
The nitrates chlorates and acetates of all metals are soluble in water. 2 Names and Identifiers Expand this section.
The nitrates chlorates and acetates of all metals are soluble in water.
Copper ii sulfate solubility. CopperII sulfate also known as copper sulphate are the inorganic compounds with the chemical formula Cu SO 4 H 2 O x where x can range from 0 to 5The pentahydrate x 5 is the most common form. Older names for this compound include blue vitriol bluestone vitriol of copper and Roman vitriol. The pentahydrate CuSO 4 5H 2 O the most commonly encountered salt is bright blue.
CopperII sulfate is a metal sulfate compound having copper2 as the metal ion. It has a role as a sensitiser a fertilizer and an emetic. It contains a copper2.
1 Structures Expand this section. 2 Names and Identifiers Expand this section. 3 Chemical and Physical Properties Expand this section.
4 Spectral Information Expand this section. 5 Related Records Expand this. TetraamminecopperII sulfate is the salt with the formula CuNH 3 4SO 4 H 2 O.
This dark blue to purple solid is a salt of the metal complex CuNH 3 4 H 2 O 2. It is closely related to Schweizers reagent which is used for the production of cellulose fibers in the production of rayon. This compound can be prepared by adding concentrated solution of ammonia to a.
Chemical Class and Type. Copper sulfate is an algaecide bactericide and fungicide. When it is mixed with calcium hydroxide it is known as Bordeaux mixture.
1 The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry IUPAC name for this active ingredient is copper 2 sulfate or copper II sulfate. Other names include copper 2 tretraoxidosulfate or copper II tretraoxidosulfate. MSDS 22700 Copper II Sulfate Anhydrous Scholar Chemistry Section 9.
Physical and Chemical Properties Molecular formula CuSO4. Appearance Off white powder. Specific Gravity 476 gmL 20C.
Vapor Density air1 NA. Solubility Soluble in water and methanol. For more Solubility Complete data for COPPERII SULFATE PENTAHYDRATE 8 total please visit the HSDB record page.
Hazardous Substances Data Bank HSDB Solubility in water g100ml at 0 C. ILO International Chemical Safety Cards ICSC 328 Density. 2284 NTP 1992 National Toxicology Program Institute of Environmental Health Sciences National Institutes of.
CopperII chloride is light brown when anhydrousIt is green when hydratedIt is a weak oxidizing agentIt reacts with aluminium foil to make hydrogen copperI oxide and aluminium chlorideThis is used in school demonstrations. It releases chlorine and turns into copperI chloride when heated very hot. It reacts with sodium hydroxide to make copperII hydroxide.
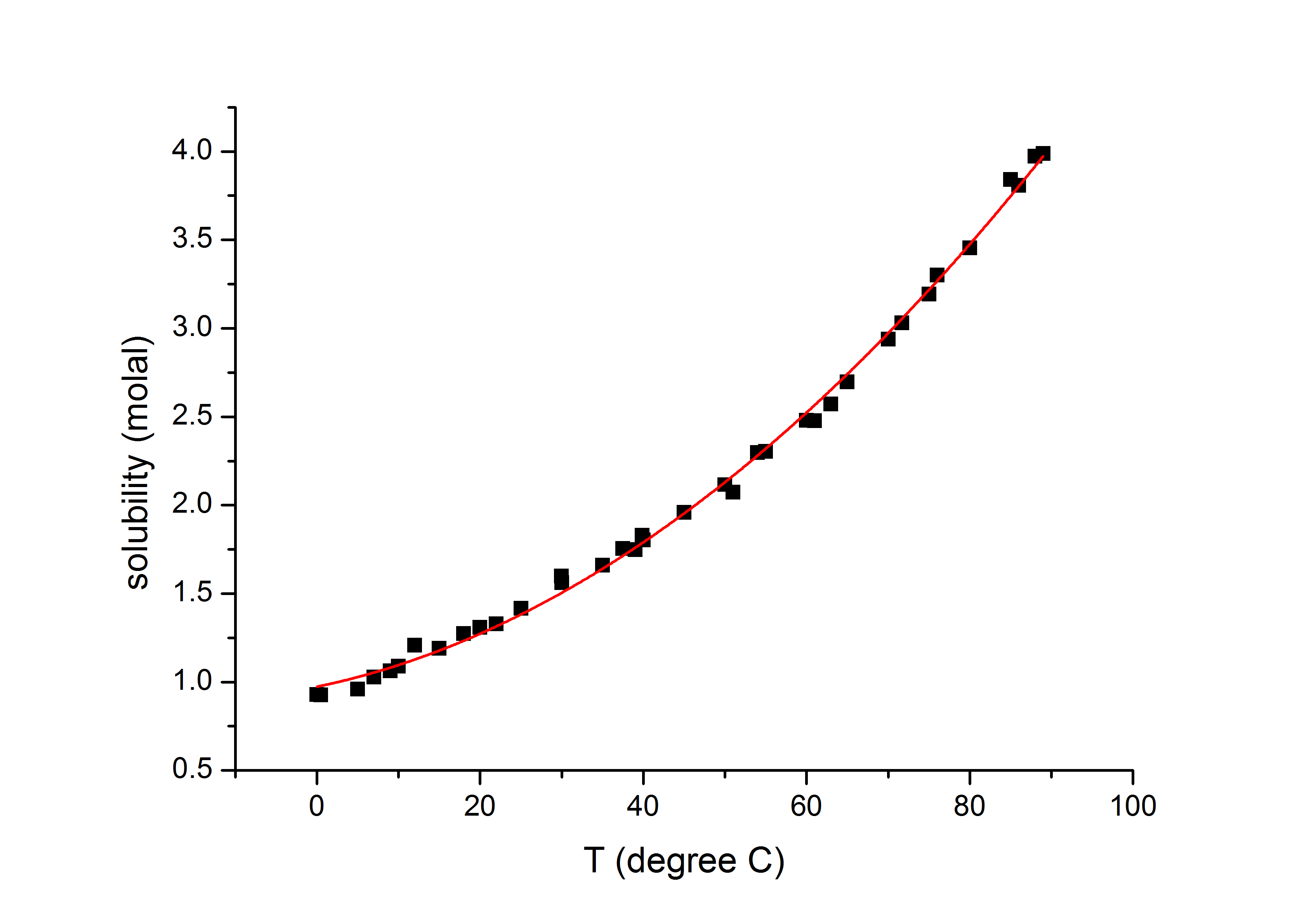
Copper sulfate is highly soluble in water with solubility values of 1055 molal and 1502 molal ate 10 o C and 30 o C respectively. A typical example of a single displacement reaction where one metal displaces another is the reaction between iron and copper sulfate given by the reaction Fe CuSO 4 FeSO 4 Cu. Uses of Copper Sulfate.
