing disease in humans infections by C.
Once released to the environment contaminants move through and across different media and some degrade altogether. Section 63 describes these processes in detail. Exposure point or area.
As Section 64 reviews this is the specific locations where people might come into contact with a contaminated medium. The route is the means by which people. These routes of exposure occur in adults or older children.
Children also have pathways of exposure that differ from those of adults due to their size and developmental stage. For example young children engage in normal exploratory behaviours including hand-to-mouth and object-to-mouth behaviours and non-nutritive ingestion which. Exposure to hazardous substances over time.
Although there are a number of methods and routes of entry for a person to acquire a harmful substance into the body the three main ones are. Inhaling- Breathing in a hazardous substance is the most common route for a hazardous substance to enter the body. Substances such as harmful fumes organic contaminates like fungi or bacteria or.
Exposure to high levels of these pollutants can lower productivity. Small and meant to be carried around testing the air as a person walks or bikes helping people plan routes that avoid bad air. Atmotube in the press.
Provides a more direct visual of just how polluted our local environment actually is. Atmotube in the press. Others have tried to create similar devices.
They were just. N Getting it into the mouth or digestive tract oral exposure. N Contact with the skin or eyes dermal exposure.
Pesticides can enter the body by any one or all three of these routes. Inhalation exposure can happen if you breathe air containing pesticide as a vapor as an aerosol or on small particles like. Exposure to estrogen or androgen mimicking EDCs can promote breast and prostate cancer growth andor interfere with hormonal cancer therapy.
Prenatal exposure to some EDCs may after mammary gland development and increase breast cancer risk later-in-life. Although evidence linking EDCs to adverse health outcomes continues to grow the cause-and-effect relationship is not yet.