Basic chemistry sets that are used as educational. Product Name CopperII sulfate Cat No. AC422875000 CAS-No 7758-98-7 Synonyms Cupric sulfate anhydrous.
Copper monosulfate Recommended Use Laboratory chemicals. Uses advised against Food drug pesticide or biocidal product use. Details of the supplier of the safety data sheet.
Solubility product constant K sp or the solubility product is the product of the molar concentrations of the constituent ions each raised to the power of its stoichiometric coefficient in the equilibrium equationFor instance if a compound A a B b is in equilibrium with its solution. SOLUBILITY PRODUCT CONSTANTS The solubility product constant K sp is a useful parameter for calculating the aqueous solubility of sparingly soluble compounds under various conditions. It may be determined by direct measure-ment or calculated from the standard Gibbs energies of formation f G of the species involved at their standard states.
Thus if K sp Mm An is the equilibrium. Temperature affects the solubility of both solids and gases but hasnt been found to have a defined impact on the solubility of liquids. Pressure can also affect solubility but only for gases that are in liquids.
Henrys law states that the solubility of a gas is directly proportional to the partial pressure of the gas. Solubility Product Constants near 25 C. Ionic Compound Formula K sp.
Aluminum hydroxide AlOH 3 1810 5 Aluminum phosphate AlPO 4 6310 19 Barium carbonate BaCO 3 5110 9 Barium chromate BaCrO 4 1210 10 Barium fluoride BaF 2 1010 6 Barium hydroxide BaOH 2 510 3 Barium sulfate BaSO 4 1110 10 Barium sulfite BaSO 3 810 7 Barium thiosulfate BaS 2 O 3. The effect of temperature. In general solids become more.
Boiling point - the temperature at which a liquid turns into a gas. Melting point - the temperature at which a solid turns into a liquid. See Standard state and enthalpy of formation Gibbs free energy of formation entropy and heat capacity for thermodynamic data for the same compounds.
For full table with Density Liquid Denity at Melting Point and Water Solubility-rotate the screen. Solubility Table g100 mL or g100 g Chemistry Tutorial Key Concepts. Solubility of a substance in a particular solvent is the concentration of its saturated solution at the temperature specified.
I nature of the solute intermolecular forces ii nature of the solvent intermolecular forces iii temperature solubility curves. The Solubility Rules 1. The nitrates chlorates and acetates of all metals are soluble in water.
Silver acetate is sparingly soluble. All sodium potassium and ammonium salts are soluble in water. The chlorides bromides and iodides of all metals except lead silver and mercuryI are soluble in water.
HgI2 is insoluble in water. PbCl2 PbBr2 and PbI2 are soluble in hot water. The sulfate ion generally forms soluble compounds but there are several exceptions.
The sulfate ion forms insoluble compounds with the following ions. Strontium Sr 2 barium Ba 2 lead Pb 2 silver Ag calcium Ca 2 radium Ra 2 and diatomic silver Ag 2 2. Note that silver sulfate and calcium sulfate dissolve just enough.
The lower solubility of the trans-isomer results in its preferential crystallization. Ii Dissolve 20. Write an equation for the preparation and calculate the percentage yield based on the quantity of copper sulfate crystals used.
Draw the structures of the cis-and trans-diaquabisoxalatochromateIII ions. The trioxalatochromate ion is also a mixture of isomers. Solubility and Related Thermodynamic Quantities of CadmiumII Carbonate in Aqueous Systems JPCRD 2011 40 043104.
Jitka Eysseltováa and Roger Bouaziz Potassium Sulfate in Water JPCRD 2012 41 013103. Copper Sulfate Crystal. Copper sulfate crystals naturally form blue diamonds.
These crystals are extremely easy to grow. Simply dissolve copper sulfate into a cup of boiling water until no more will dissolve. Allow the container to rest undisturbed overnight.
Its best to collect the crystals with a spoon or toothpick since touching the solution will turn your skin blue and.